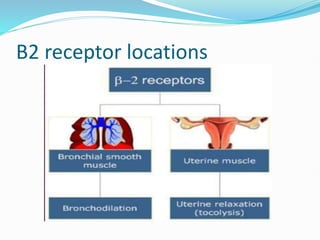
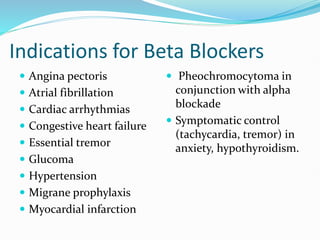
Beta blockers are a class of drugs that block the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine on beta receptors in the sympathetic nervous system. They have several indications including hypertension, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and myocardial infarction. There are non-selective beta blockers that block both beta 1 and beta 2 receptors and selective beta blockers that mainly block beta 1 receptors. Common adverse effects include bradycardia, hypotension, fatigue, and dyspnea. They must be used cautiously in patients with asthma or heart failure.