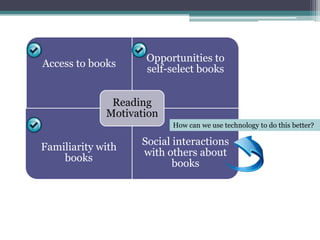
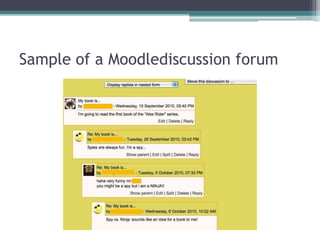
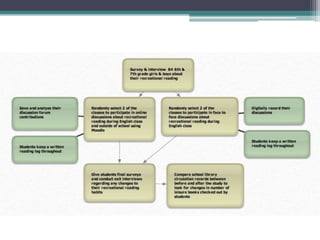
This study aims to examine whether participation in online book discussion forums can motivate middle school students to read more for pleasure. The researchers plan to have 84 6th and 7th grade students from four classrooms participate. Two classrooms will engage in biweekly discussions on Moodle forums about books they have read for 18 weeks, while the other two classrooms will not participate. Surveys, interviews, reading logs, and library records will be used to collect data and compare reading motivation between the two groups before and after the study. The researchers hope to gain insight into how social interactions about books online can influence reading motivation in adolescents.