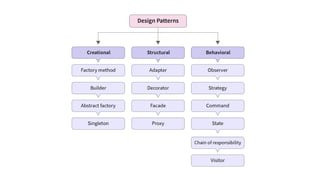
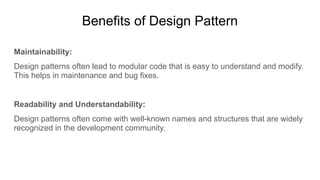
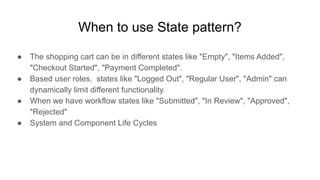
A design pattern is a reusable solution for common software design problems, serving as a template rather than specific code. It offers benefits such as reusability, scalability, maintainability, and improved performance, while drawbacks include potential complexity and overengineering. Various patterns like Singleton, Builder, and Facade address specific situations, enhancing code flexibility and adaptability.