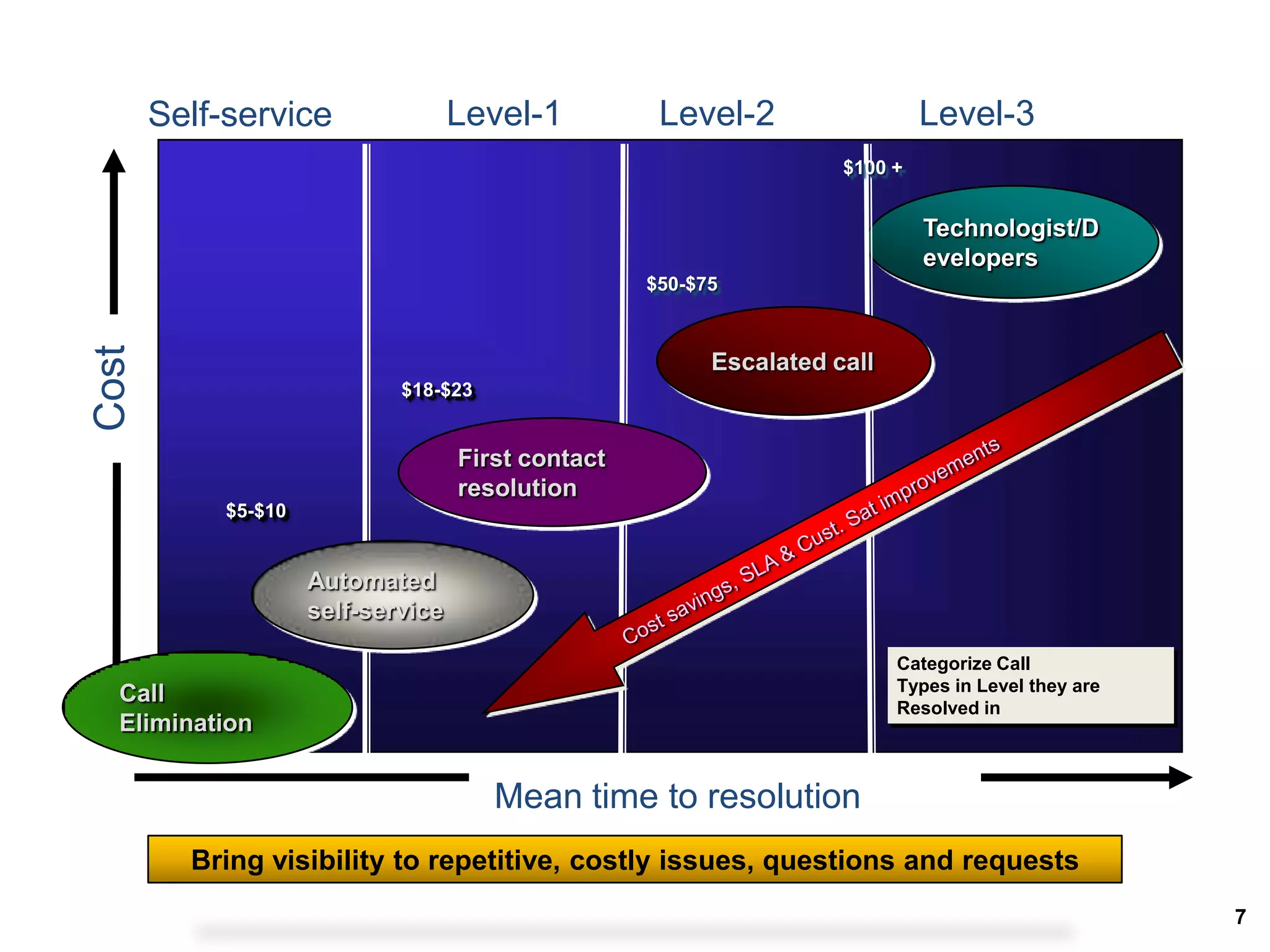
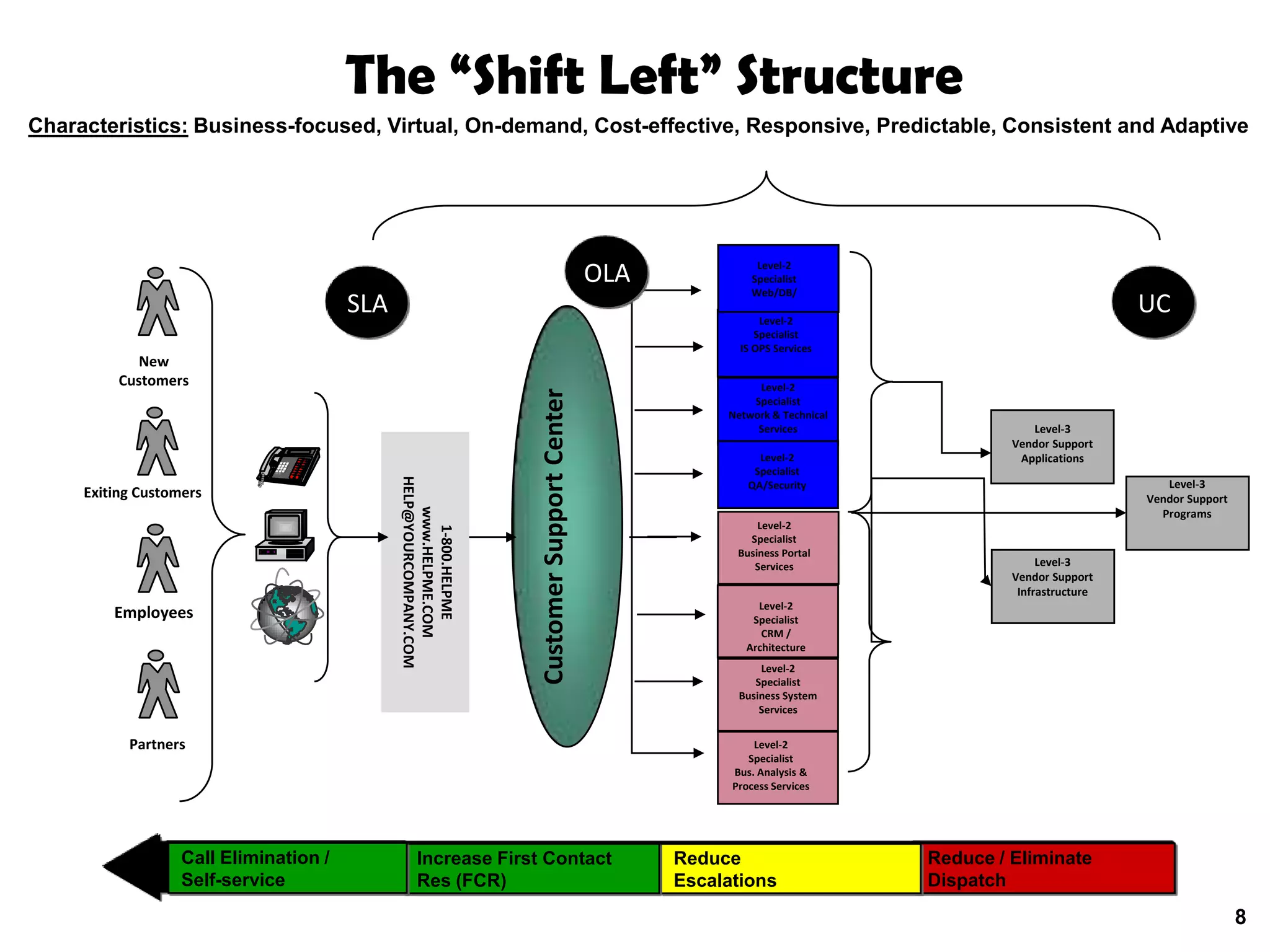
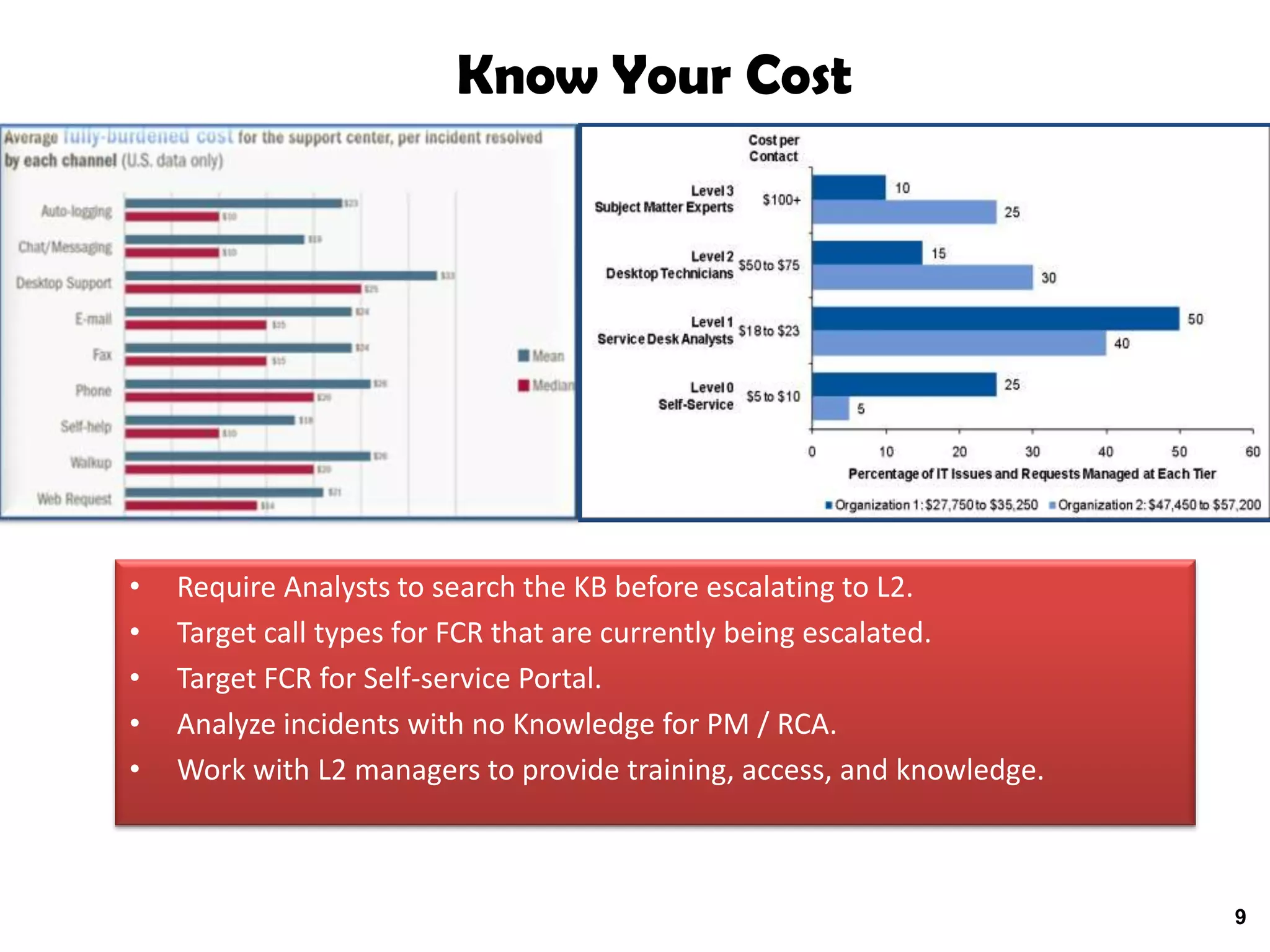
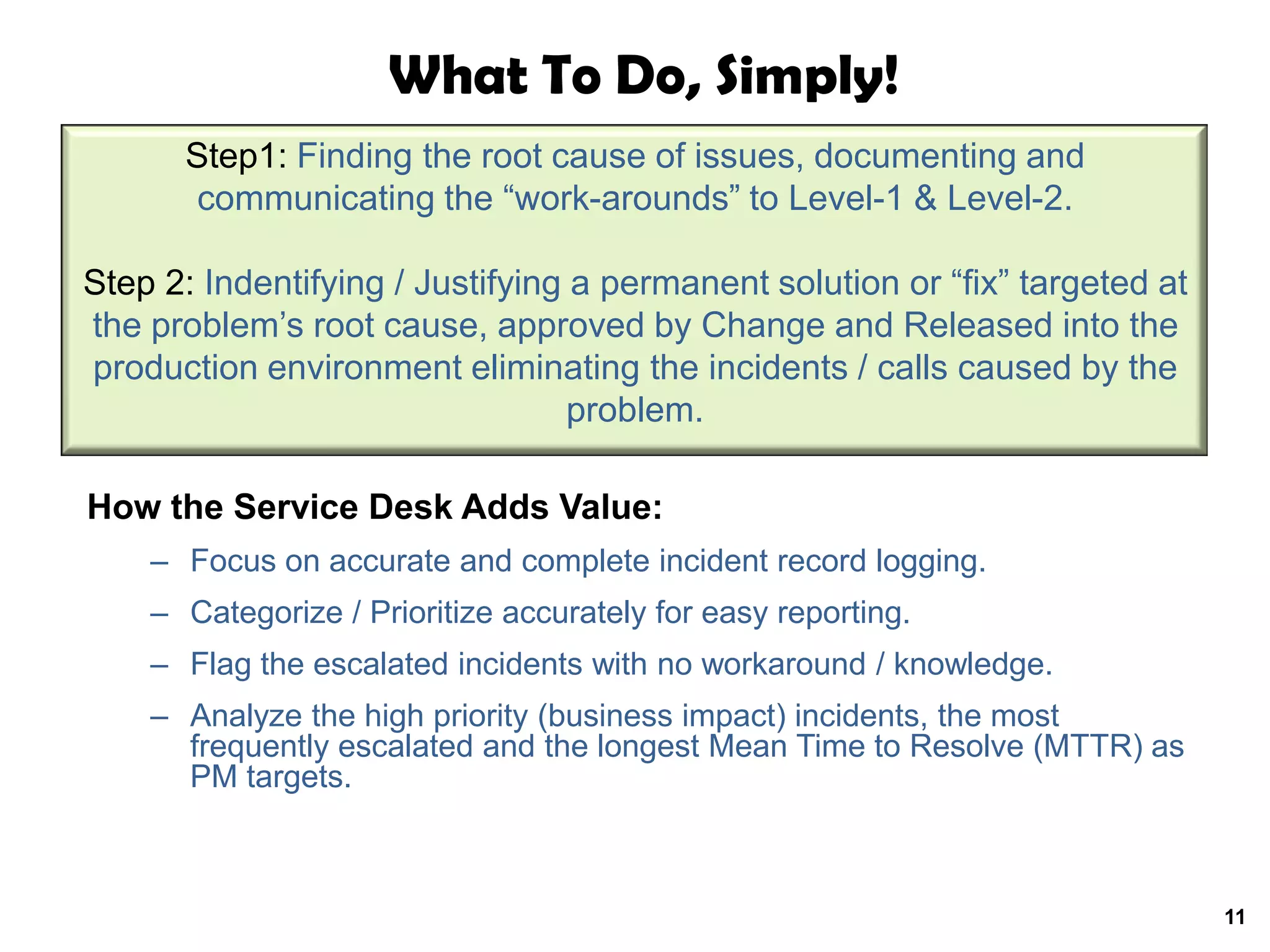
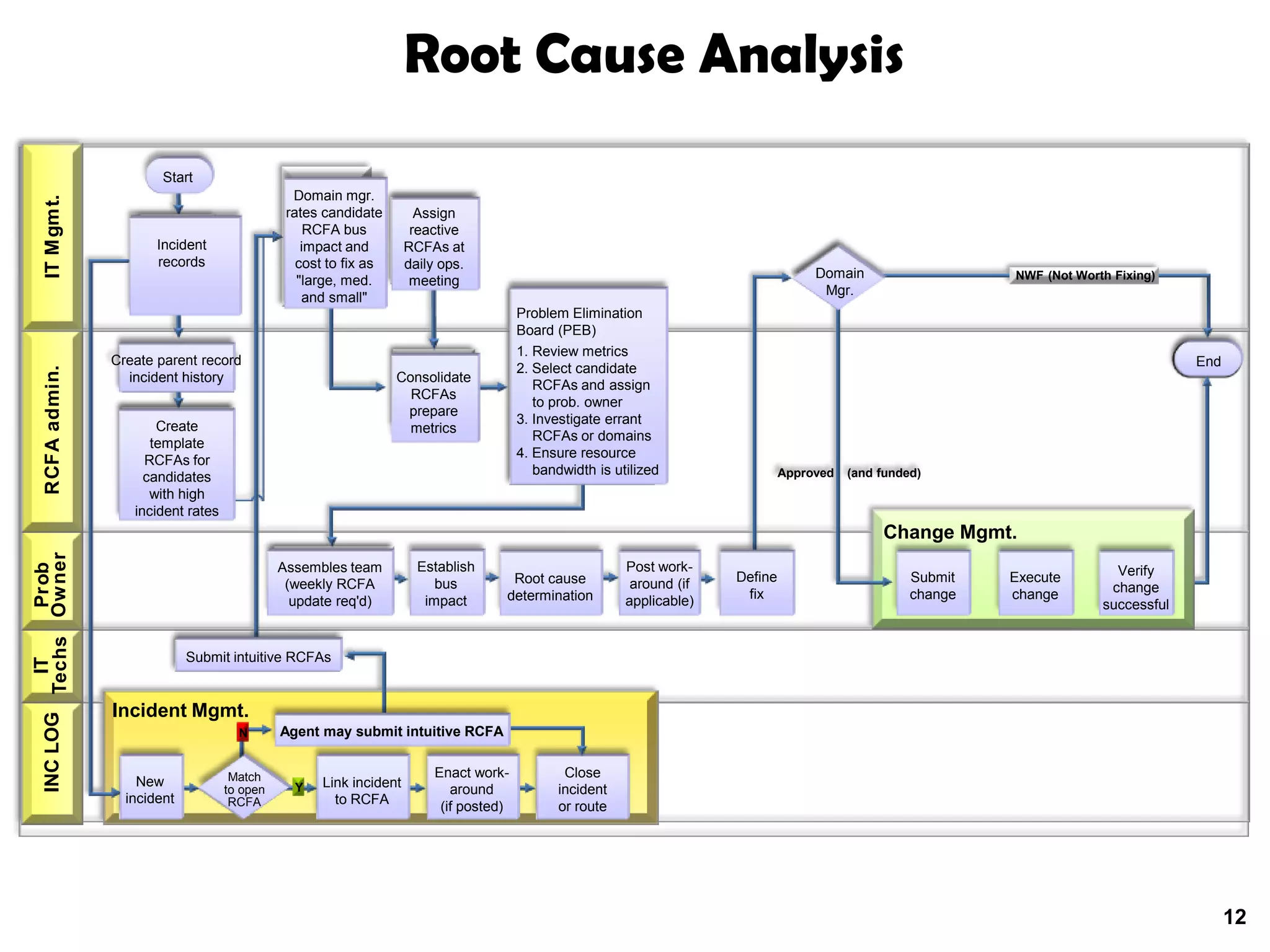
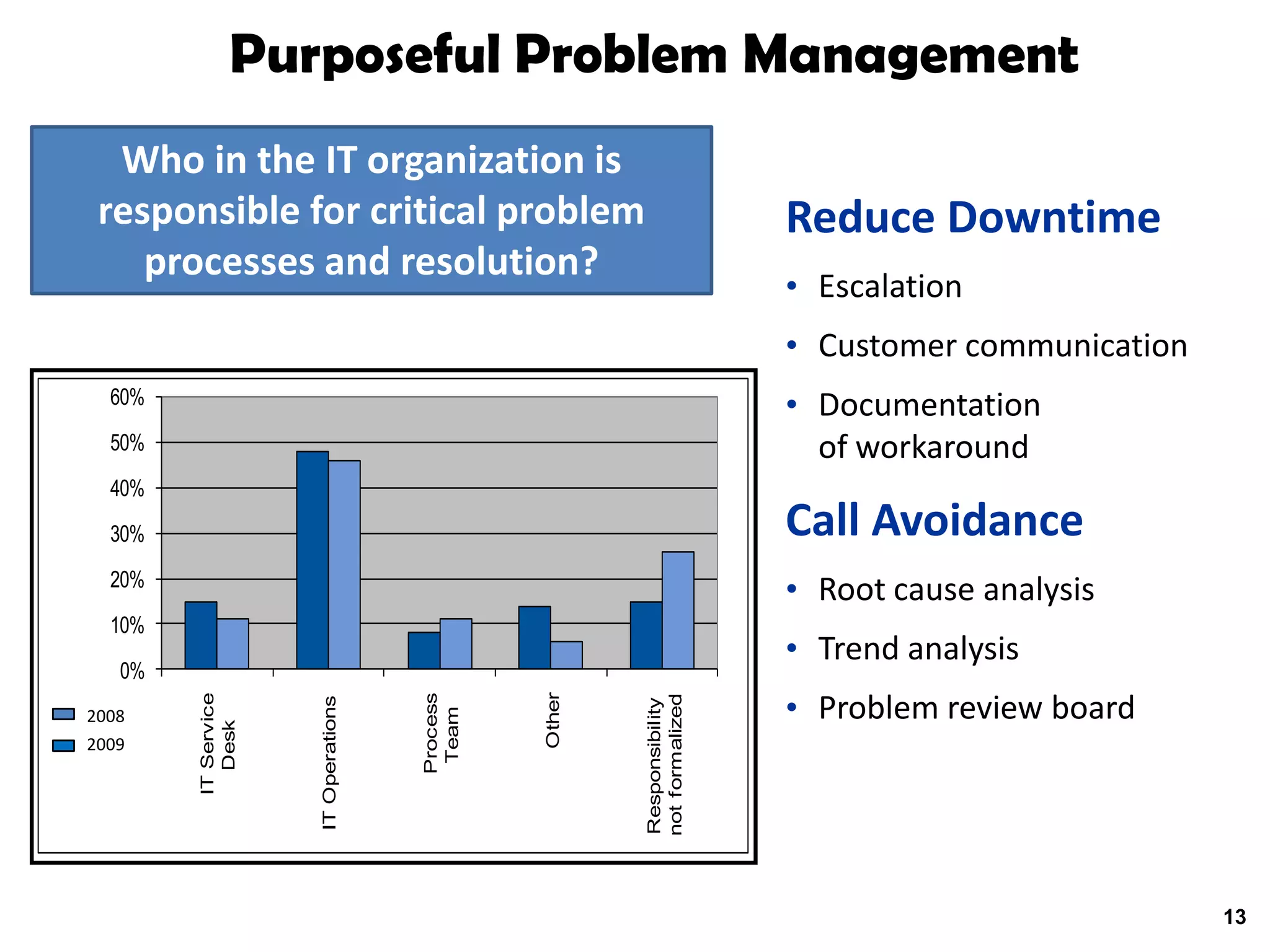
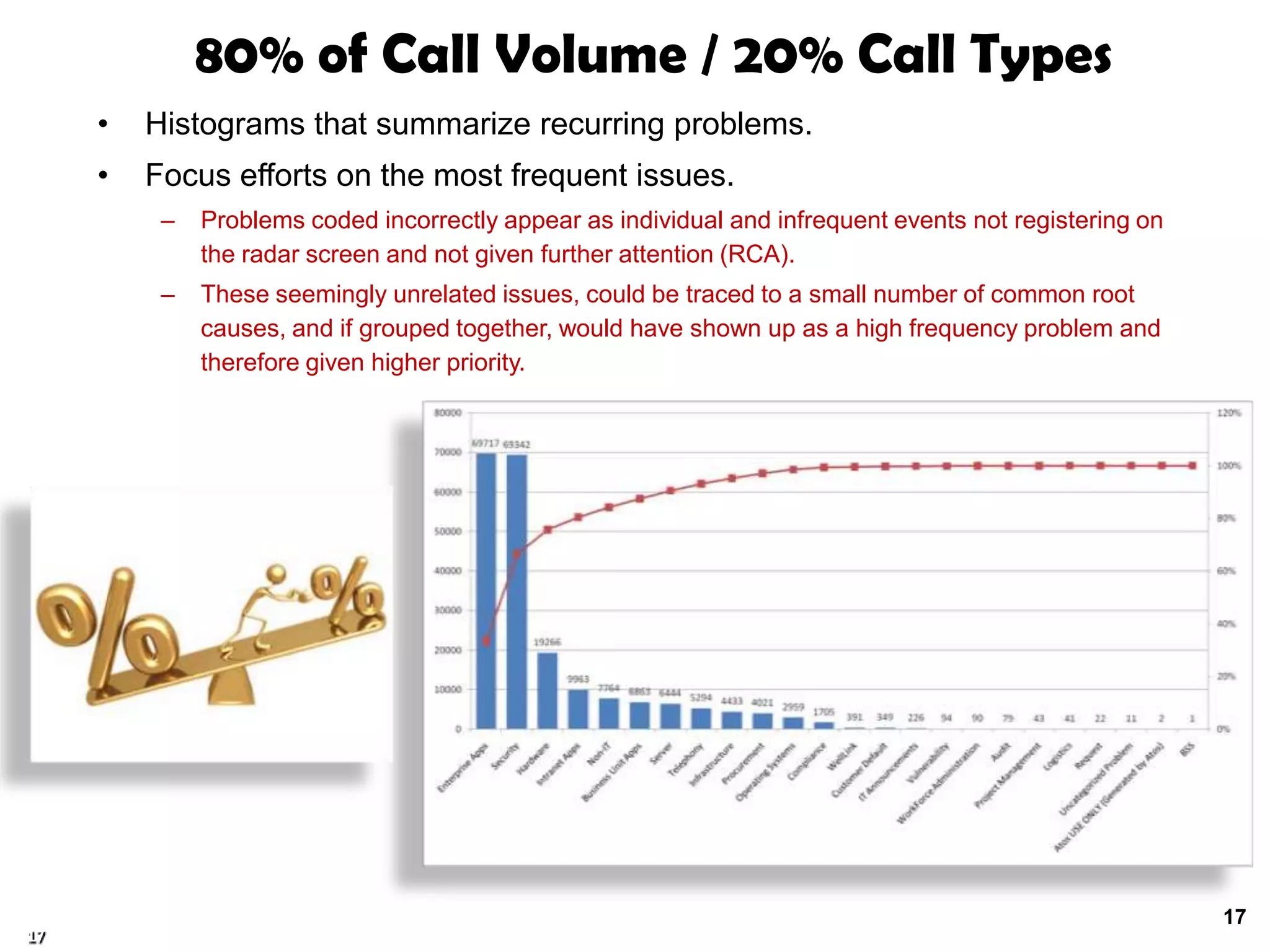
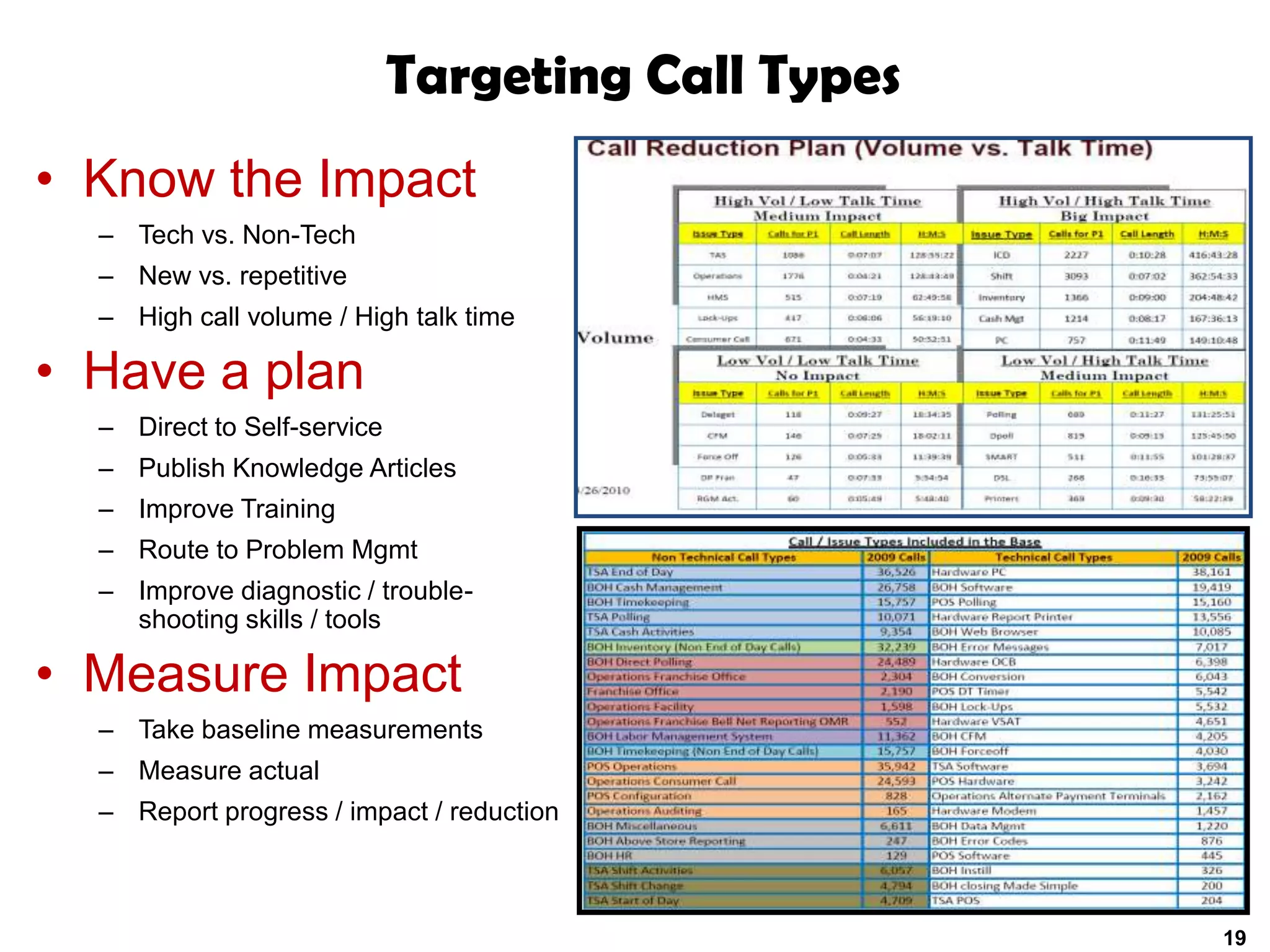
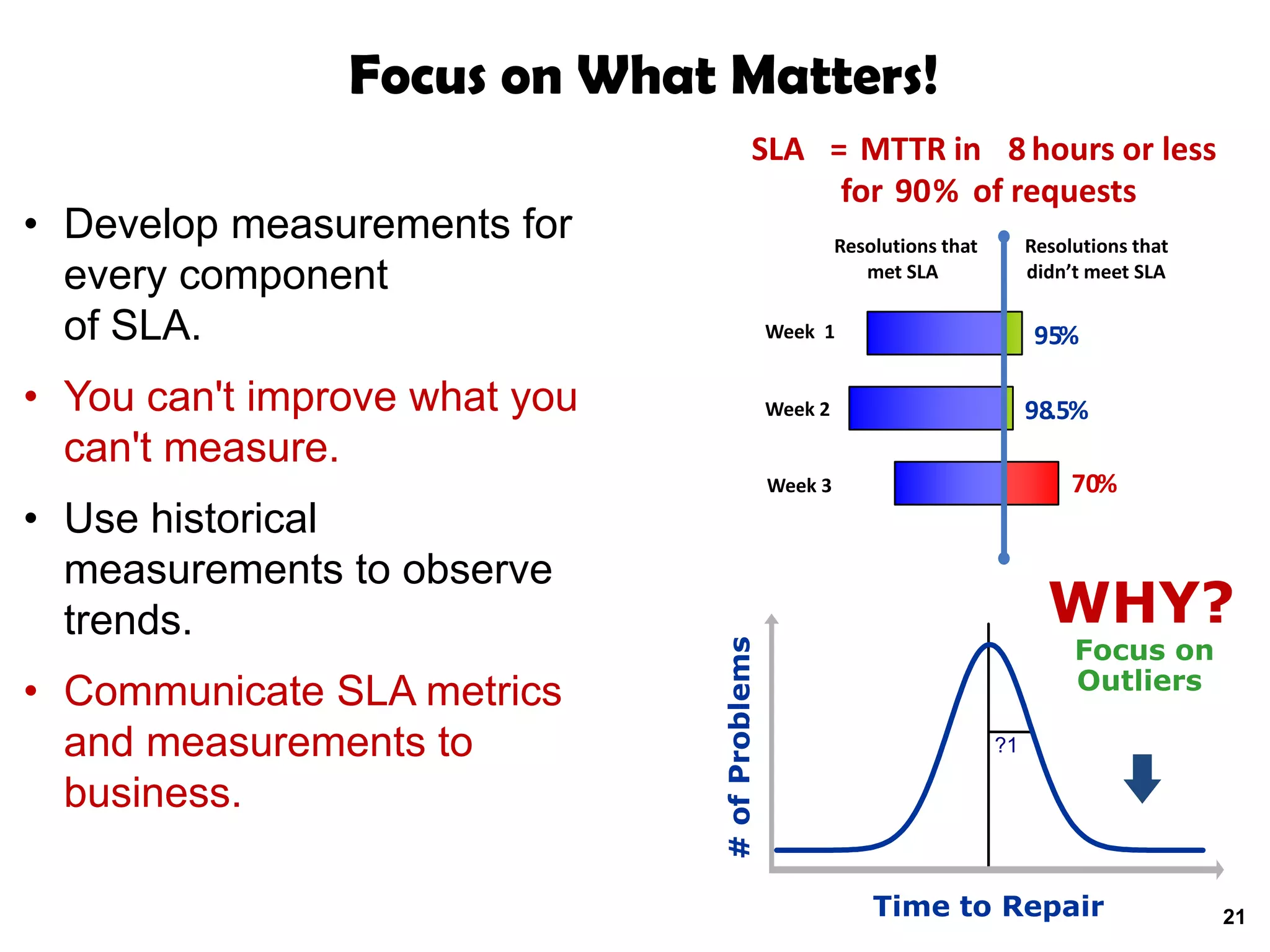
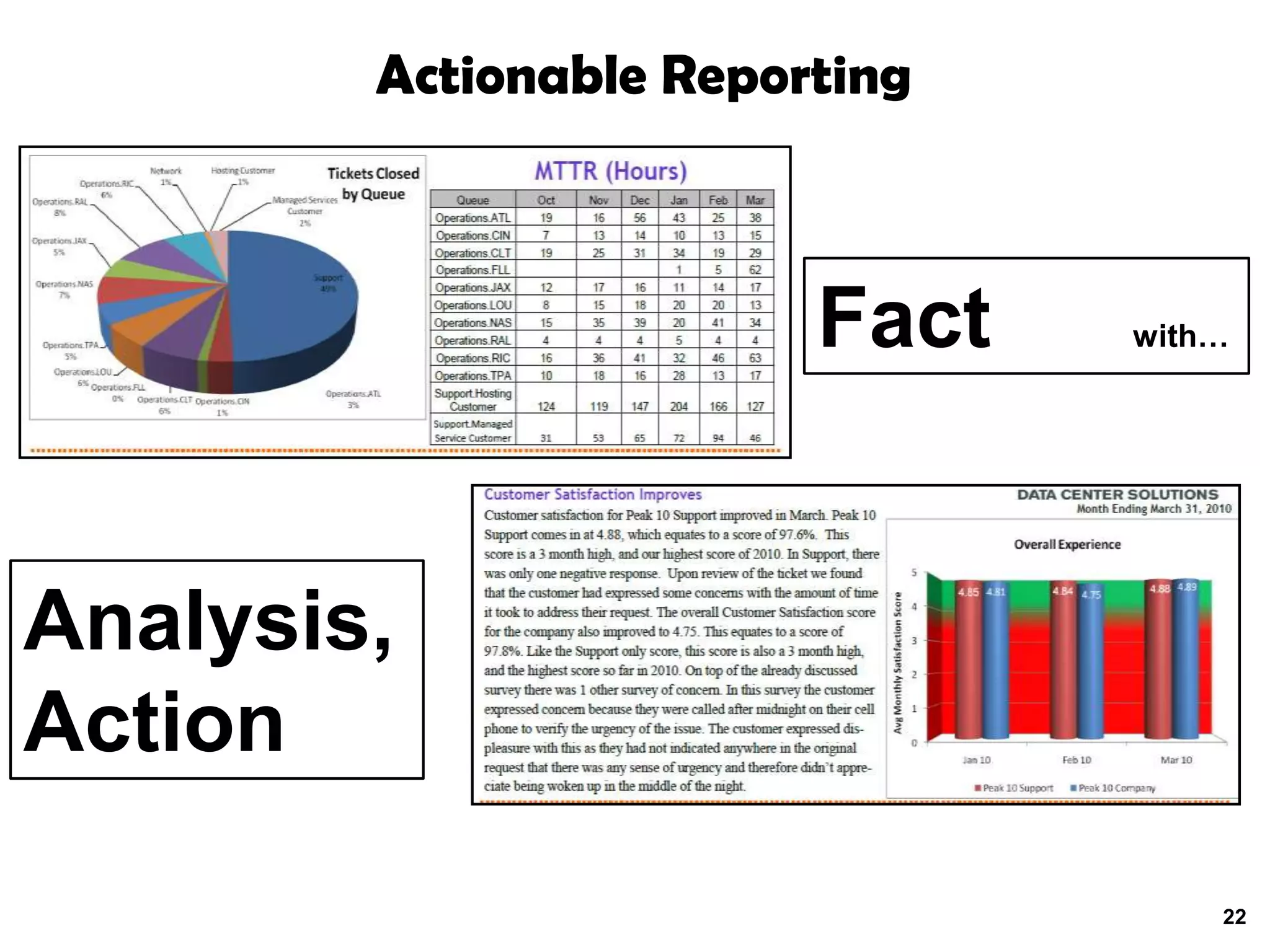
A quality problem management program can eliminate recurring problems that impact an organization's productivity and increase support costs. Implementing problem management requires integrating tools, processes, and people to generate measurable results through data analysis, trend reporting, and ensuring follow-up actions are taken. The value of a problem management program is defined by the measurable benefits it provides and how it communicates resolutions to stakeholders.