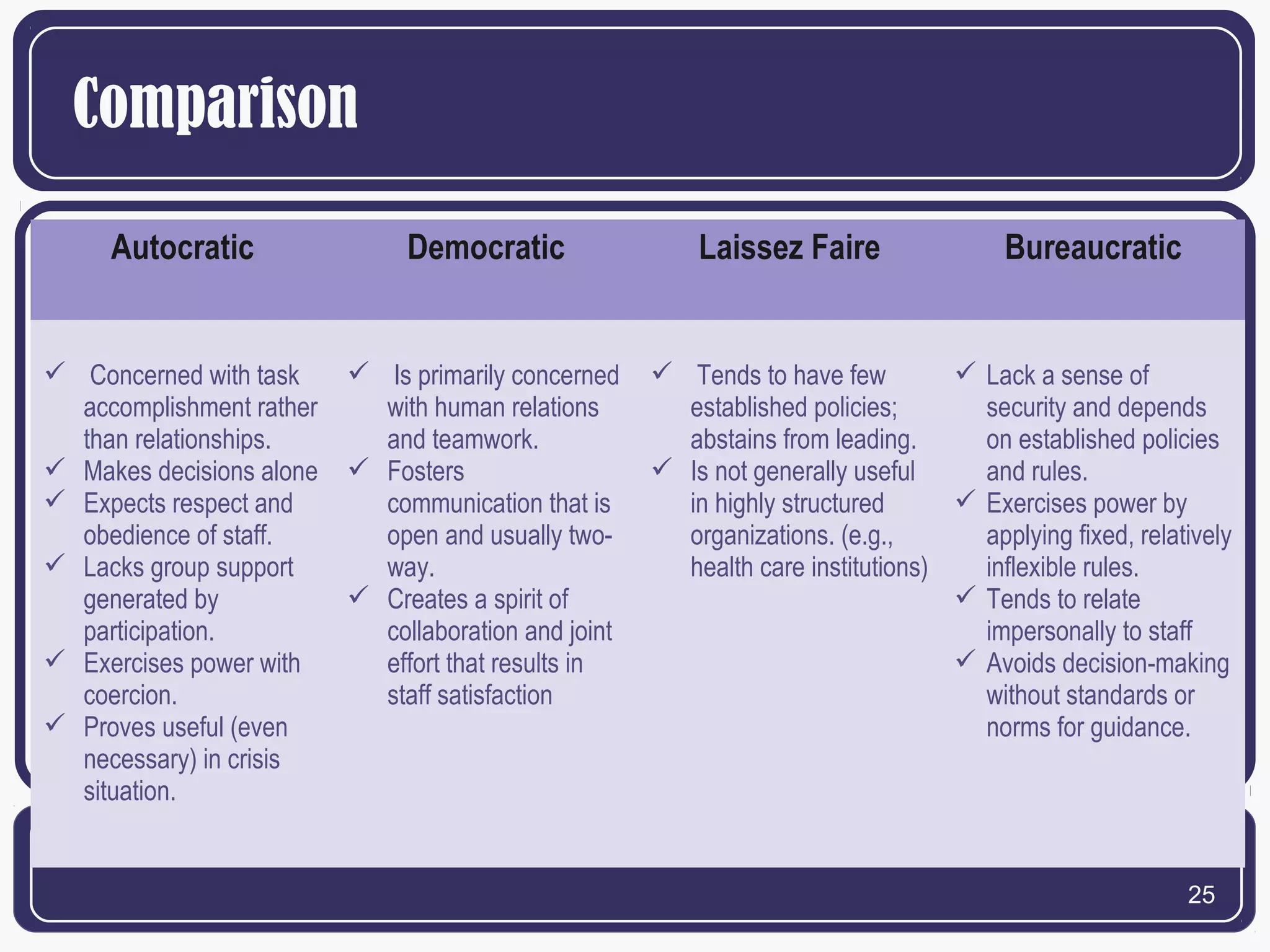
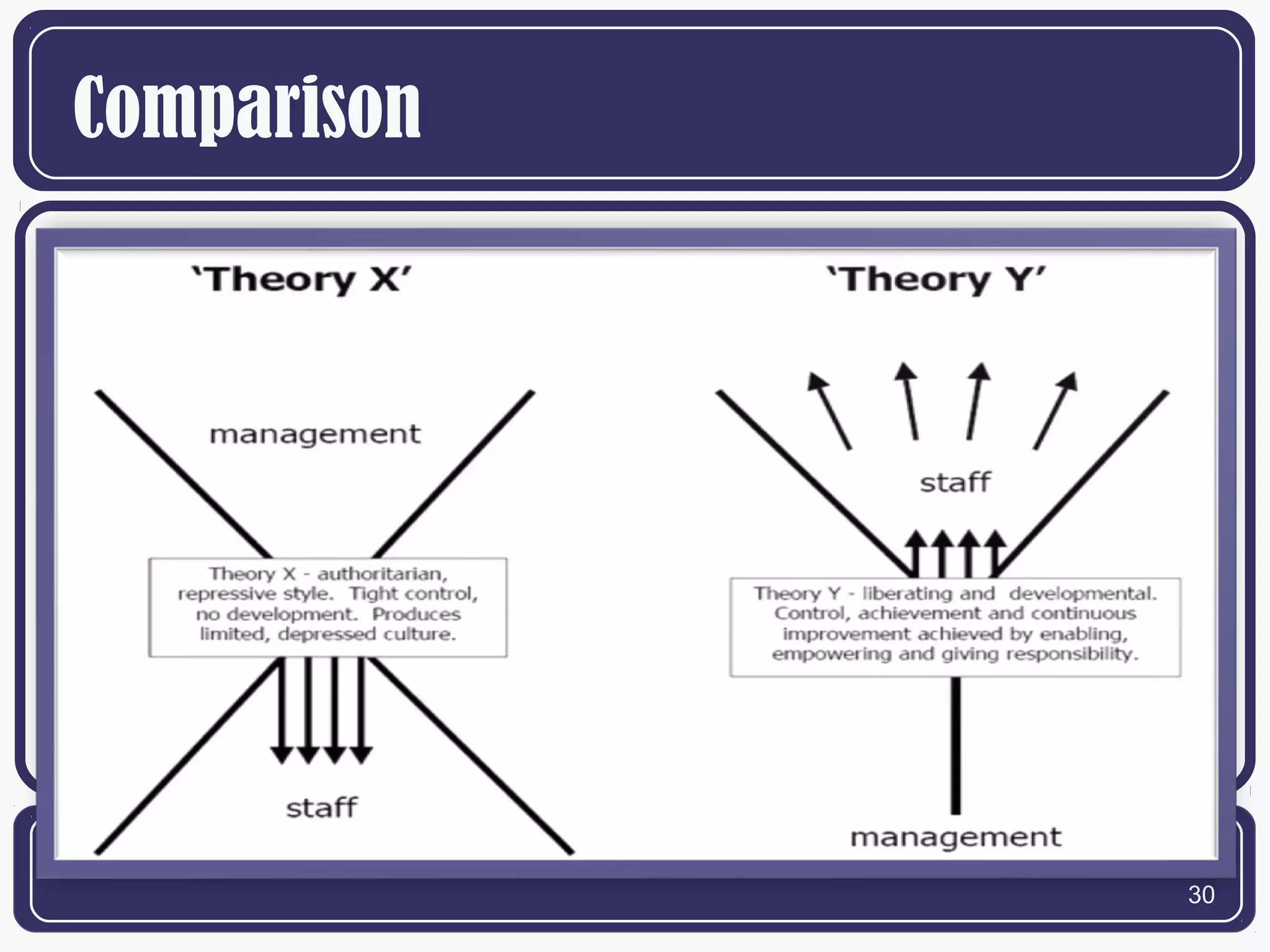
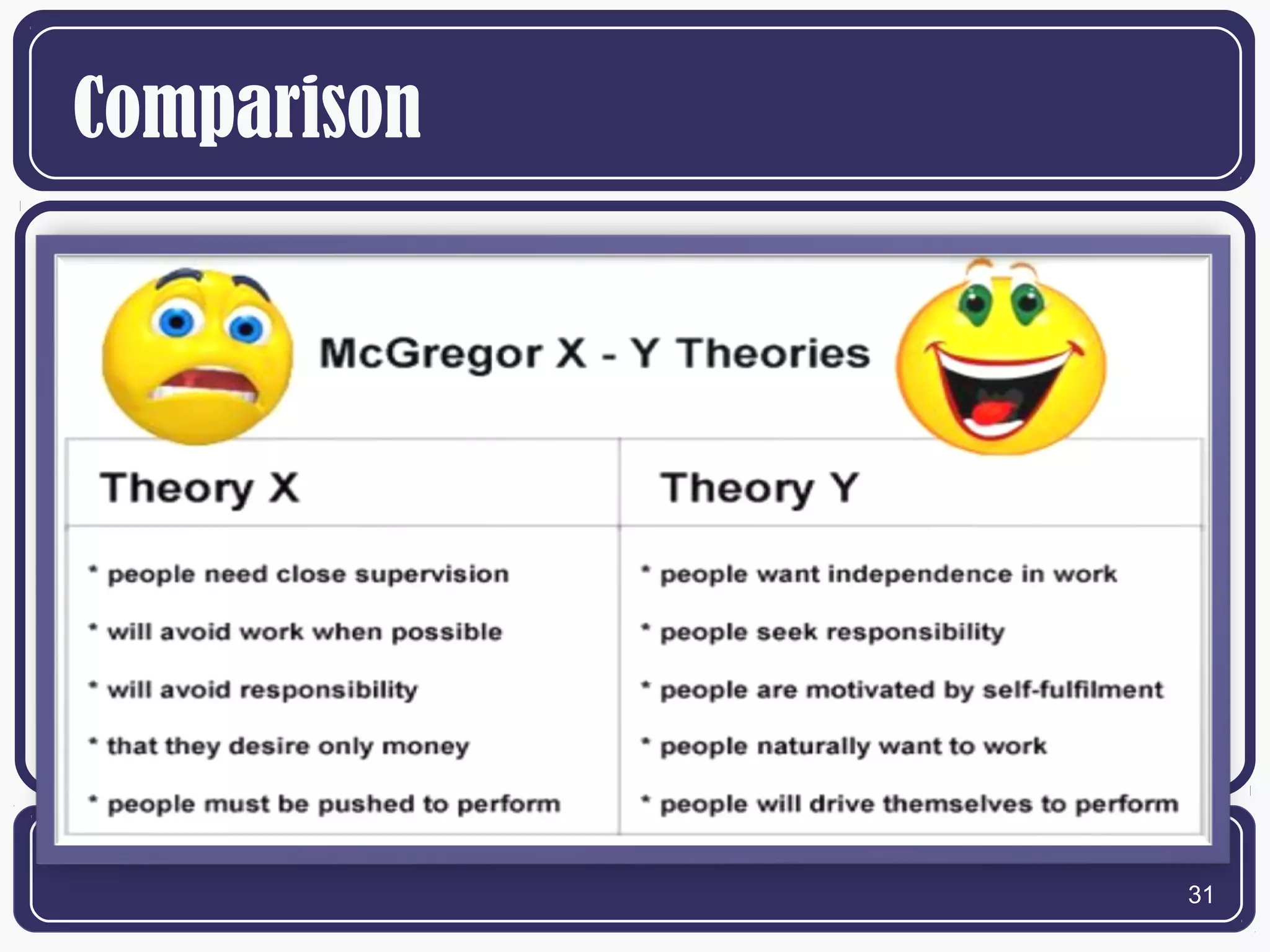
The document summarizes behavioral leadership theories proposed by several theorists. It discusses Kurt Lewin's three leadership styles of authoritarian, democratic, and laissez-faire. It also examines Jenkins and Henderson's bureaucratic leadership style. McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y are presented, with Theory X assuming people dislike work while Theory Y sees work as potentially satisfying. The behavioral view is that leadership is learned rather than innate, and effective leaders acquire behaviors through experience.