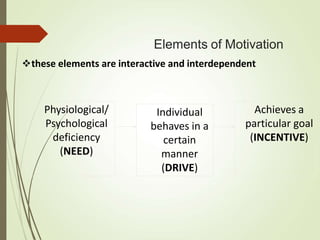
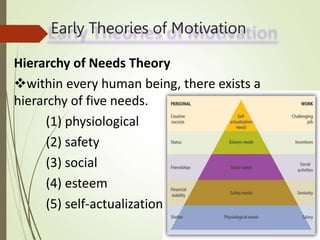
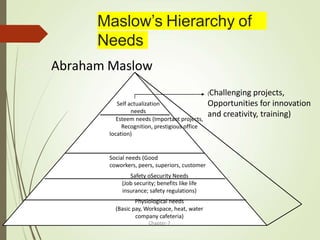
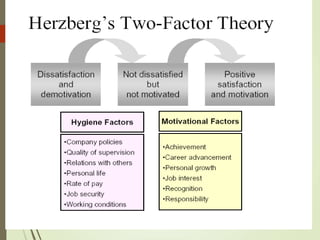
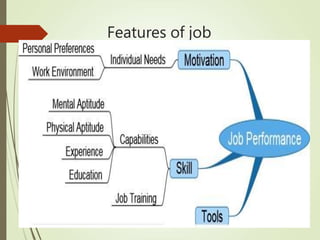
Motivation is influenced by physiological and psychological needs that drive behavior toward goals. Early theories proposed motivation as arising from a hierarchy of needs (Maslow) or as stemming from job satisfaction factors (Herzberg). More recent theories view motivation in terms of expectations of outcomes (Vroom) or as learned through reinforcement (Skinner). Effective leadership styles for motivation include democratic, which shares decision-making, and transactional, which appeals to self-interest through rewards for good performance. Autocratic leadership concentrates power in the leader while bureaucratic leadership relies on standardized procedures.