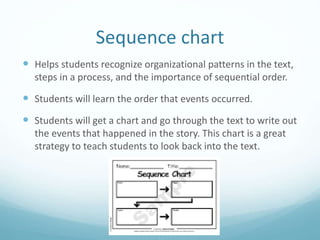
This document provides an overview of strategies to use before, during, and after reading to improve student comprehension. Some strategies outlined include using a K-W-L chart to activate prior knowledge before reading, having students ask questions while reading with the ReQuest strategy, and using exit slips as an informal assessment after reading to evaluate student understanding. The document also describes graphic organizers like story maps, umbrellas, and sequence charts to help students organize information from texts.