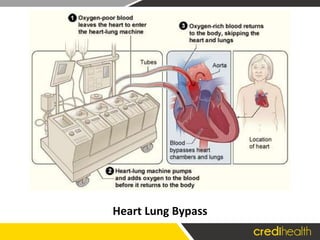
Beating heart bypass surgery, also known as CABG, is performed while the heart is still beating and is increasingly common. It is recommended for patients with severe angina, multiple artery blockages, or in emergency situations like heart attacks when other treatments are ineffective. The procedure involves grafting blood vessels to bypass blockages and has been linked to shorter recovery times and fewer complications compared to traditional methods.