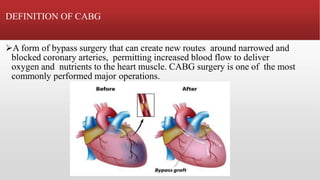
Heart bypass surgery involves surgical operations to correct life-threatening heart conditions. There are two main types: open heart surgery and closed heart surgery. The first successful open heart surgery was performed in 1893. Cardiac surgery aims to improve quality of life and lifespan by restoring blood flow to the heart. Key procedures include coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), where new routes are created around blocked arteries to increase blood flow to the heart muscle. CABG involves harvesting grafts, examining and stabilizing the heart, placing chest tubes, and monitoring the patient in intensive care after surgery, though there are risks such as infection, bleeding, and stroke.