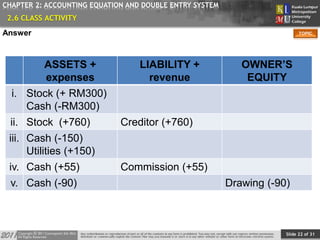
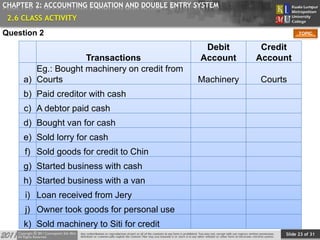
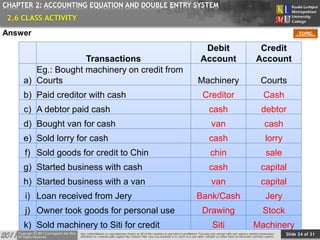
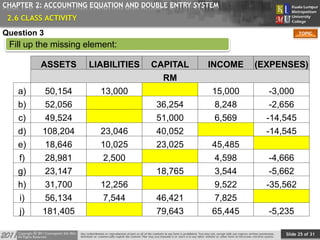
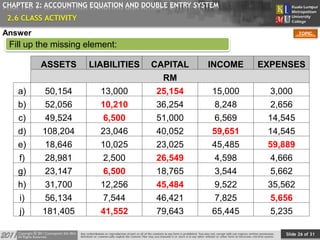
This document provides an overview of Chapter 2 from a financial accounting textbook. The chapter covers the accounting equation and double-entry system. It defines the accounting equation as assets equaling liabilities plus owner's equity. It also explains the double-entry system where every transaction affects at least two accounts with equal and opposite entries. The document outlines the chapter topics, provides examples of classifying accounts and double-entry transactions, and previews the next chapter on business documents used in accounting.



![Slide 6 of 31
TOPIC
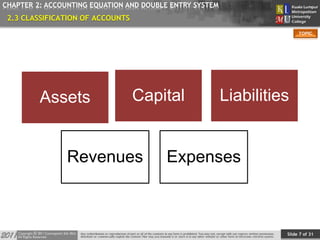
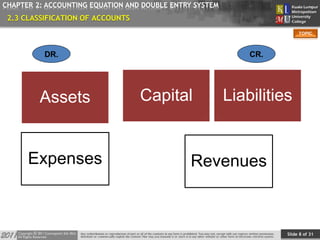
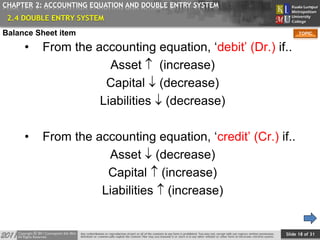
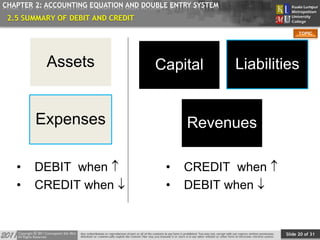
CHAPTER 2: ACCOUNTING EQUATION AND DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM
• If the equation is expanded then it becomes….
ASSETS = (OPENING CAPITAL + NET PROFIT-
DRAWINGS) + LIABILITIES
and…..
ASSETS = (OPENING CAPITAL
+[REVENUES –EXPENSES]-
DRAWINGS) + LIABILITIES
2.2 ACCOUNTING EQUATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bdc10102-150604085039-lva1-app6891/85/Bdc-101-02-6-320.jpg)