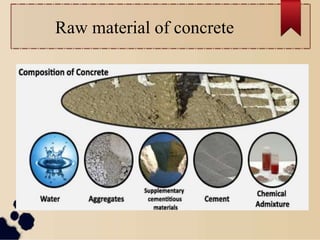
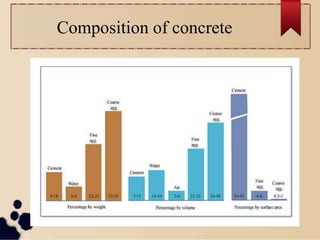
This document provides an overview of different types of concrete. It begins by defining concrete as a composite material composed mainly of water, aggregate, and cement. Concrete is then described as being widely used in architectural structures, foundations, pavements, bridges, and other infrastructure projects. The document goes on to summarize the main raw materials used in concrete and its basic composition. It also outlines several types of concrete including normal concrete, high strength concrete, high performance concrete, light weight concrete, and self compacting concrete. For each type, it provides a brief definition and notes on characteristics and applications.