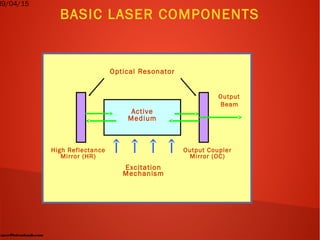
The laser is an optical amplifier that works on the principle of stimulated emission of radiation. Einstein first predicted stimulated emission in 1917, but it was not utilized until the 1950s when the maser was developed. In 1960, Maiman built the first laser, a ruby laser, and shortly after the first gas laser was developed. The basic components of a laser are an active medium to amplify light, an excitation mechanism to energize the medium, and optical resonators with at least one mirror to provide feedback. Common laser types include He-Ne, CO2, and semiconductor lasers which have various applications like optical storage, surgery, manufacturing.