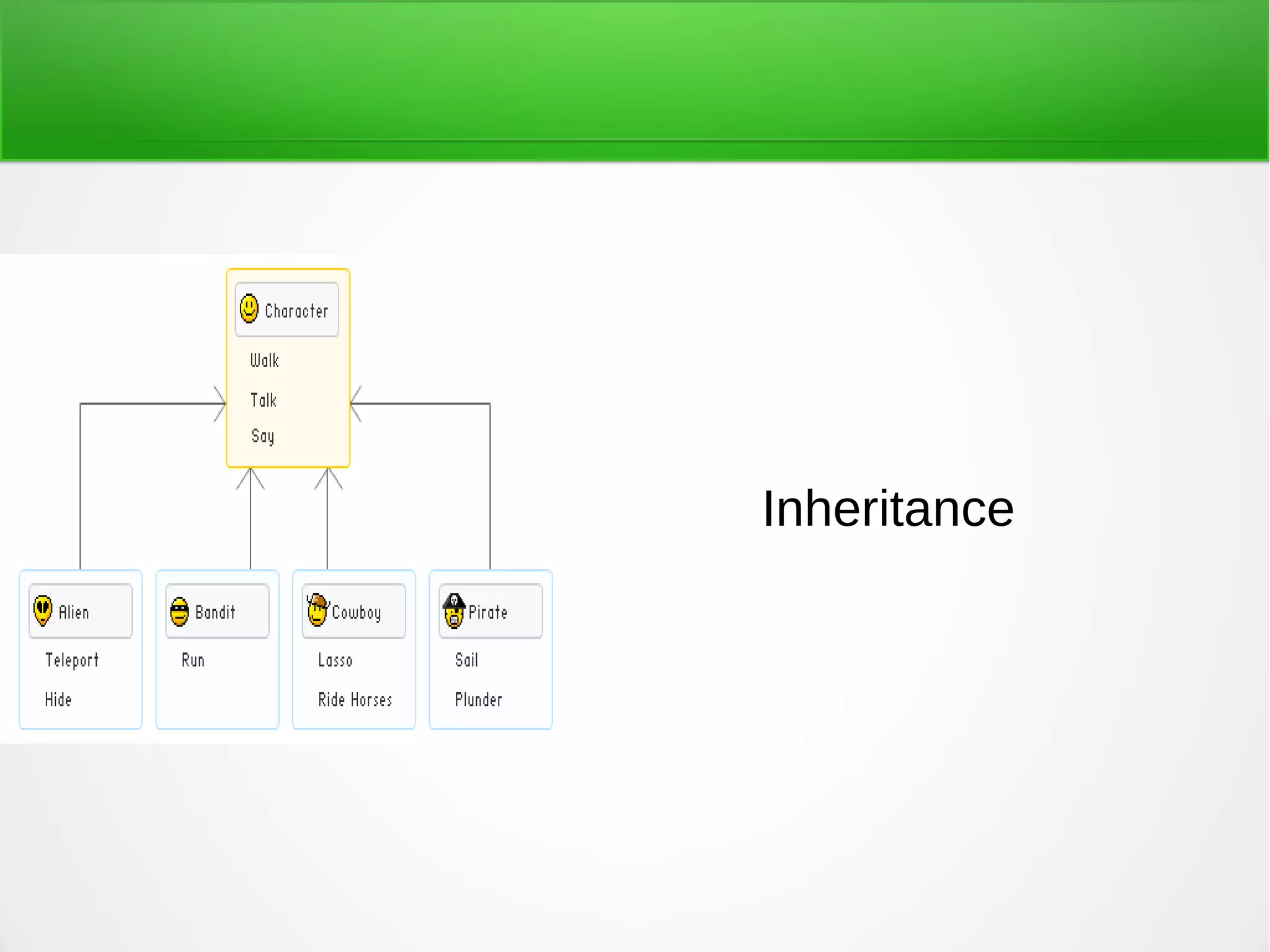
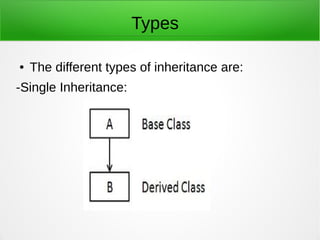
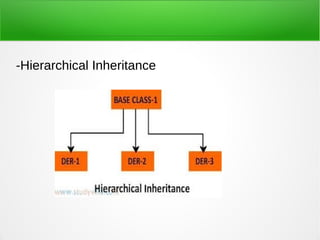
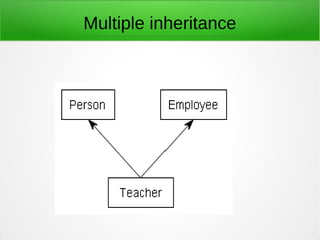
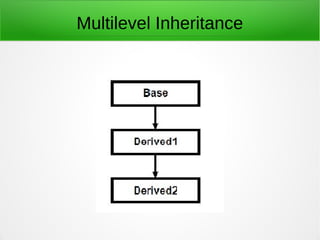
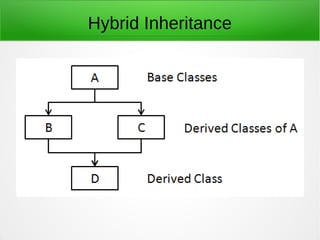
Inheritance in object-oriented programming enables new objects to take on the properties of existing objects. A superclass or base class is used as the basis for inheritance. Inheritance is useful when classes represent an "is-a" relationship, when code can be reused from base classes, or when the same methods need to be applied to different data types within a reasonably shallow class hierarchy. It allows global changes by modifying a base class and types include single, hierarchical, multiple, multilevel, and hybrid inheritance. Advantages are reusability, extensibility, data hiding, and overriding while disadvantages include tight coupling between base and inherited classes that makes independent use and maintenance more difficult.