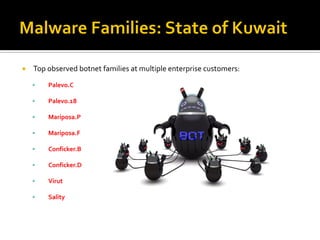
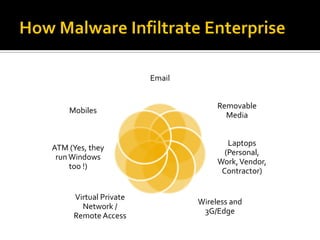
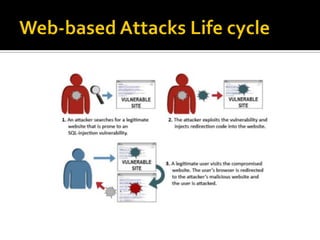
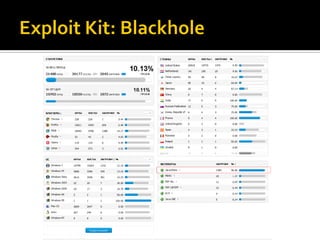
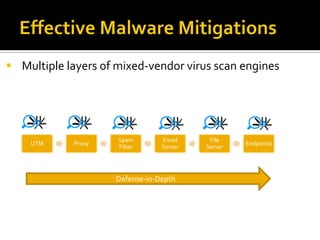
The document discusses trends in malware and effective mitigation strategies. It notes that in 2012, mobile malware increased through SMS and social media. Malware also targeted corporate networks through espionage. The document then provides statistics on prevalent botnet families and malware infiltration methods like compromised websites and social networks. It recommends multiple defenses including device control, application whitelisting, patch management, web filtering, threat intelligence integration, and geo-blocking of high-risk countries.