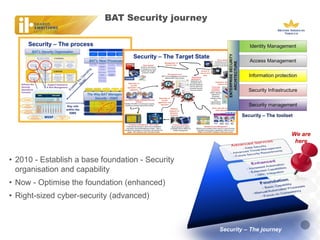
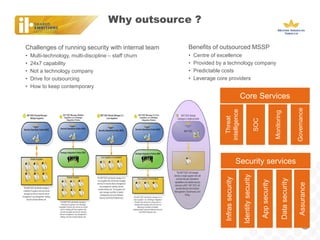
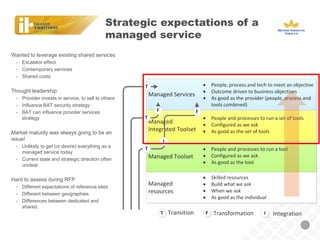
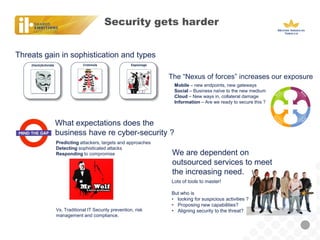
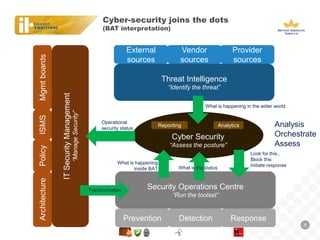
BAT, a large tobacco company, is undergoing a business transformation and looking to consolidate IT systems. It has outsourced some security functions to a managed security service provider (MSSP) to gain efficiencies. The outsourcing has had some successes like a global firewall and endpoint security, but also issues around costs, customization needs, and meeting expectations. As threats grow more sophisticated, BAT will need to ensure its outsourced security controls can address advanced attacks and that the MSSP aligns with its strategic security needs.