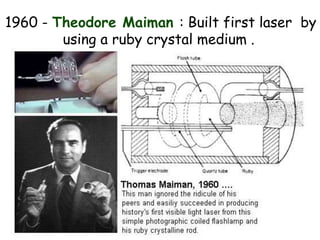
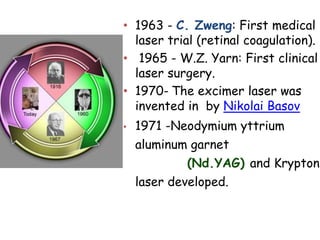
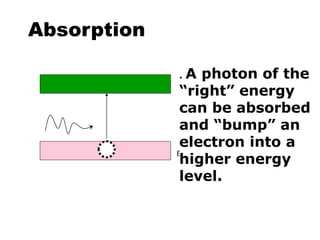
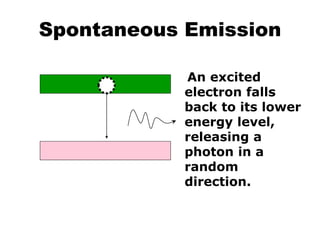
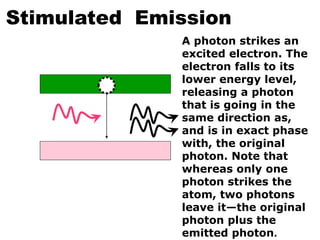
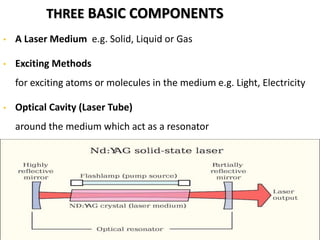
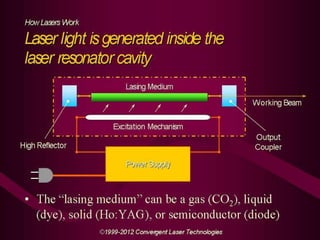
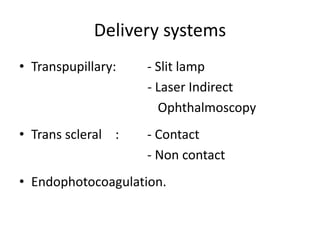
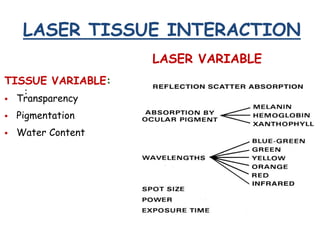
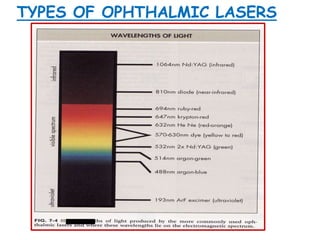
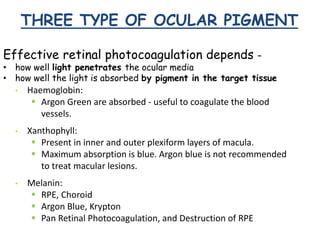
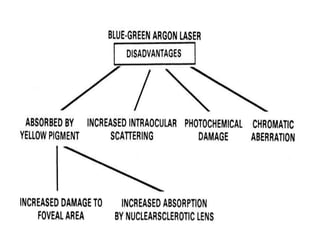
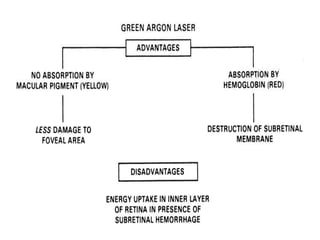
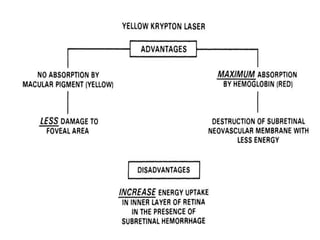
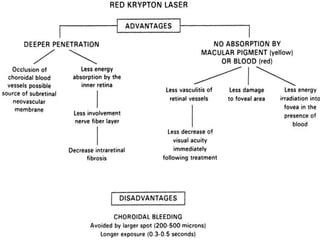
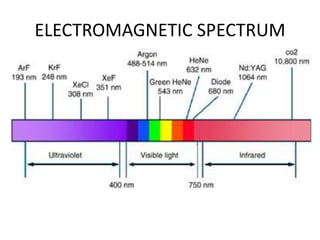
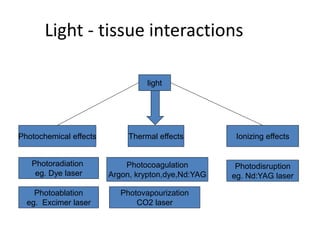
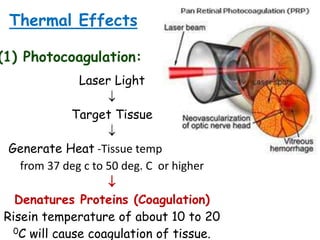
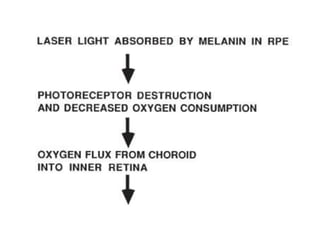
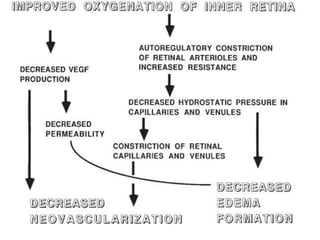
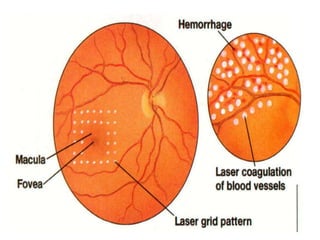
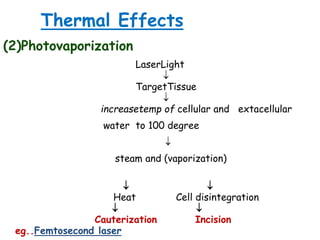
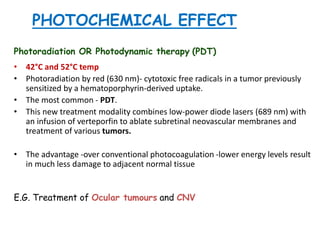
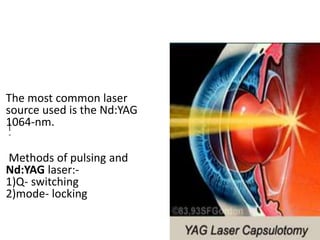
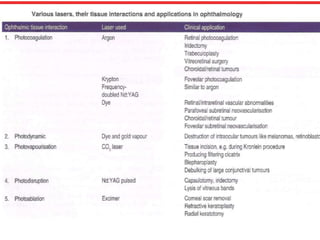
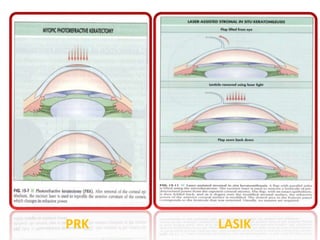
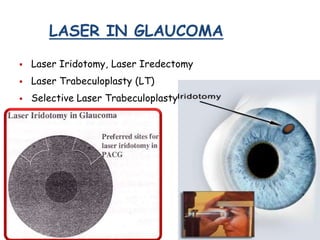
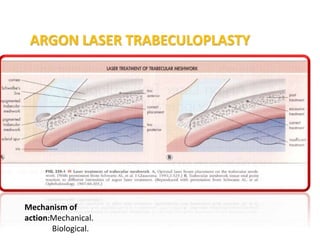
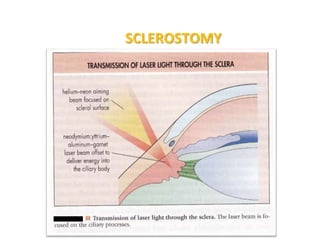
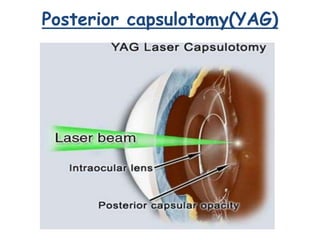
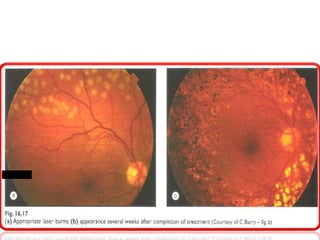
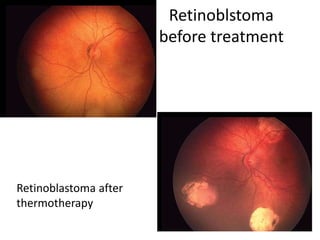
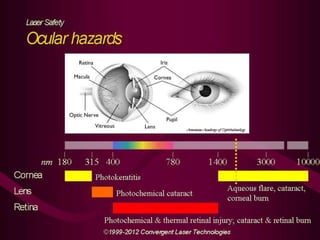
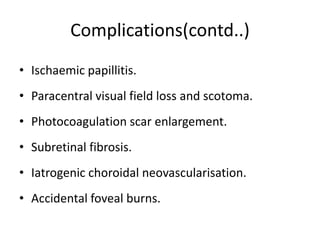
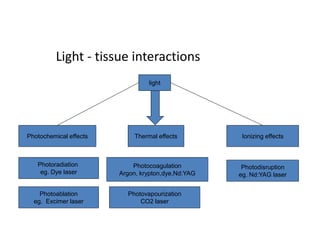
This document provides an overview of lasers and their use in ophthalmology. It begins with definitions of laser and its key properties such as monochromatic, coherent, and collimated light. It then discusses the history and development of lasers from Einstein's work in 1917 to the first laser created by Maiman in 1960. Common laser types and their applications in ophthalmology are covered such as Nd:YAG for retinal photocoagulation and femtosecond lasers for corneal surgery. Safety considerations and potential complications of laser treatment are also summarized.