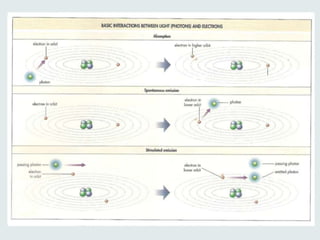
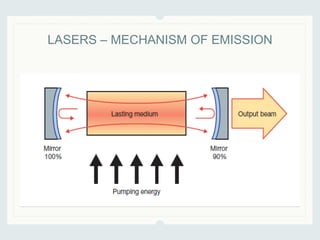
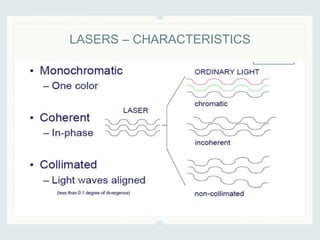
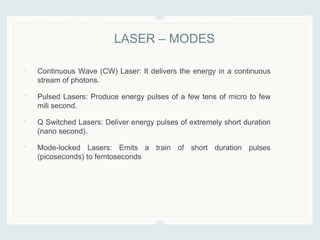
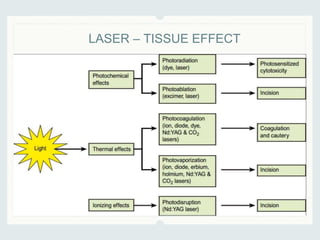
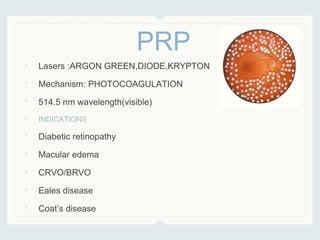
This document discusses lasers used in ophthalmology. It defines lasers and describes their basic mechanisms of emission and characteristics such as wavelength, power, modes. It discusses the tissue effects of different lasers and how they are absorbed by structures like haemoglobin, xanthophyll, and melanin. Examples of common lasers used include the argon green, Nd:YAG, excimer, and diode lasers. It explains the different mechanisms of laser tissue interaction including photocoagulation, photodisruption, photoablation, and photoactivation.