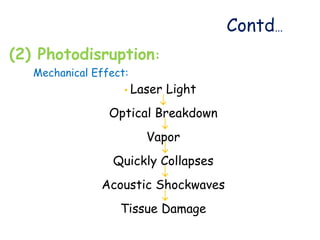
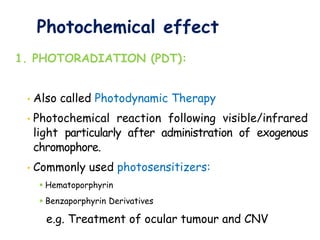
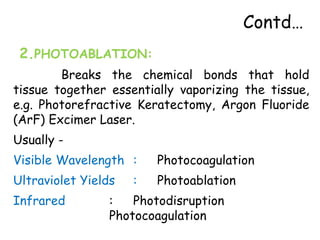
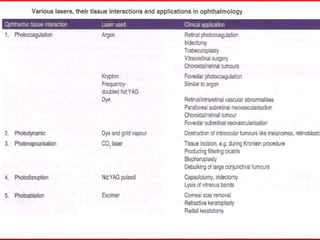
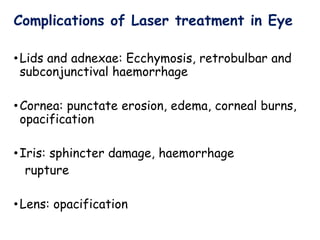
The document provides an overview of lasers, including:
1. It defines what a laser is, describing the acronym LASER and how lasers emit a useful form of light energy.
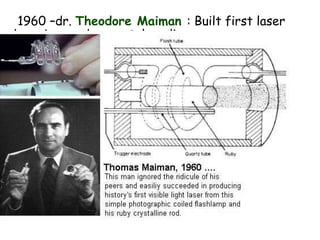
2. It discusses the history and development of lasers, including milestones such as the first laser built in 1960 and early medical uses starting in 1963.
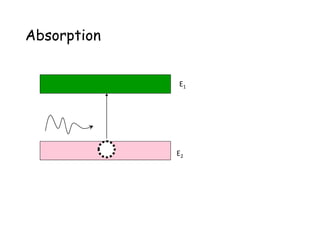
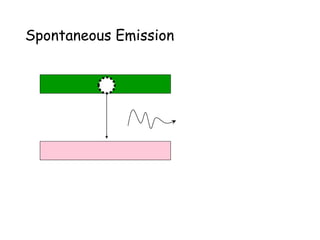
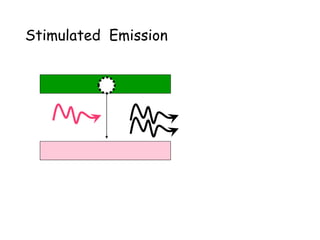
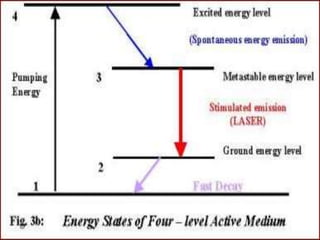
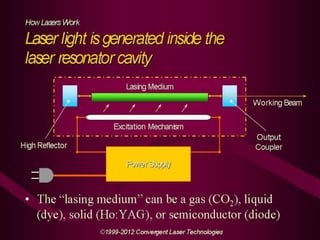
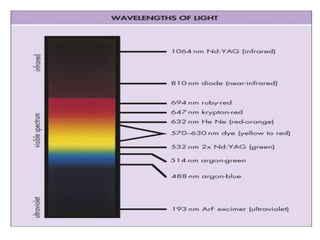
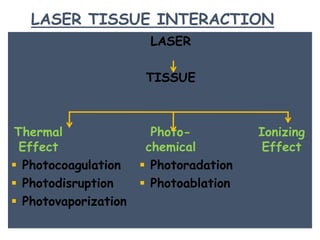
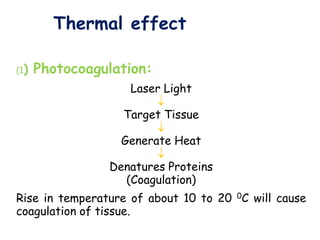
3. It describes the key principles and components of how lasers work, including stimulated emission, the pumping system, and optical cavity that contains the lasing medium.