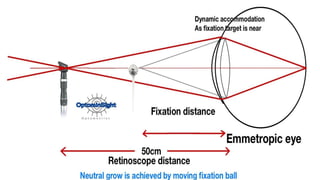
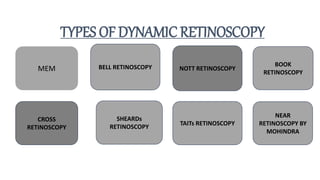
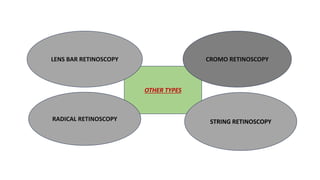
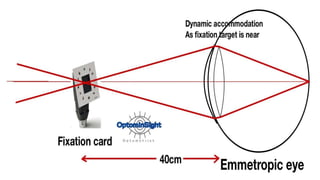
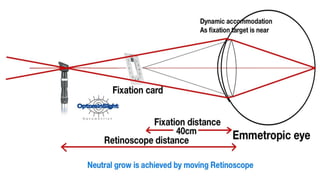
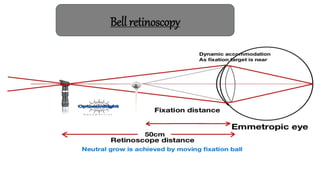
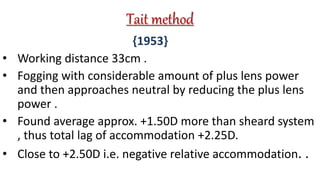
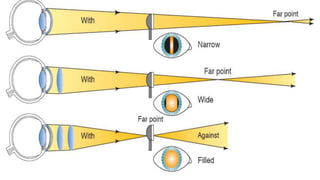
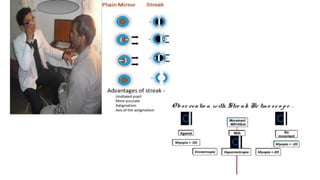
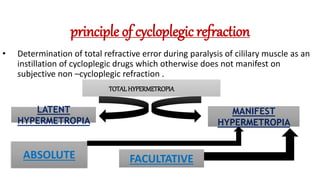
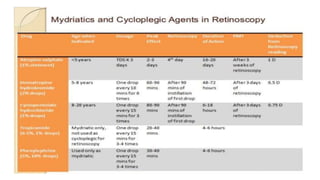
The document discusses dynamic and static retinoscopy techniques for assessing refractive errors in patients, highlighting the types, procedures, and uses of these methods. It details various dynamic retinoscopy techniques like Mohindra near retinoscopy and the procedures involved, as well as static retinoscopy involving cycloplegic agents. It also emphasizes the significance of these methods in diagnosing accommodative disorders and determining suitable refraction for different age groups.


















![Pmt {post mydriatic test }
Assessment of the finding of cyclo-refraction by
subjective means after the effect of cycloplegia is
eliminated .
In case of cycloplegia this test is usually done after
3-5 days and 1 month later on in case of atropine .
*NOTE –IF PATIENT IS HYPERMETROPIC ,GIVE
THE MOST PLUS [+] POWER POSSIBLE
WITHOUT REDUCING VISUAL ACUITY .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dynamicandstaticretinoscopy-240630040059-c475fd4a/85/BASICS-DYNAMIC-AND-STATIC-RETINOSCOPY-31-320.jpg)

