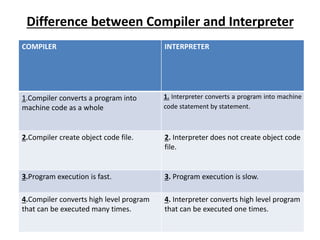
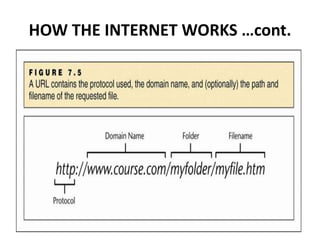
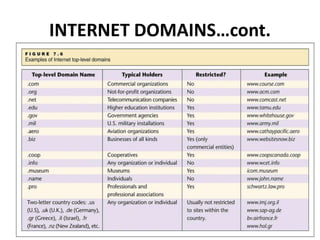
The document provides an introduction to computers, programming languages, and networks, detailing components of computers such as input/output devices, storage devices, and types of memory. It explains programming languages, differentiating between low-level and high-level languages and their compilers and interpreters. Additionally, the document covers networking basics, classifications, architectures, and the workings of the internet, emphasizing its importance in communication and resource sharing.