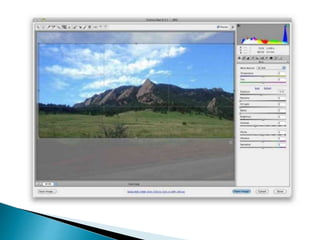
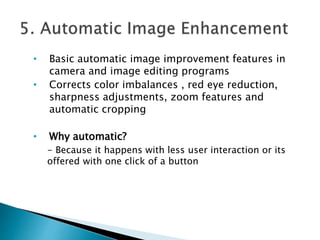
This document provides an overview of basic photo editing concepts and skills to be learned in the quarter, including exploring Adobe Photoshop. It defines image and photo editing as altering, changing, or modifying photographs, illustrations, or digitally processed photos. Common photo editing tools allow users to manipulate, enhance, and transform images, and are also used to create computer art. Basic editing techniques like cropping, resizing, adjusting brightness and contrast, sharpening and softening are described. The document also covers image file formats, layers in Photoshop, selections, resolution, and color modes.