The document provides an overview of key concepts in the Australian legal system. It discusses:
- Main topics covered in the course syllabus and resources available to students
- How laws evolve from traditions and values and aim to keep up with societal changes
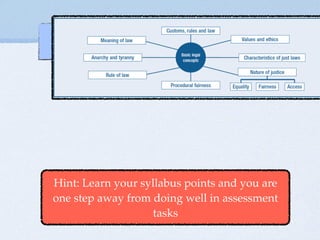
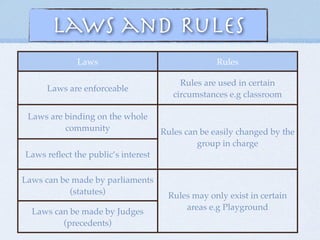
- Distinctions between laws, rules, customs, and nation-states
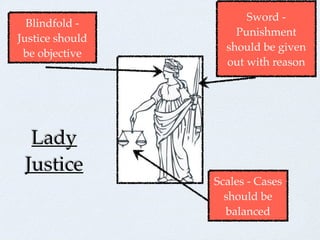
- Characteristics of just laws and ensuring justice through fairness, equality, and access
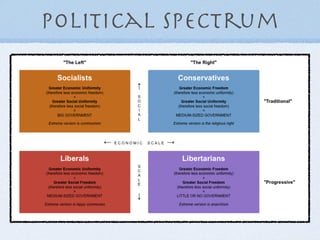
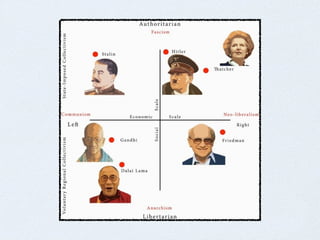
- Philosophies like utilitarianism and libertarianism that influence the legal system
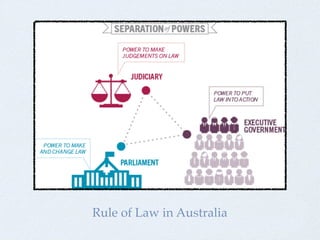
- Features needed to maintain the rule of law like separation of powers and an independent court system