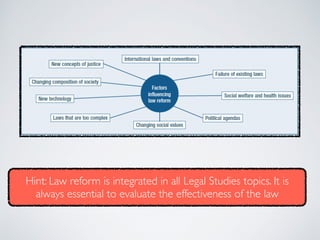
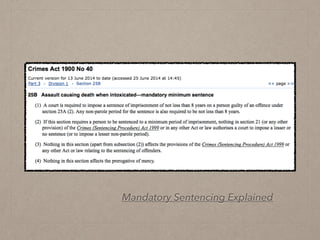
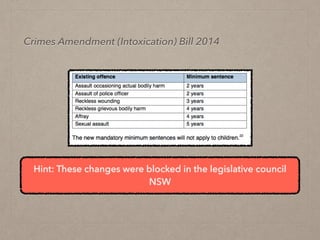
This document discusses law reform in Australia. It provides examples of law reform processes that have occurred, including mandatory sentencing laws for assaults involving intoxication in NSW and debates around euthanasia. It outlines the various mechanisms of law reform, including law reform commissions, parliamentary committees, media, non-government organizations, and international bodies. Law reform aims to modernize and simplify laws, remedy injustices, and adapt to changing social values and new technologies.