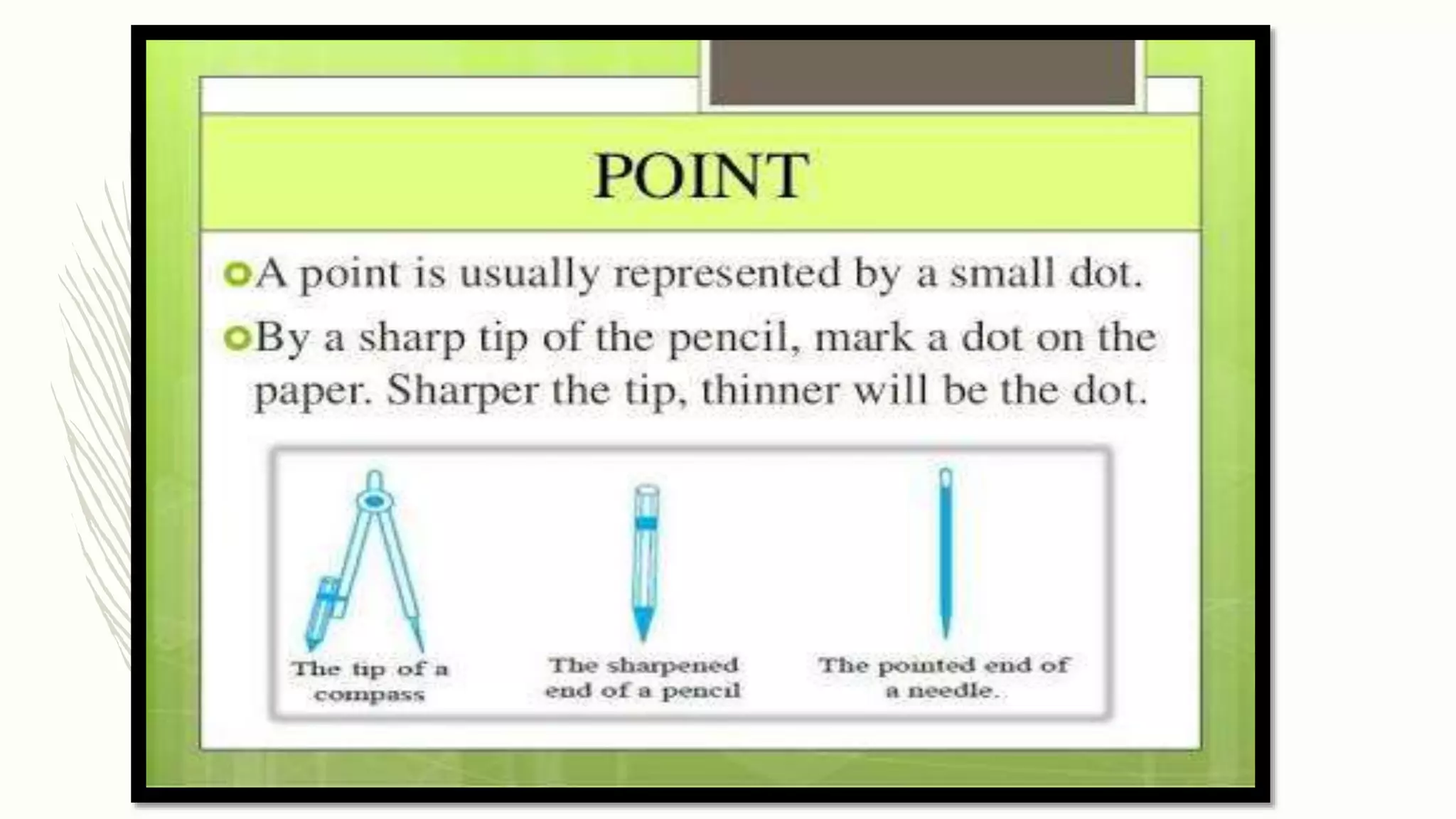
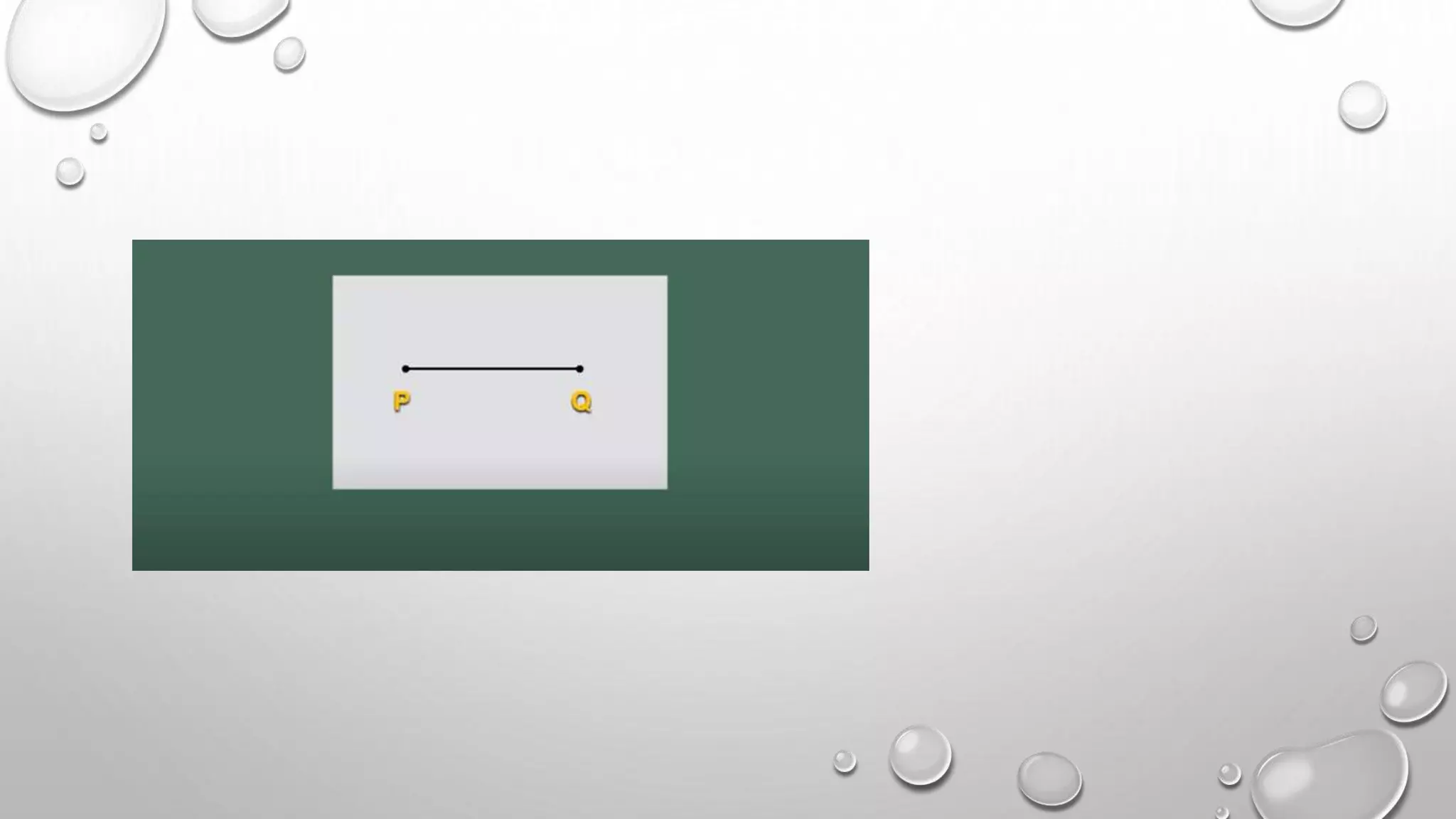
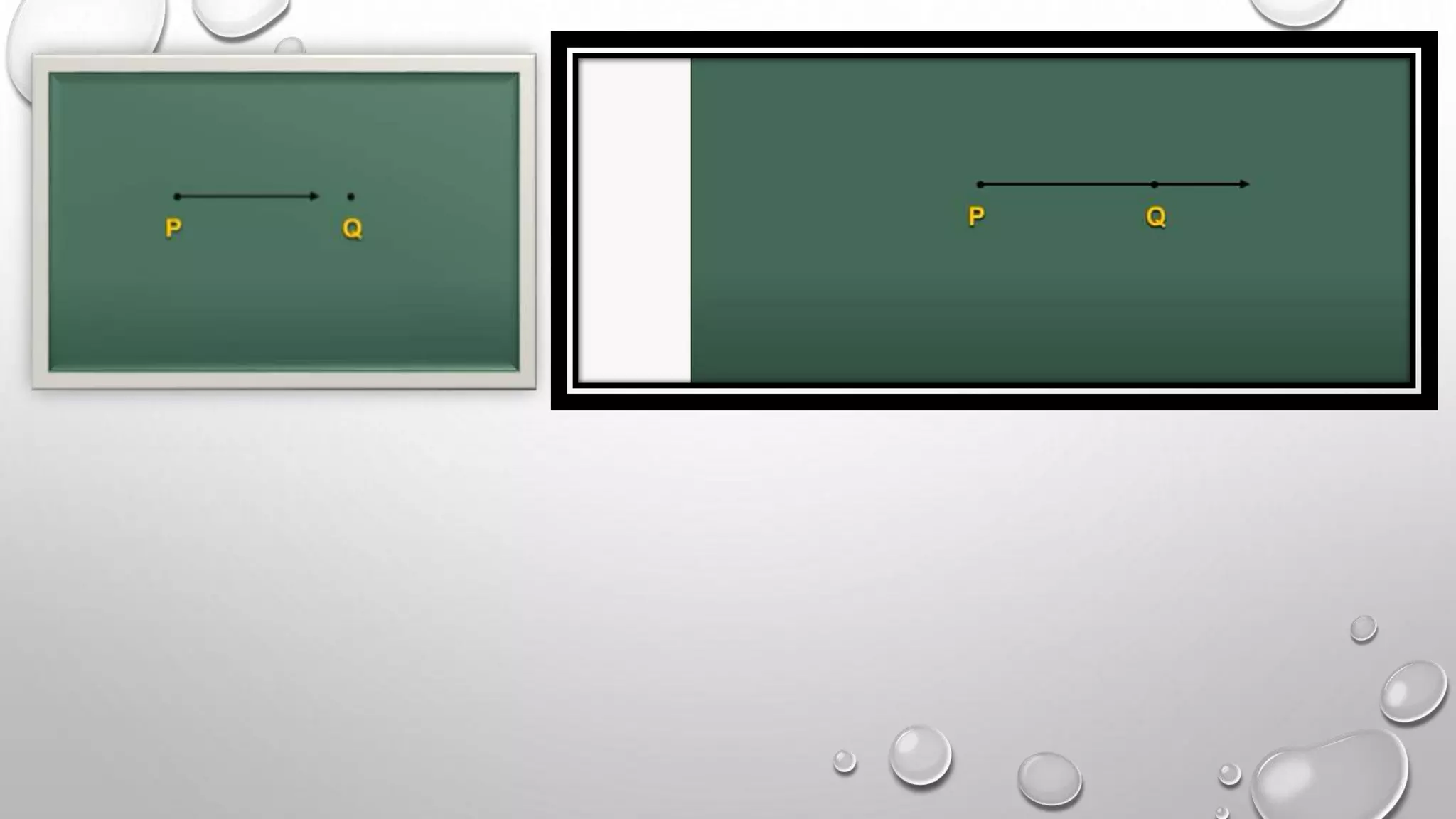
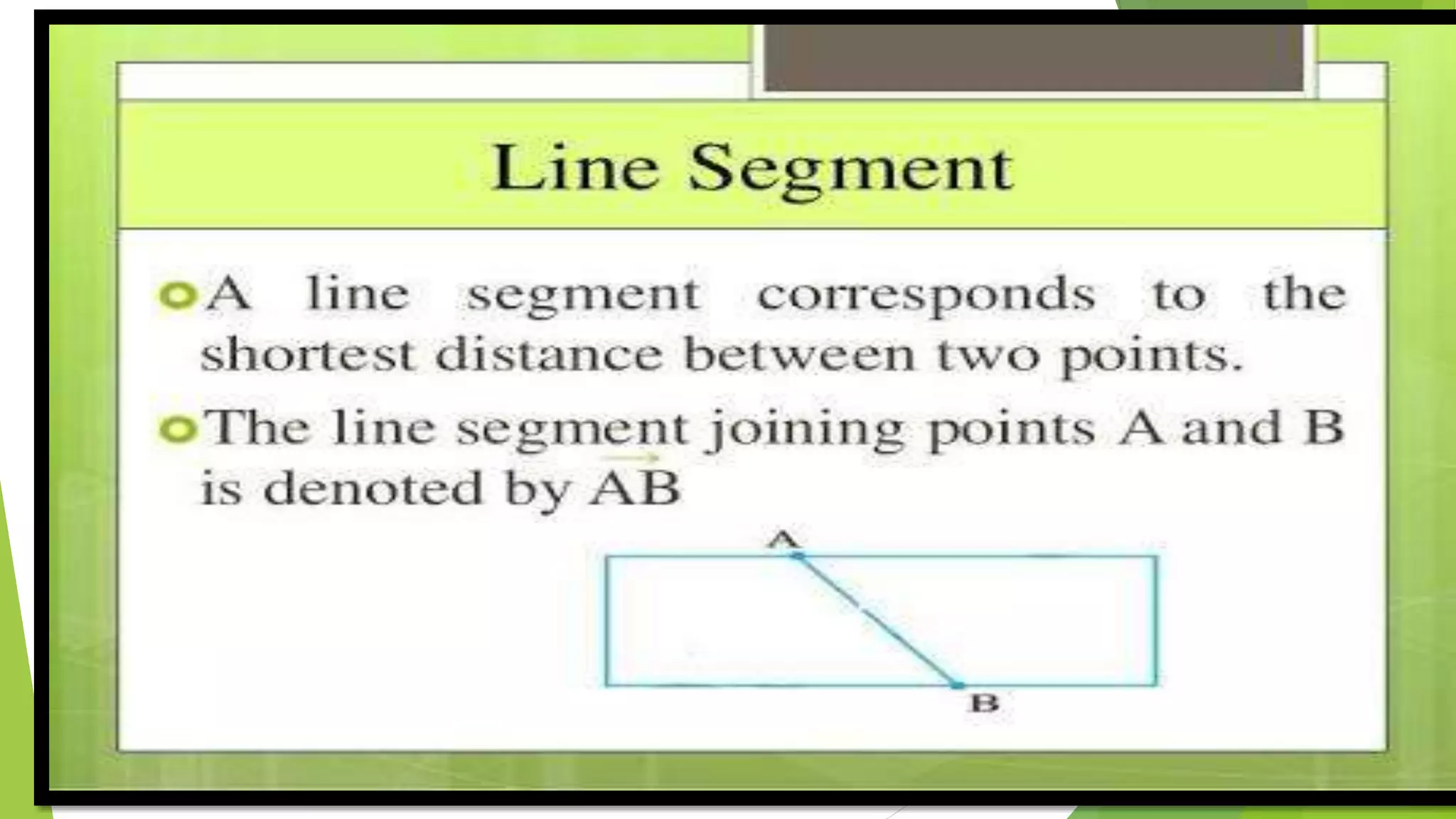
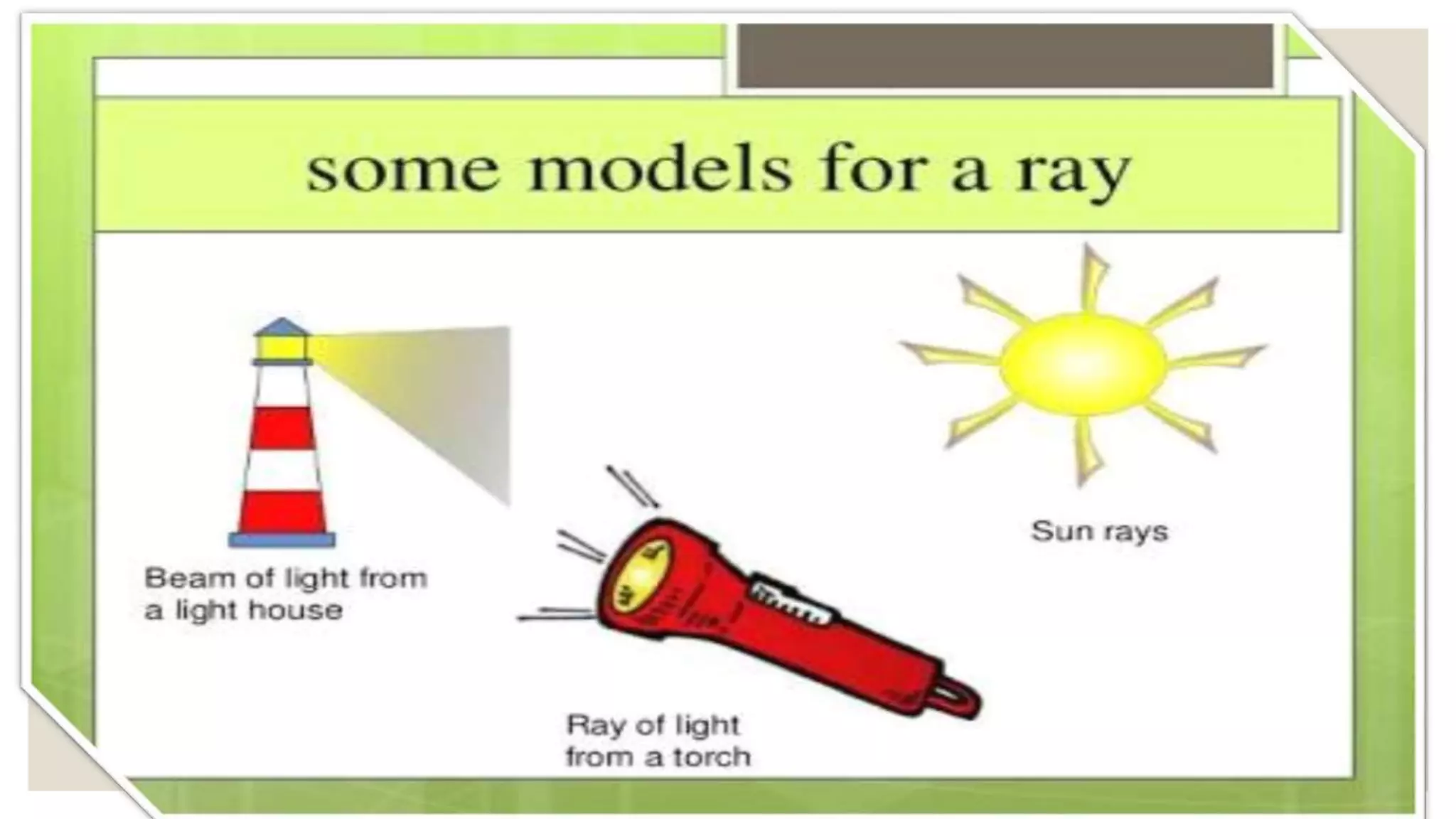
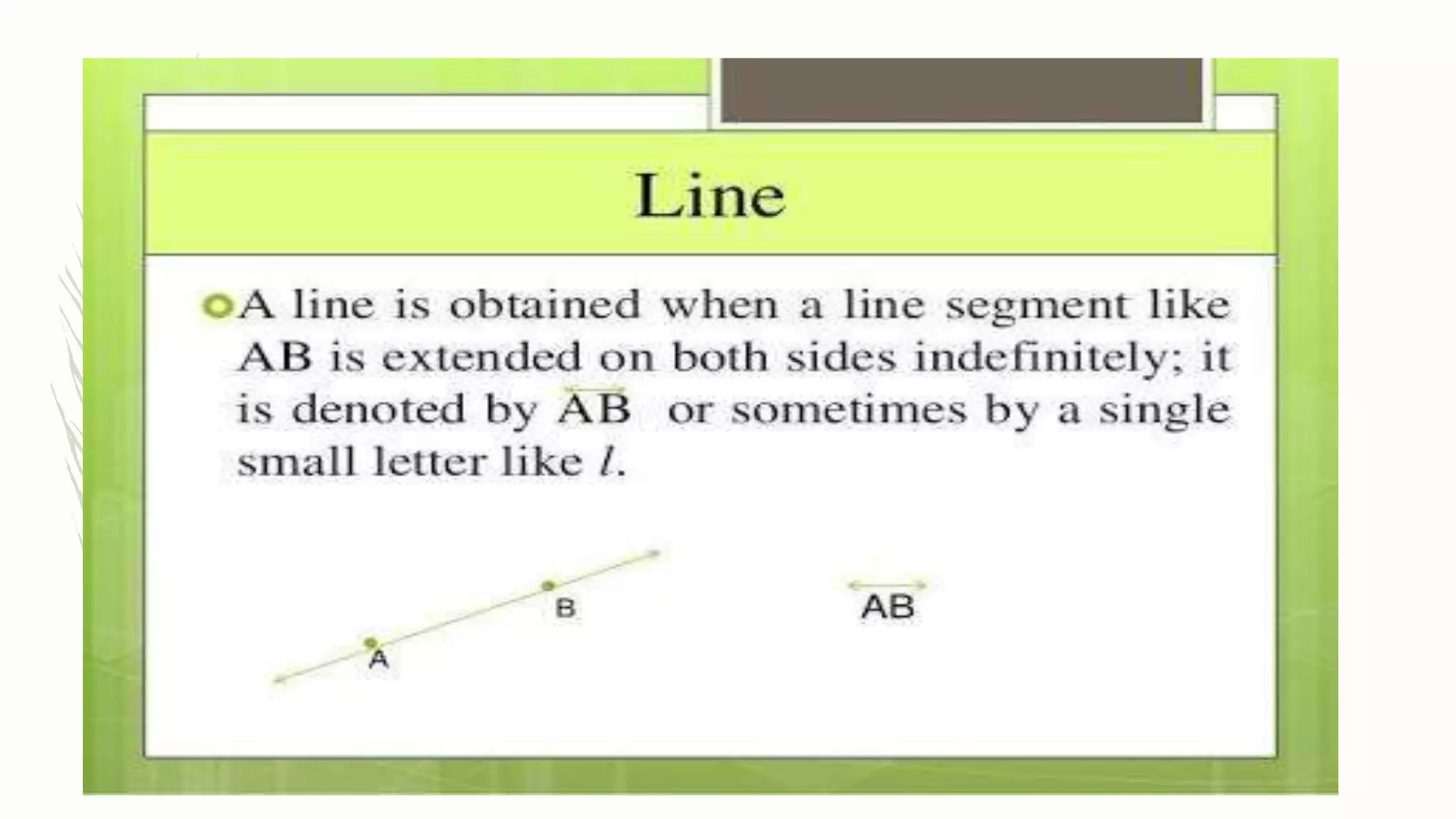
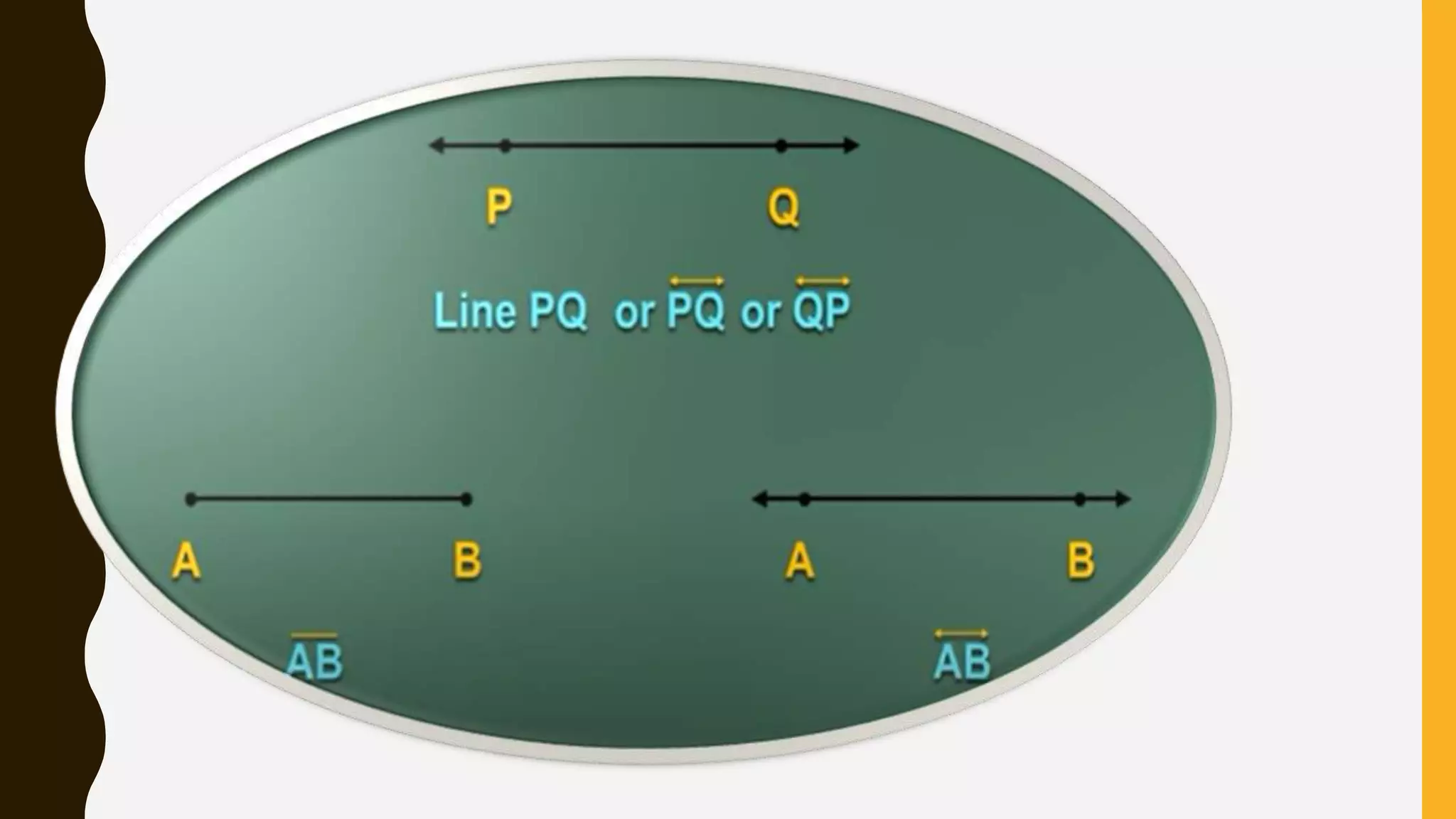
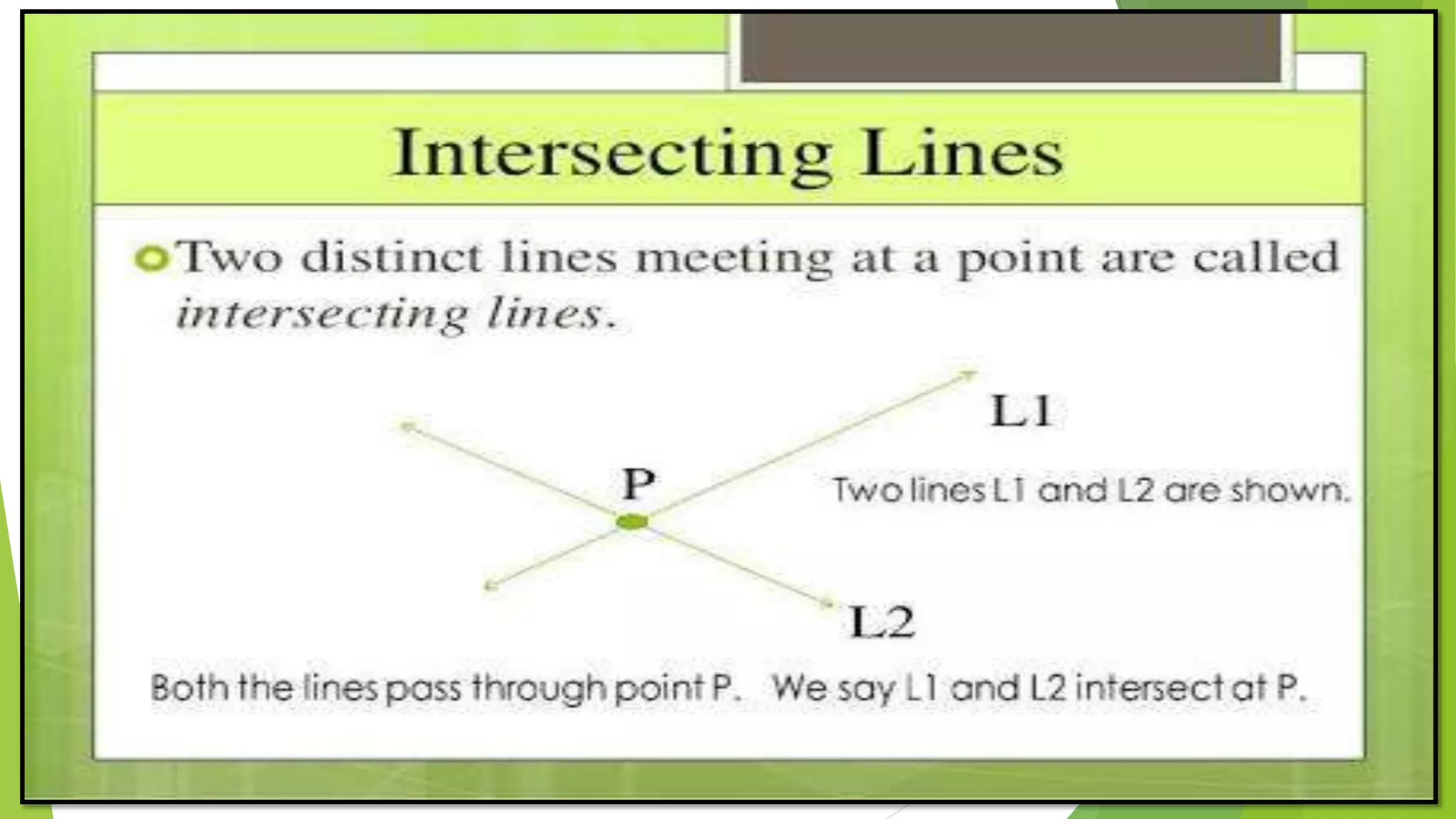
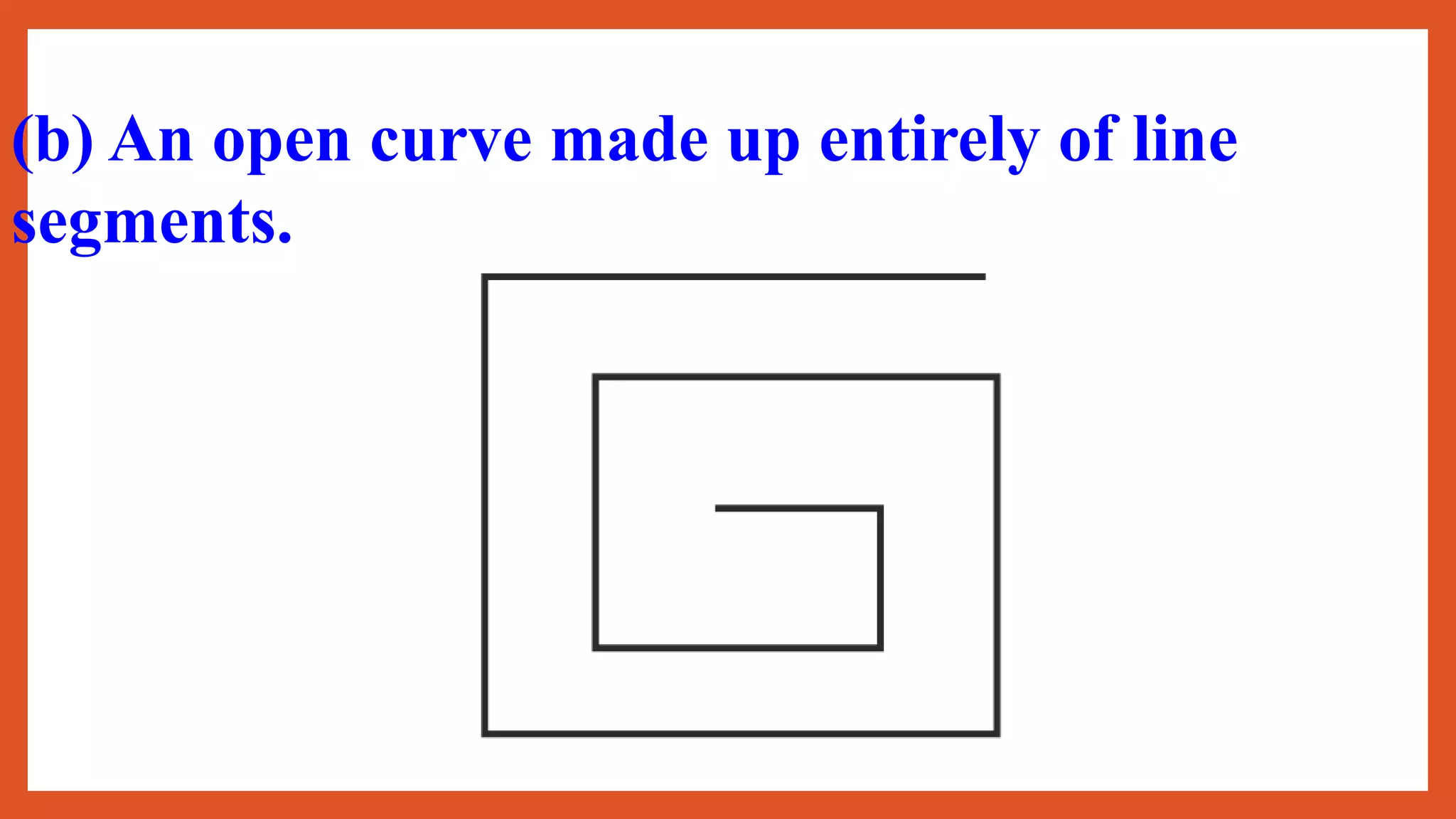
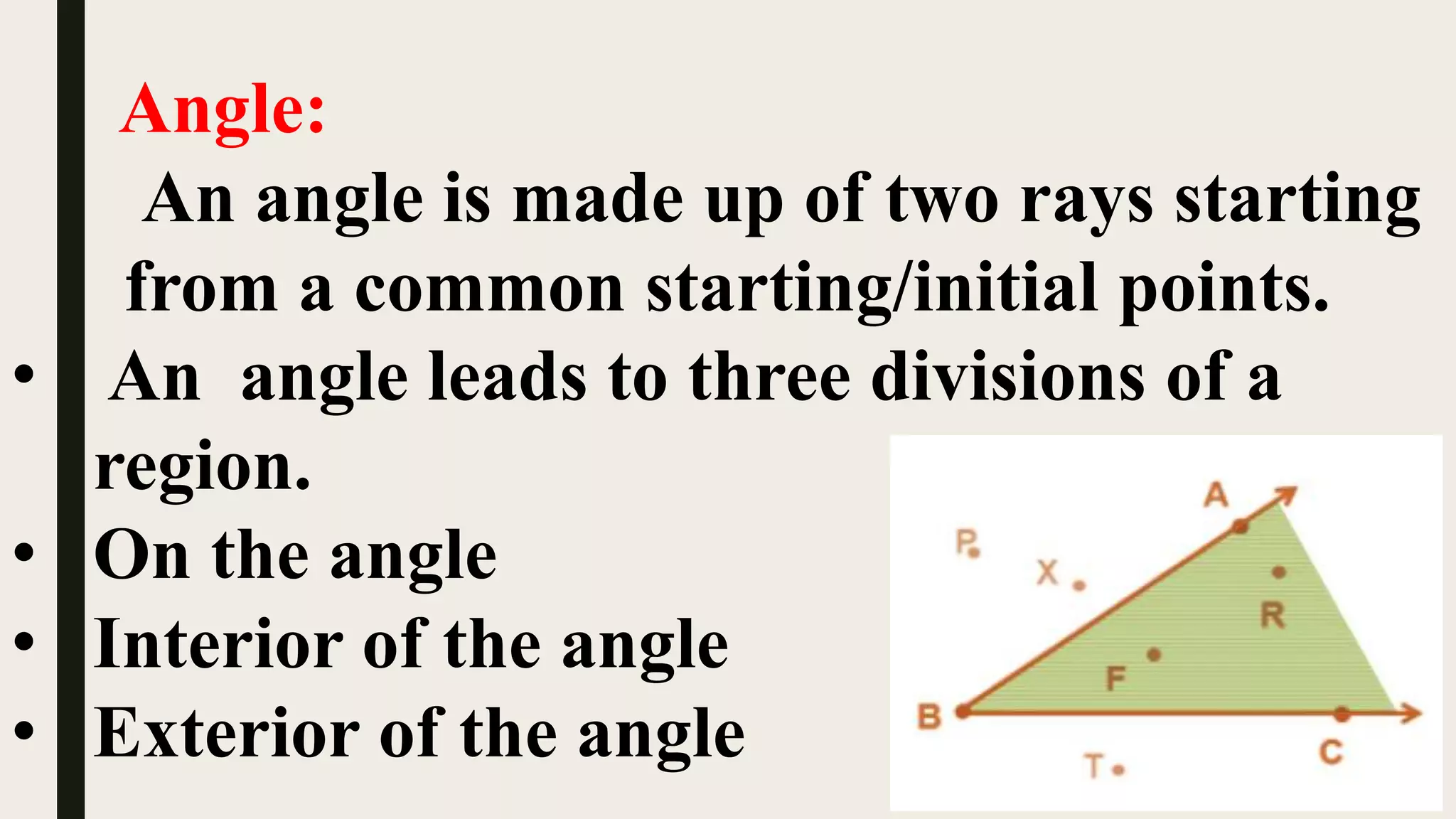
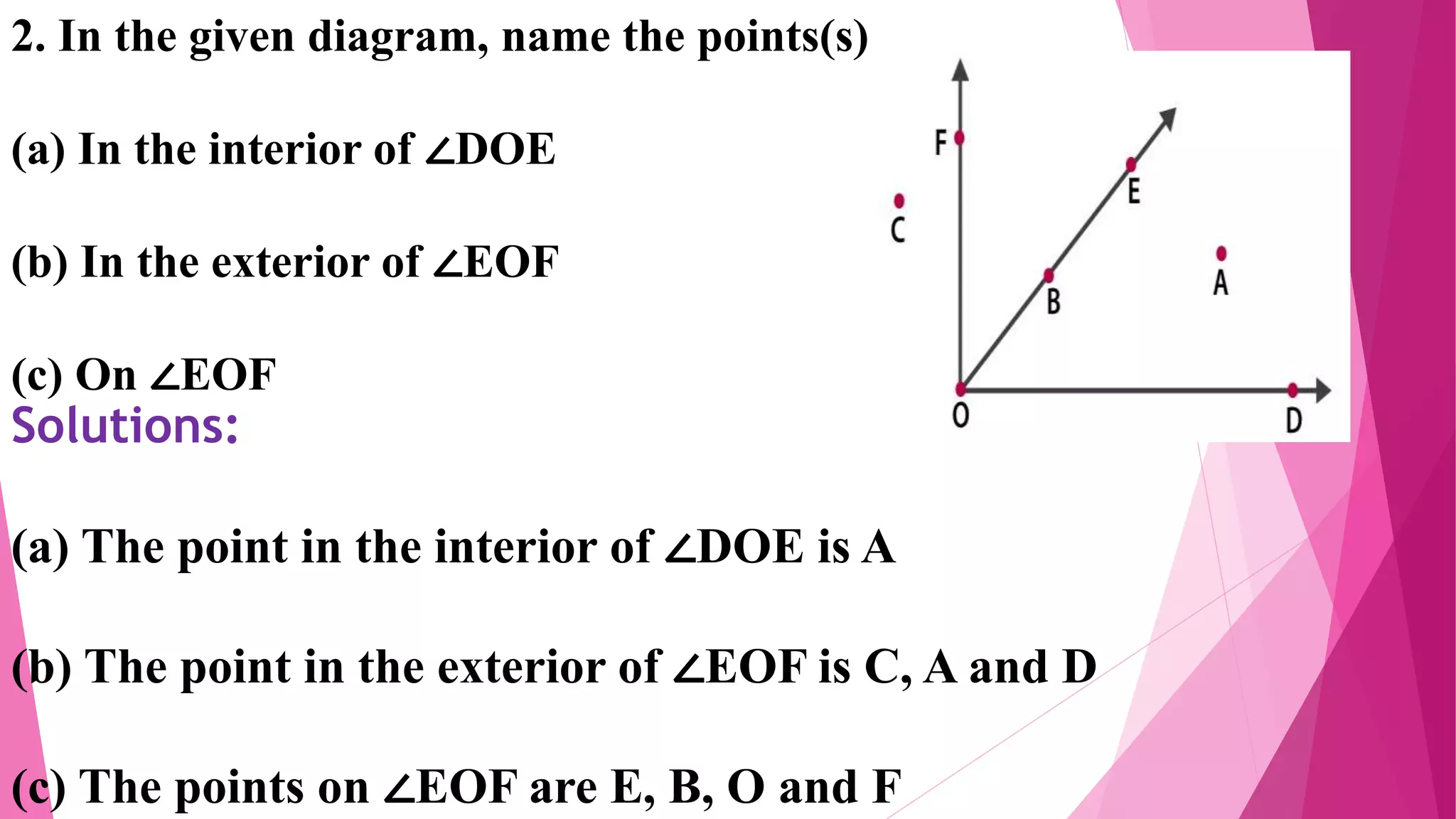
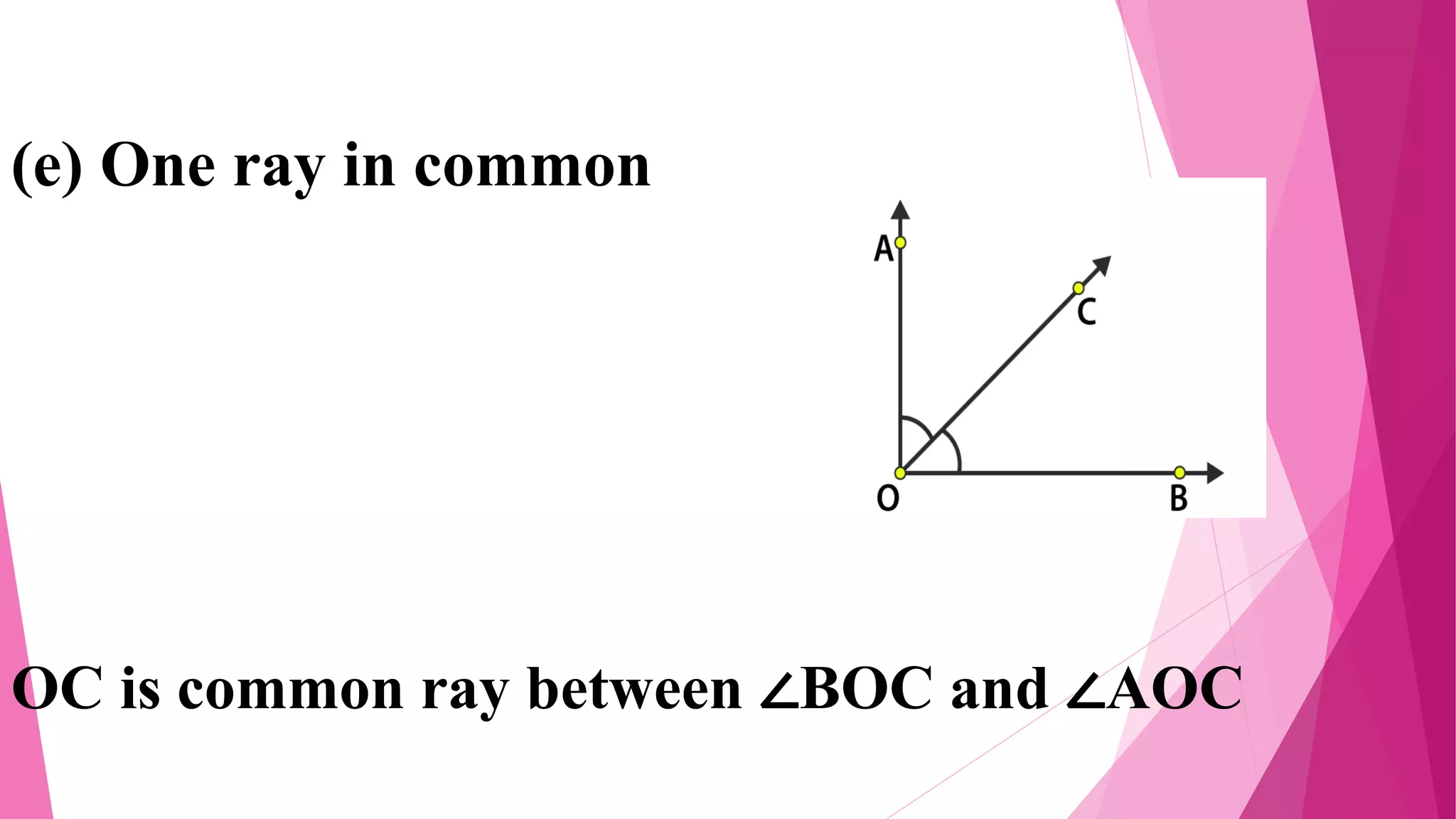
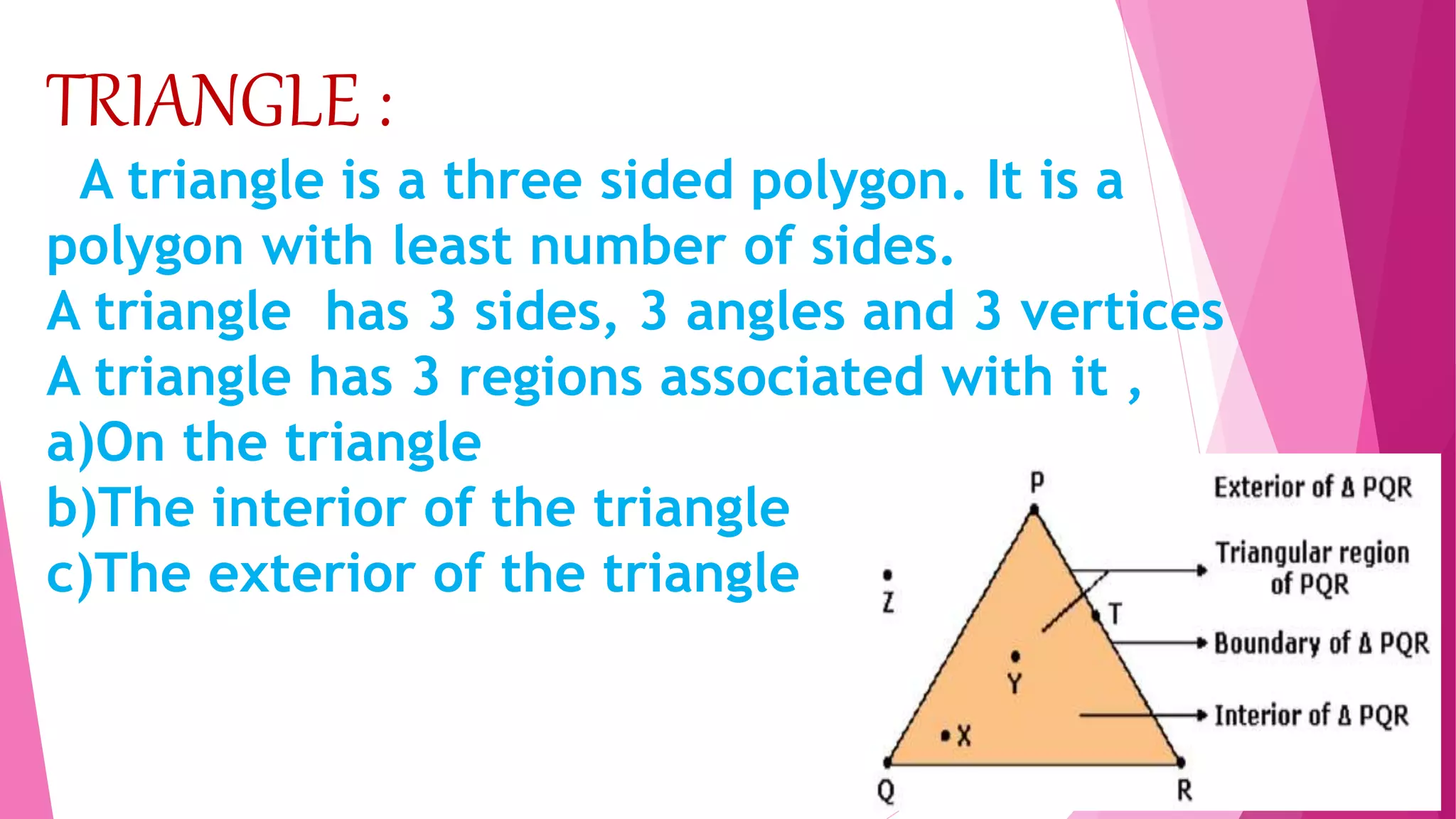
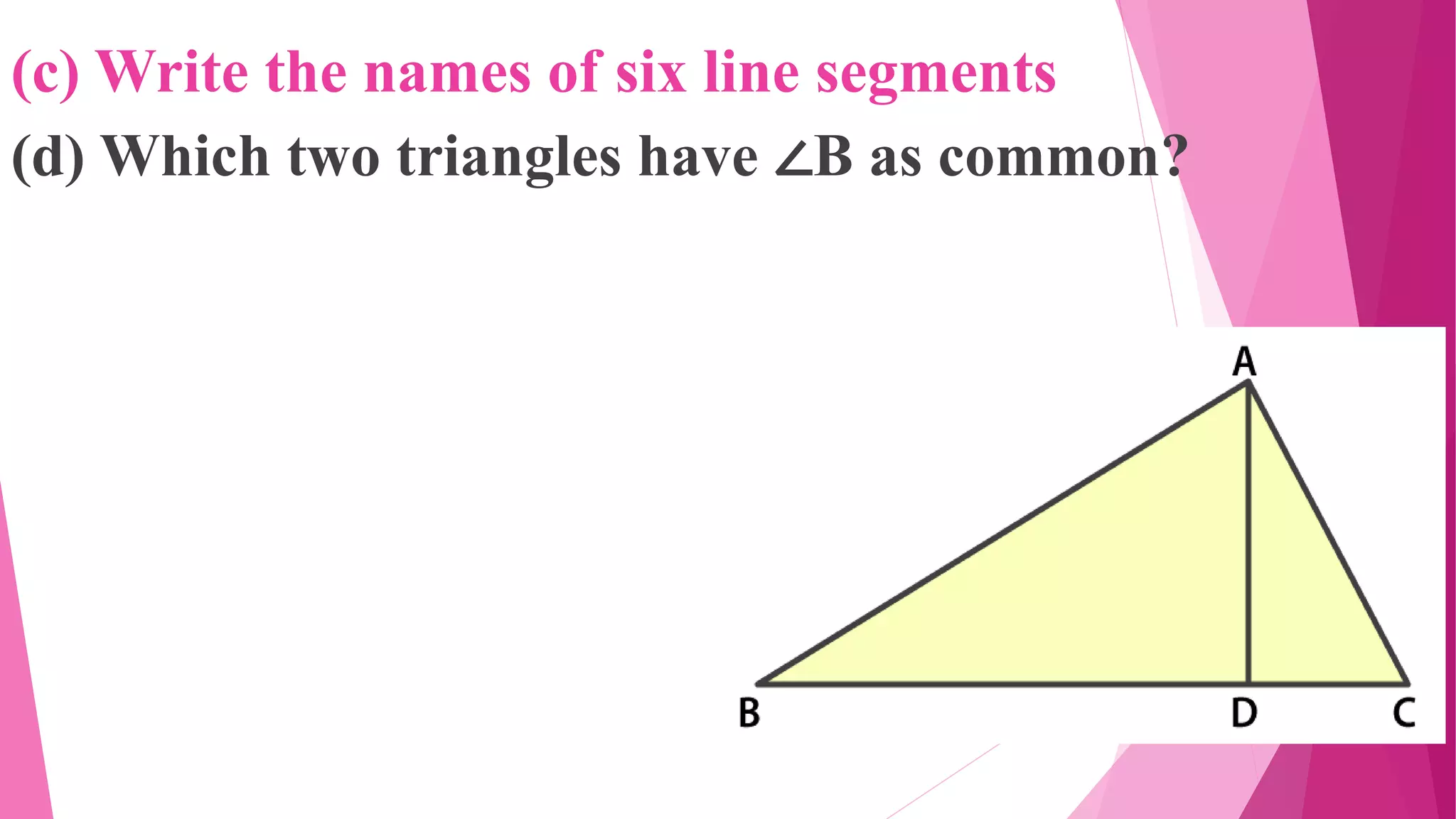
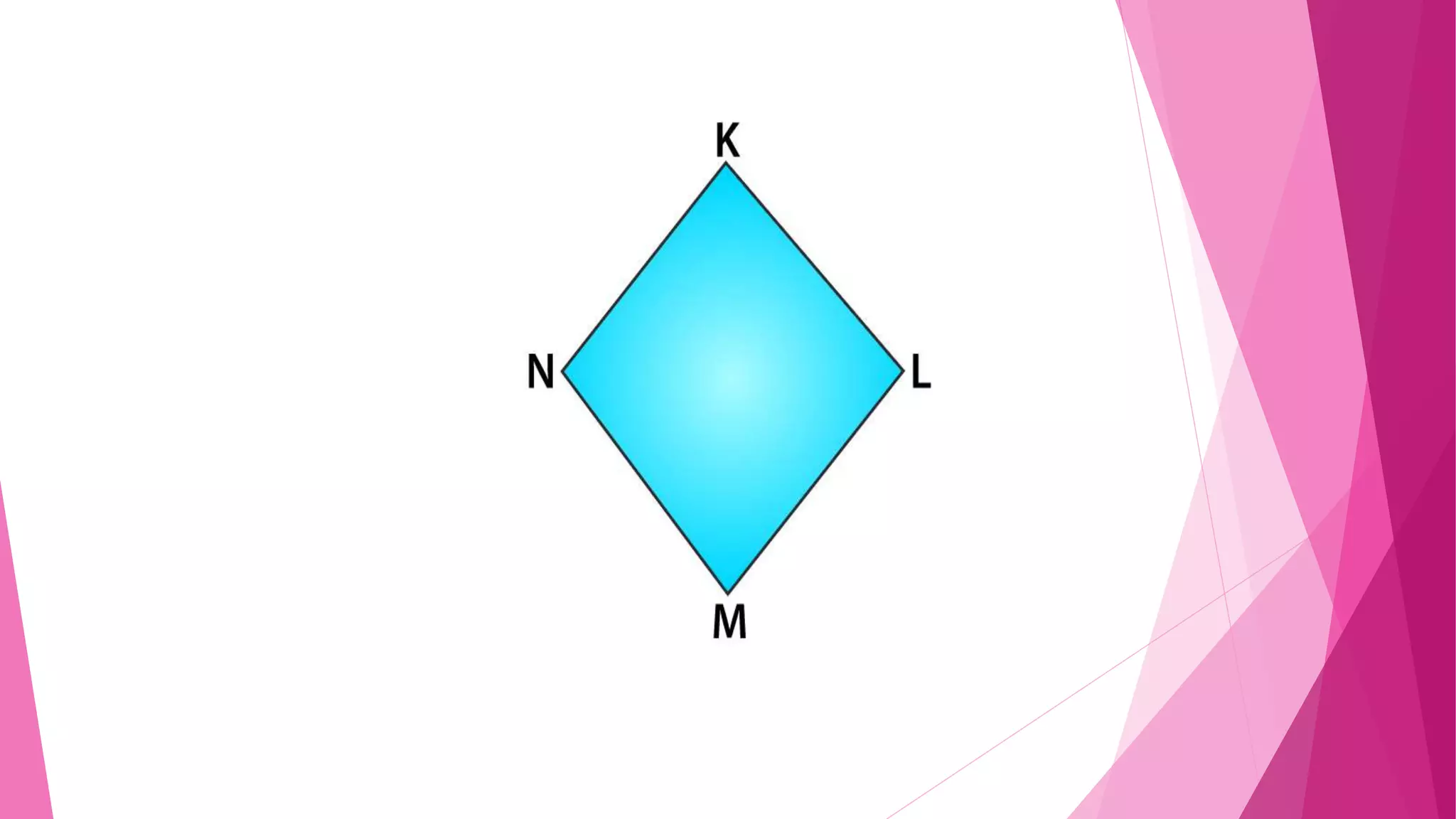
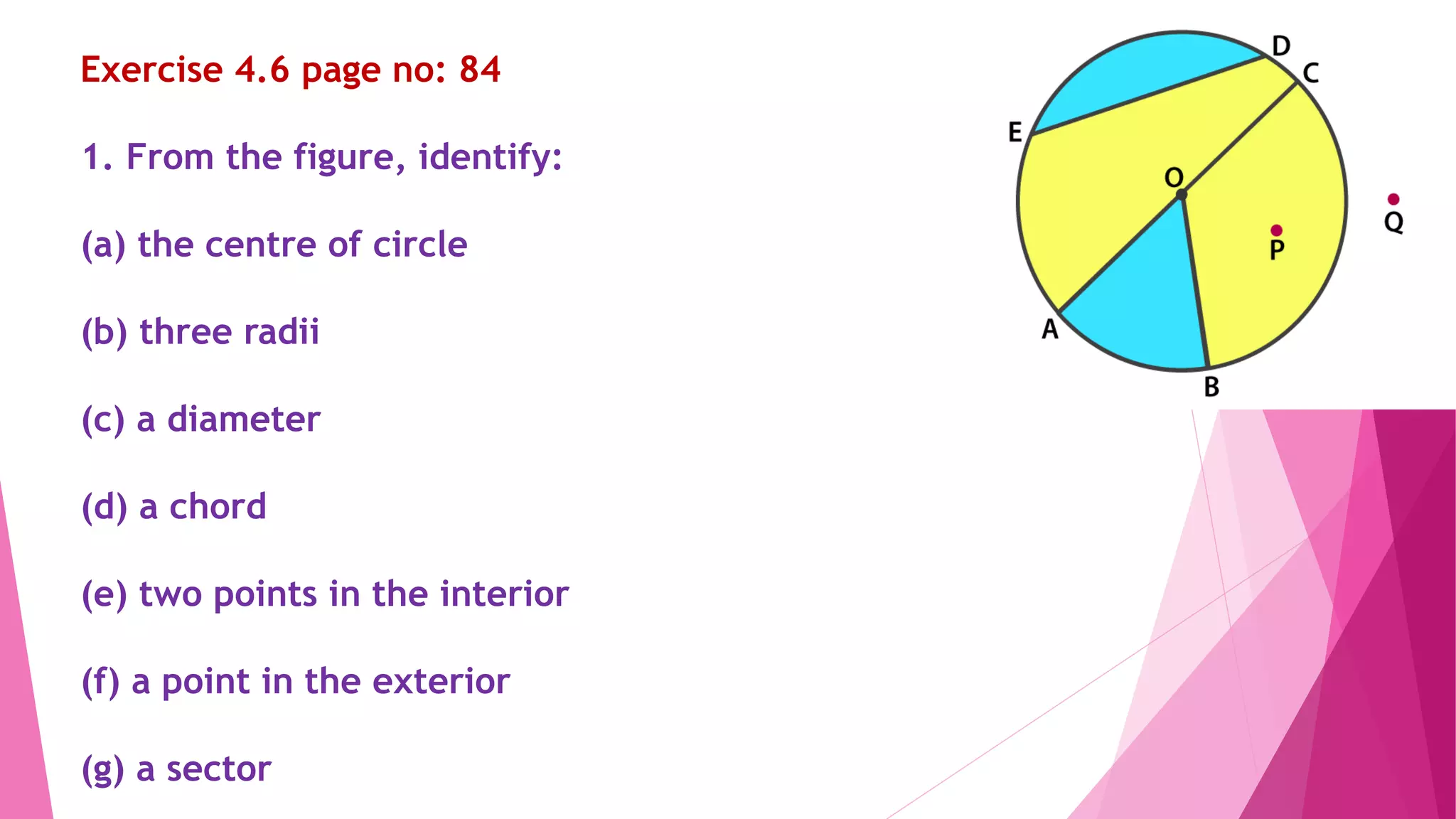
This document provides an overview of basic geometrical concepts including points, lines, curves, polygons, angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles. It begins with definitions of points, lines, and line segments. It then covers intersecting and parallel lines, rays, curves (simple, closed, and open), and polygons. Key details about angles, triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles are also summarized, along with examples and exercises related to each topic.