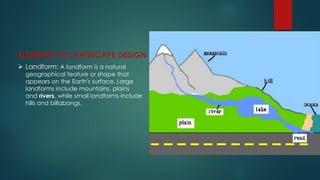
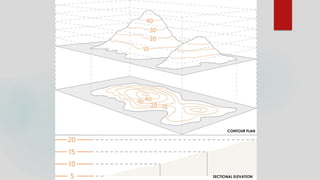
This document provides an overview of a university course on landscape design. It defines key terms related to landscape architecture and design. It discusses the different elements that make up a landscape design, including landforms, hardscapes, plantings, water features, site furniture, lighting, and pedestrian circulation. It also provides examples of different types of landscapes and discusses the importance of landscape design for environmental, social, and economic outcomes. The document concludes with discussing the various fields incorporated in landscape design and the components and process of landscape design.