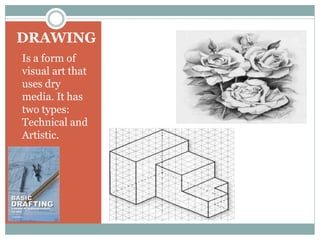
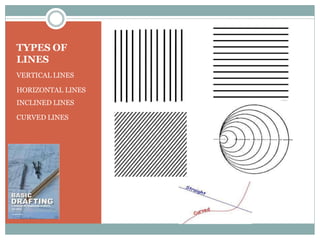
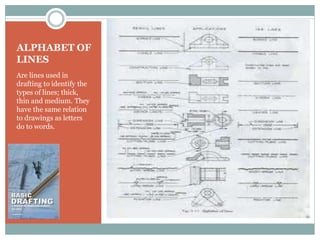
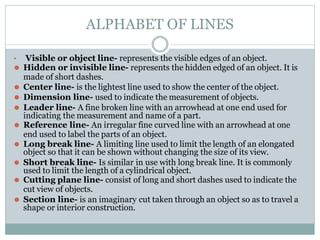
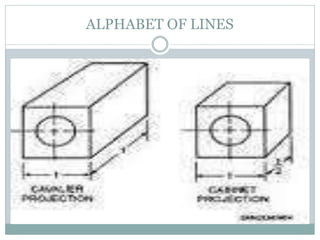
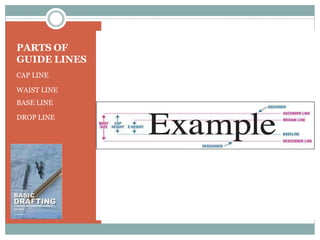
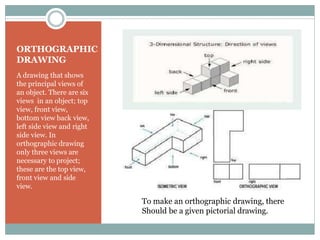
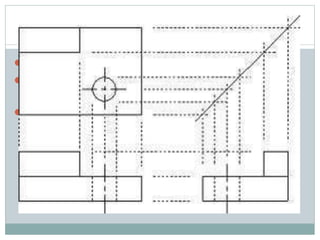
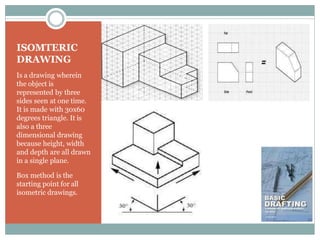
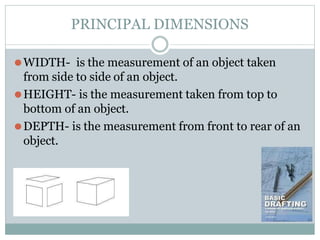
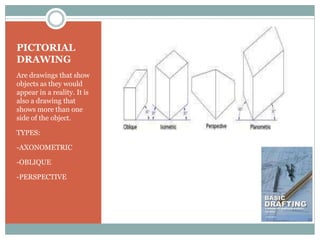
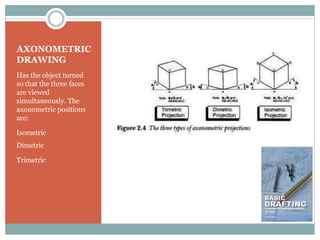
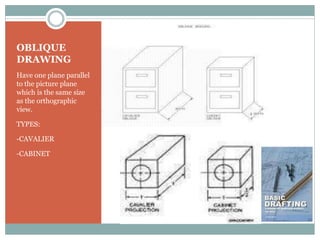
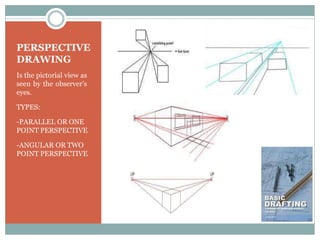
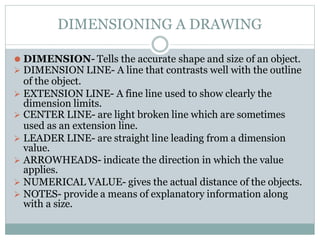
This document discusses the basics of technical drawing and drafting. It defines technical drawing as the visual communication of how objects function and are constructed through precise representations and dimensional specifications. The goals of technical drawings are accuracy, proper technique, and neatness. There are different types of drawings including orthographic, isometric, axonometric, oblique, and perspective. Key tools used in drafting are listed along with the different types of lines, lettering styles, and guidelines for dimensioning drawings.