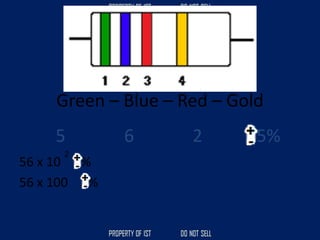
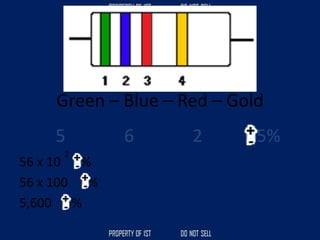
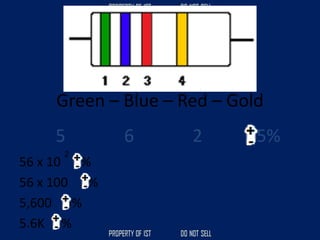
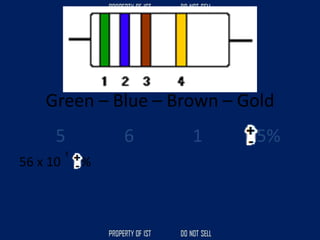
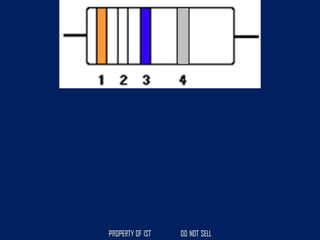
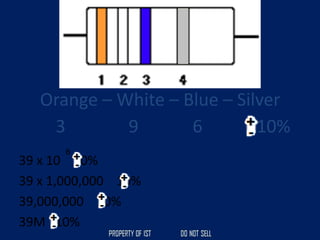
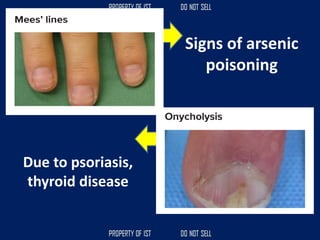
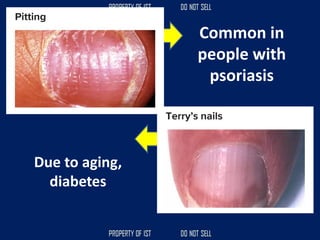
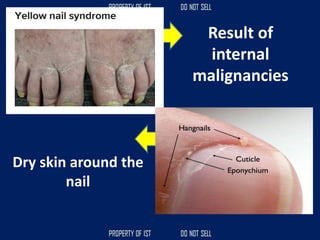
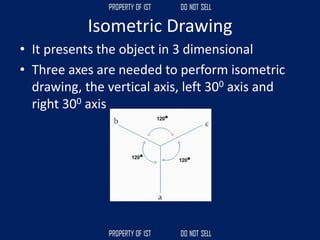
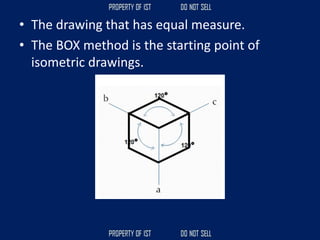
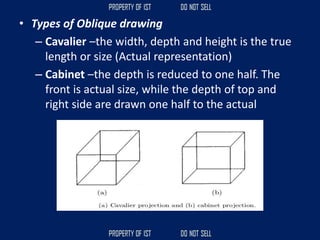
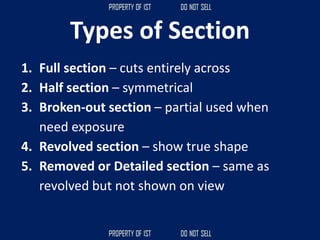
Drafting is used as a medium of communication between designers, clients, architects and builders. There are four common terms used in drafting: drawing, freehand drawing/sketching, mechanical drawing, and orthographic projection. Mechanical drawing uses drawing instruments and orthographic projection to describe object shapes completely and exactly. Drafting instruments include a T-square for horizontal lines, triangles for vertical lines, a divider for equal distances, and a French curve for curved lines. Lettering guidelines like cap, waist, base and drop lines are used for consistency in letter height and placement.




































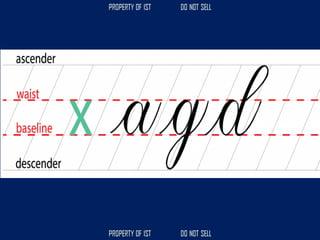
![Lettering (Guidelines)
• [1]Cap line – the uppermost line for uppercase
letters and for ascender.
• [2]Waist line – line between Cap and Base
lines, used to determine the height of the lower
case letters.
• [3]Base line – line where all the letters rest or
stand.
• [4]Drop line – a line for letters with strokes that
extend downward known as descender.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-46-320.jpg)























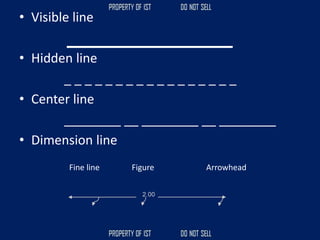
![[1]Dimension line - used to indicate the
measurement of objects which are represented by
dark solid lines.
[2]Extension line – fine line used to show clearly
the dimension limits.
[3]Center line – light broken lines used in circles,
sometimes as extension line
[4]Leader line – line leading from a dimension
value, or explanatory note to the feature on the
drawing. An arrowhead is used in pointing end but
not in note end.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-76-320.jpg)
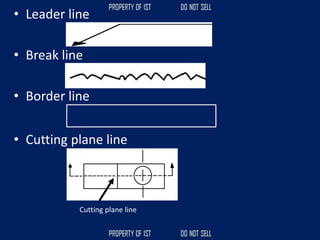
![[5]Long break – a limiting line used to limit the
length of elongated object.
[6]Invisible line - a series of light dash line that
represents parts of a drawing that are not seen.
[7]Border line - is considered as the darkest lines
that surround a drawing usually in rectangular
shape](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-77-320.jpg)







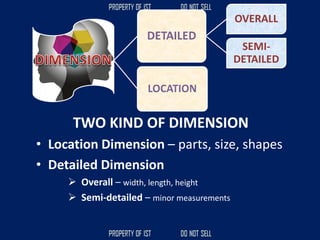












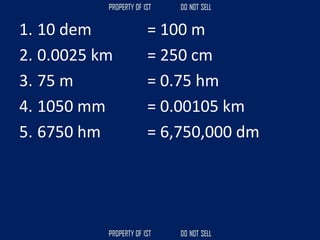











































































































































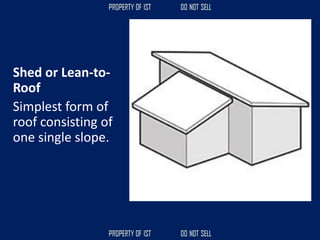
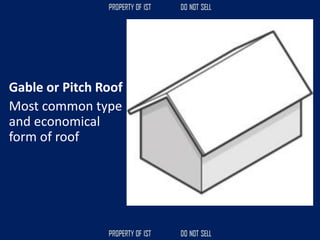
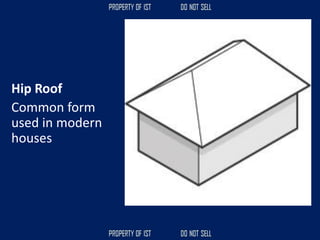

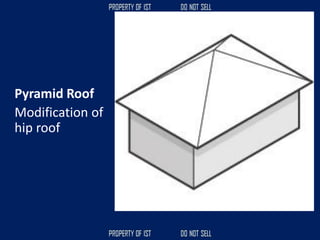
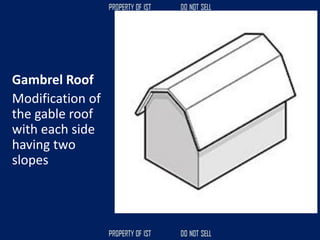
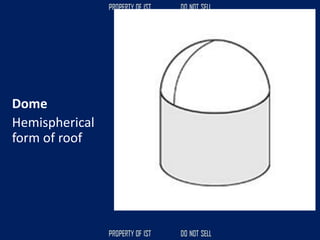
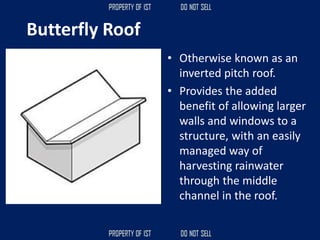



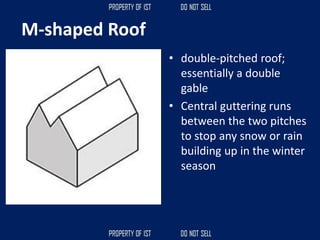


















































































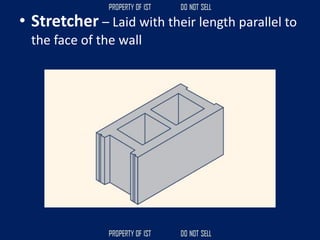
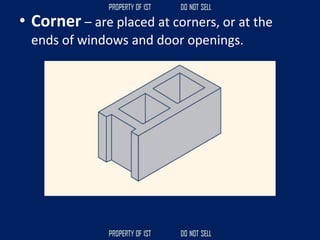
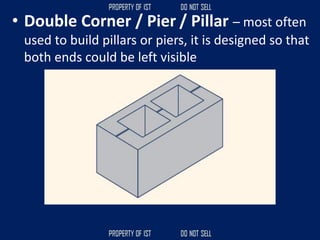

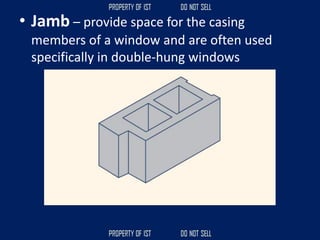




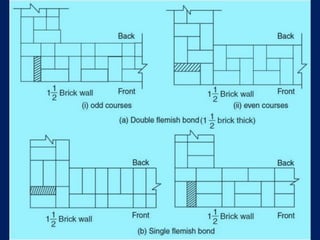
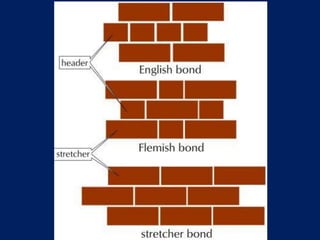
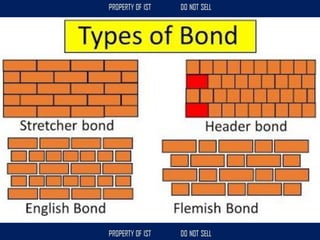









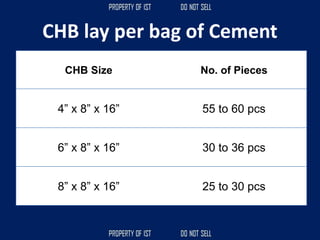








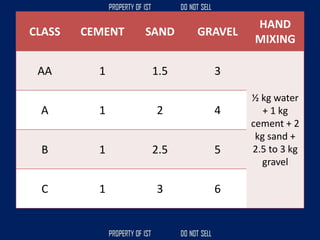
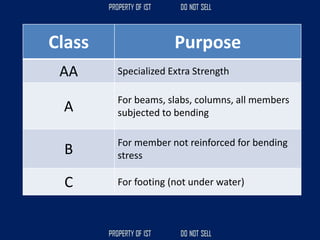
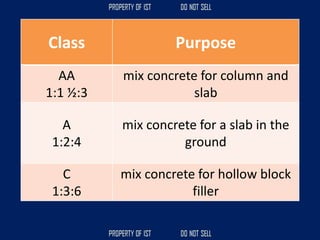



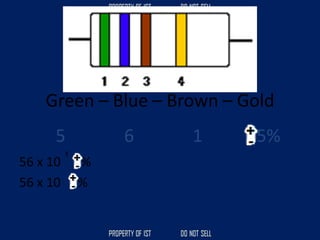
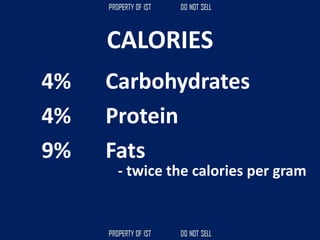
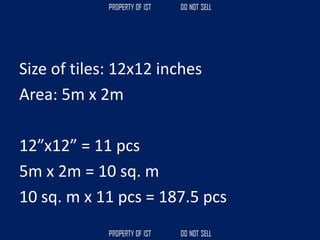
![Volume Concrete;
• VC = L x W x H
Formula to get the cubic meter (m3);
• Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
• Sand = [ ( S / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
• Gravel = [ ( G / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-390-320.jpg)


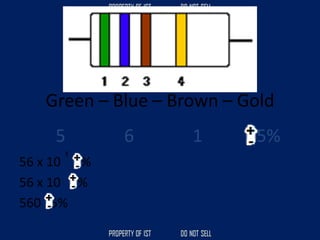
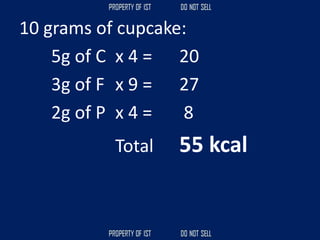
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-393-320.jpg)


![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-396-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-397-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ 0.117 m3 x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-398-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ 0.117 m3 x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= 0.0936 x 1440 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-399-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ 0.117 m3 x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= 0.0936 x 1440 kg
= 134.78 kg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-400-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ 0.117 m3 x 0.80 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= 0.0936 x 1440 kg
= 134.78 kg or 2.695 bags of cement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-401-320.jpg)

![Volume Concrete = 0.80 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] / 0.0347
= [ (1 / (1+2.5+5)) x 0.80 m3 ] / 0.0347
= [ ( 1/8.5) x 0.80 m3 ] / 0.0347
= [ 0.117 m3 x 0.80 m3 ] / 0.0347
= 0.0936 / 0.0347
= 2.697 bags of cement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-403-320.jpg)

![Volume Concrete = 0.50 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class C / 1:3:6
Cement = [ ( C / ( C + S + G )) x VC ] x 1440 kg
= [ (1 / (1+3+6)) x 0.50 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ ( 1/10) x 0.50 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= [ 0.1 m3 x 0.50 m3 ] x 1440 kg
= 0.05 x 1440 kg
= 72 kg or 1.44 bags of cement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-405-320.jpg)


![Volume Concrete = 0.20 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Sand = [ ( 2 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-408-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.20 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Sand = [ ( 2 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 2 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 0.20 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-409-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.20 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Sand = [ ( 2 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 2 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 0.20 ]
= [ ( 2 / 7 ) x 0.20 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-410-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.20 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Sand = [ ( 2 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 2 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 0.20 ]
= [ ( 2 / 7 ) x 0.20 ]
= 0.286 x 0.20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-411-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.20 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Sand = [ ( 2 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 2 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 0.20 ]
= [ ( 2 / 7 ) x 0.20 ]
= 0.286 x 0.20
= 0.057 cu m3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-412-320.jpg)


![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Sand = [ ( 2.5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 2.5 / ( 1 + 2.5 + 5 )) x 0.80 ]
= [ ( 2.5 / 8.5 ) x 0.80 ]
= 0.294 x 0.80
= 0.235 cu m3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-415-320.jpg)


![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Gravel = [ ( 5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-418-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Gravel = [ ( 5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 5 / ( 1 + 2.5 + 5 )) x 0.80 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-419-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Gravel = [ ( 5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 5 / ( 1 + 2.5 + 5 )) x 0.80 ]
= [ ( 5 / 8.5 ) x 0.80 ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-420-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Gravel = [ ( 5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 5 / ( 1 + 2.5 + 5 )) x 0.80 ]
= [ ( 5 / 8.5 ) x 0.80 ]
= 0.588 x 0.80](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-421-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.8 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class B / 1:2.5:5
Gravel = [ ( 5 / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 5 / ( 1 + 2.5 + 5 )) x 0.80 ]
= [ ( 5 / 8.5 ) x 0.80 ]
= 0.588 x 0.80
= 0.470 cu m3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-422-320.jpg)

![Volume Concrete = 0.40 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class AA / 1:1.5:3
Gravel = [ ( G / ( C + S + G )) x VC ]
= [ ( 3 / ( 1 + 1.5 + 3 )) x 0.40 ]
= [ ( 3 / 5.5 ) x 0.40 ]
= 0.545 x 0.40
= 0.218 cu m3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-424-320.jpg)


![Volume Concrete = 0.35 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-427-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.35 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]
= [ ( 1 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 1000 L ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-428-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.35 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]
= [ ( 1 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 1000 L ]
= [ ( 1/7 ) x 1000 L ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-429-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.35 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]
= [ ( 1 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 1000 L ]
= [ ( 1/7 ) x 1000 L ]
= 0.143 x 1000 L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-430-320.jpg)
![Volume Concrete = 0.35 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class A / 1:2:4
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]
= [ ( 1 / ( 1 + 2 + 4 )) x 1000 L ]
= [ ( 1/7 ) x 1000 L ]
= 0.143 x 1000 L
= 143 L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-431-320.jpg)

![Volume Concrete = 0.50 m3
Mixing Proportion = Class C / 1:3:6
Water = [(Cement in cubic x 0.45) x 1000 L]
= [ ( 1 / ( 1 + 3 + 6 )) x 1000 L ]
= [ ( 1/10 ) x 1000 L ]
= 0.1 x 1000 L
= 100 L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-433-320.jpg)






























































































































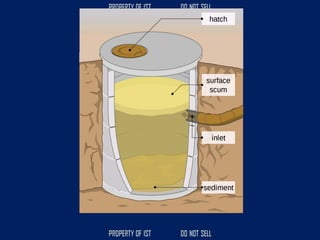
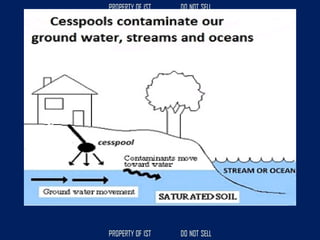

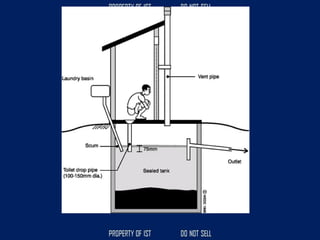
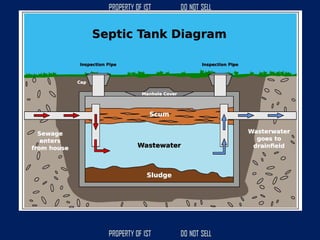






























































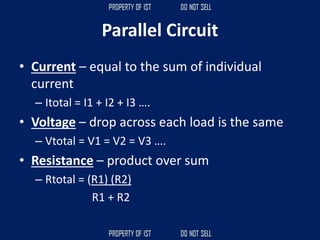



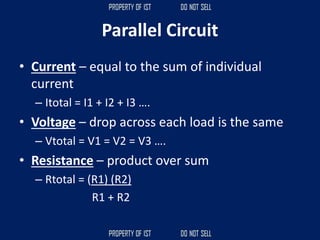



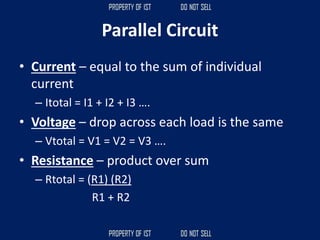







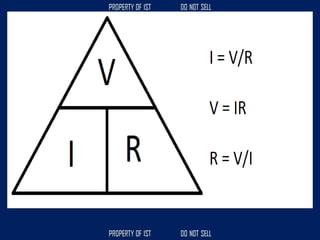
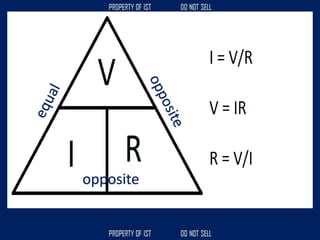
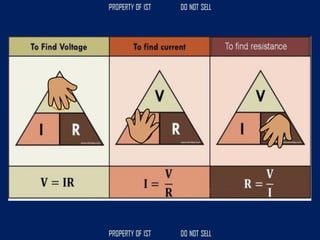
![SERIES CIRCUIT PARALLEL CIRCUIT
CURRENT = [equals/as is] CURRENT + higher, increase
VOLTAGE + higher, increase VOLTAGE = [equals/as is]
RESISTANCE + higher, increase RESISTANCE x/+ lower, decrease](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tle-reviewer2022-240218172026-5e7cf0af/85/Technology-and-Livelihood-Education-REVIEWER_2022-pdf-656-320.jpg)