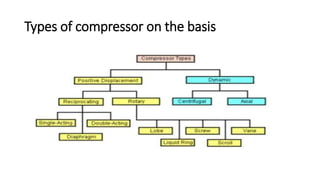
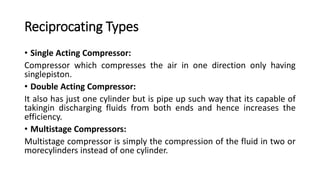
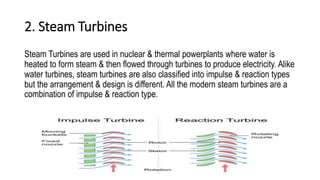
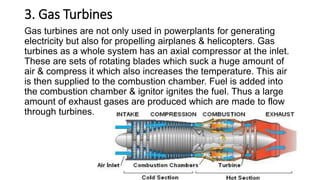
The document discusses the basic components of a power plant, including compressors, cooling towers, and turbines. It provides details on the types and workings of positive displacement and rotary compressors, natural draft, mechanical draft, and hybrid draft cooling towers, and water, steam, gas, and wind turbines. The summaries explain the key components and how they function to compress air or fluids, remove heat, and convert the kinetic or potential energy of water, steam, gas, or wind into rotational motion and ultimately electricity.