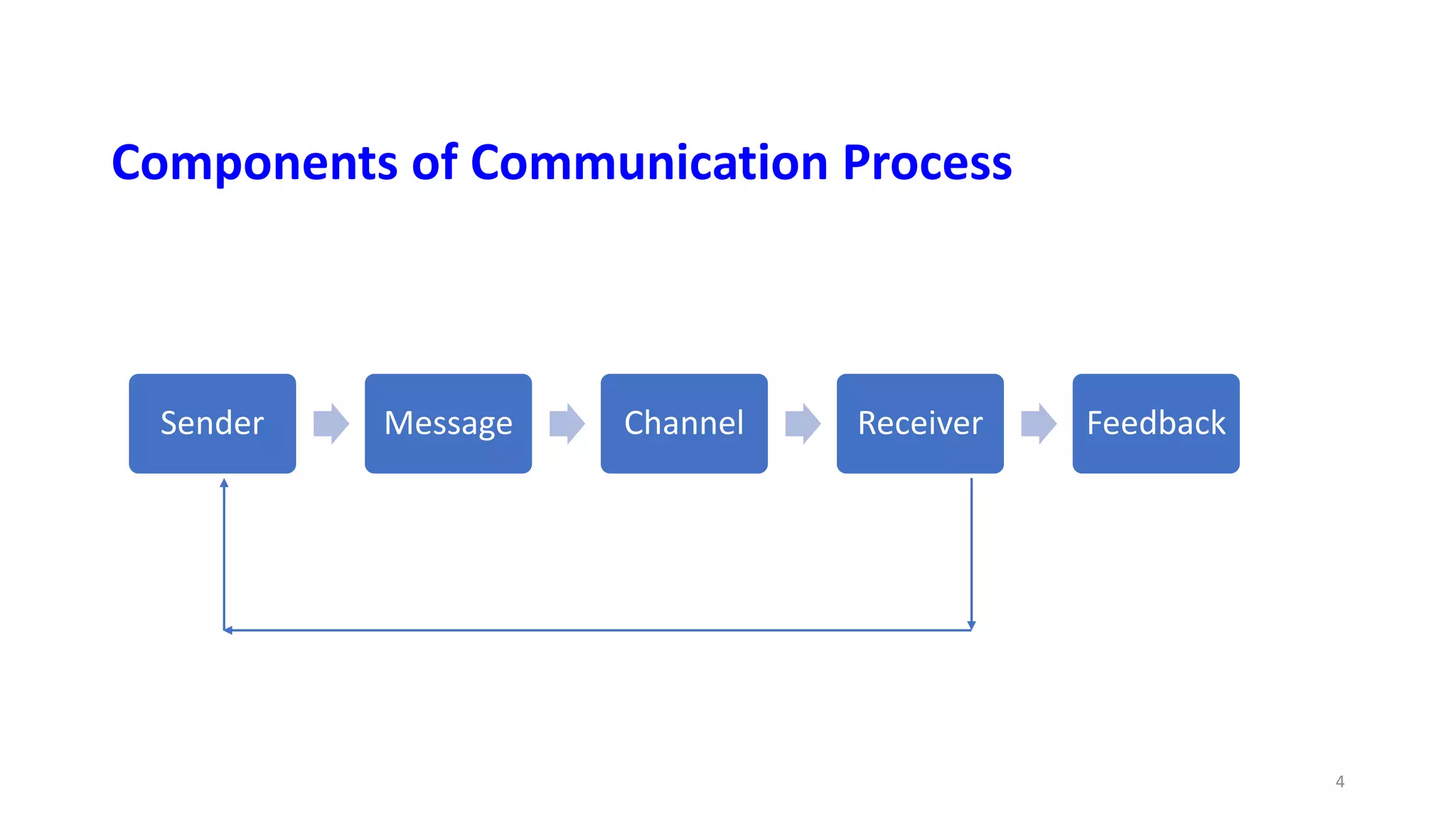
Basic Communication Skills outlines the key components of the communication process. Communication is defined as the mutual process of relating and interacting with others through various means. The aims of communication are to promote effective interaction with patients, caregivers, colleagues and professionals, and to create desired changes through information exchanged. The core components that enable communication are the sender, message, channel, receiver, and feedback between the sender and receiver. Barriers like physiological, psychological, environmental and cultural factors can also interfere with effective communication.