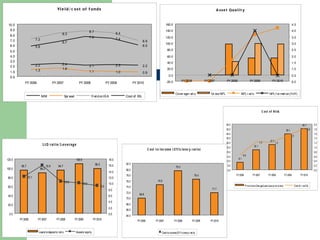
The document provides an overview of the banking sector from multiple perspectives including business segments, macroeconomic factors, asset-liability structures, revenue drivers, performance ratios, risk management, capital adequacy frameworks like Basel, and analytical tools like stress testing and scenario analysis. It discusses the various risks banks are exposed to and how they are measured and managed.