The document provides an overview of various topics in banking including:
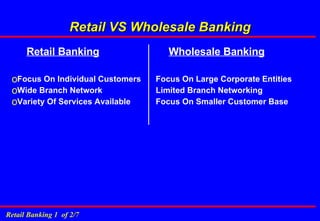
1. It introduces retail banking, corporate banking, investment banking and private banking and the various services offered under each.
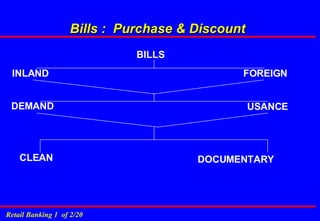
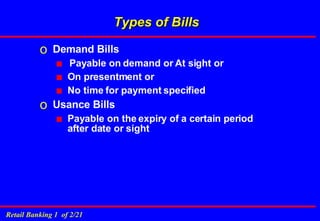
2. It discusses key banking terminology like CASA (current and savings accounts), time deposits, loans, remittances and non-branch delivery channels.
3. It covers banking principles, regulations, accounting practices, lending, types of accounts, and legal and regulatory aspects of banking.