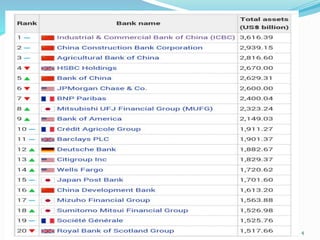
The document provides an overview of the banking domain, including:
- Defining key terms like money, financial instruments, assets and liabilities, and non-performing assets.
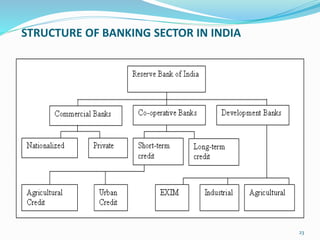
- Describing the structure of the banking sector in India including the roles of the central bank and different types of banks.
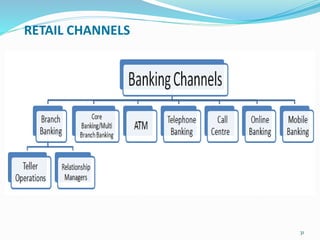
- Explaining various retail banking services offered to individuals and businesses like deposits, loans, credit/debit cards, ATMs, online and mobile banking.
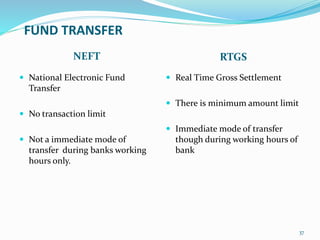
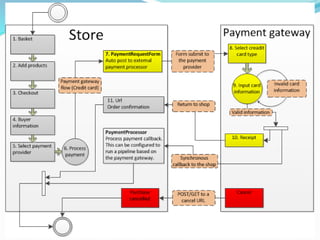
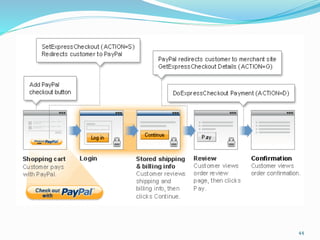
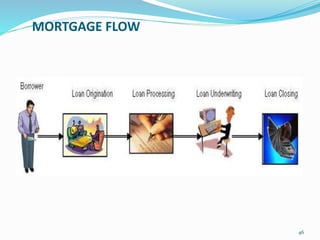
- Providing details on deposit products, retail channels, funds transfer mechanisms, and the services offered by banks in areas like corporate, retail, and investment banking.