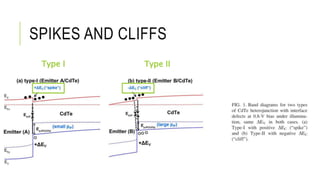
The document discusses lessons that can be learned from CdTe photovoltaics and applied to CZTS solar cells. Specifically, it examines how to engineer defect-tolerant heterojunction interfaces through three key factors: 1) the conduction band offset between materials, 2) emitter doping and thickness, and 3) the type of interface defects. Interface recombination can be reduced by creating a spike in the conduction band for type I heterojunctions or avoiding a cliff for type II heterojunctions. Defect-tolerant interfaces also depend on absorber inversion induced by emitter doping. However, comparisons between materials require consideration of interface mixing and surface reconstruction challenges.