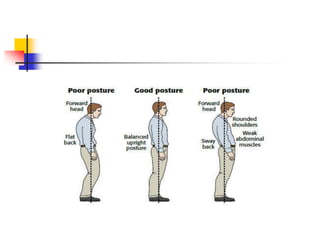
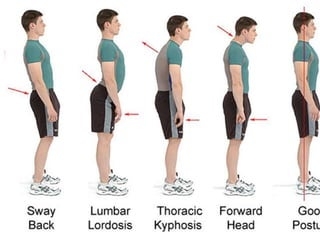
Poor posture is defined as when the spine is positioned in unnatural positions with emphasized curves, putting joints, muscles and vertebrae in stressful positions. Prolonged poor positioning can lead to build up of pressure and cause pain conditions like low back pain and neck, shoulder, and arm pain. Symptoms include body aches and pains, muscle fatigue, and headaches. Physiotherapy can help assess and diagnose postural habits, provide postural education and training, manual therapy, corrective exercises, and advice on activity modification and ergonomics to improve flexibility, strength, and posture.