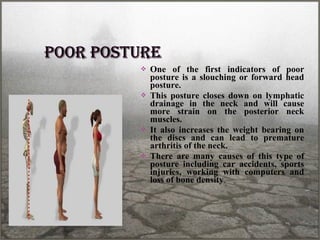
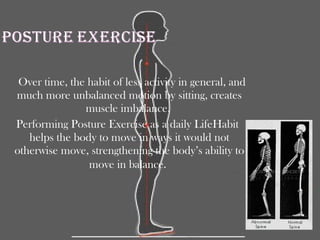
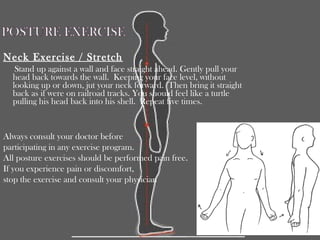
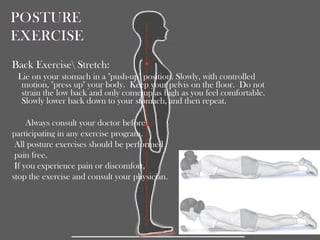
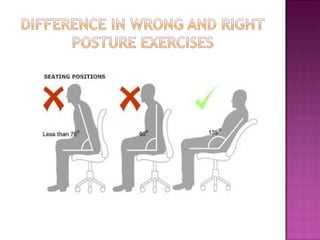
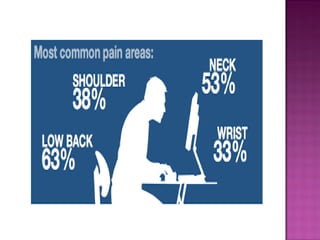
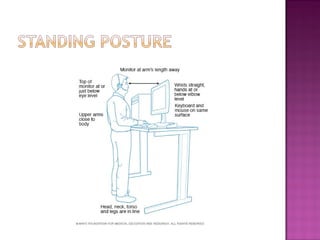
Posture refers to the position and alignment of the body, influencing overall balance and health, with good posture helping to reduce strain and fatigue while promoting muscular efficiency. Poor posture can stem from various factors including physiological conditions and psychological issues, and correcting it may involve therapies like yoga, physical therapy, and specific exercises. Maintaining awareness of body alignment is essential for improving appearance, preventing pain, and enhancing performance in physical activities.