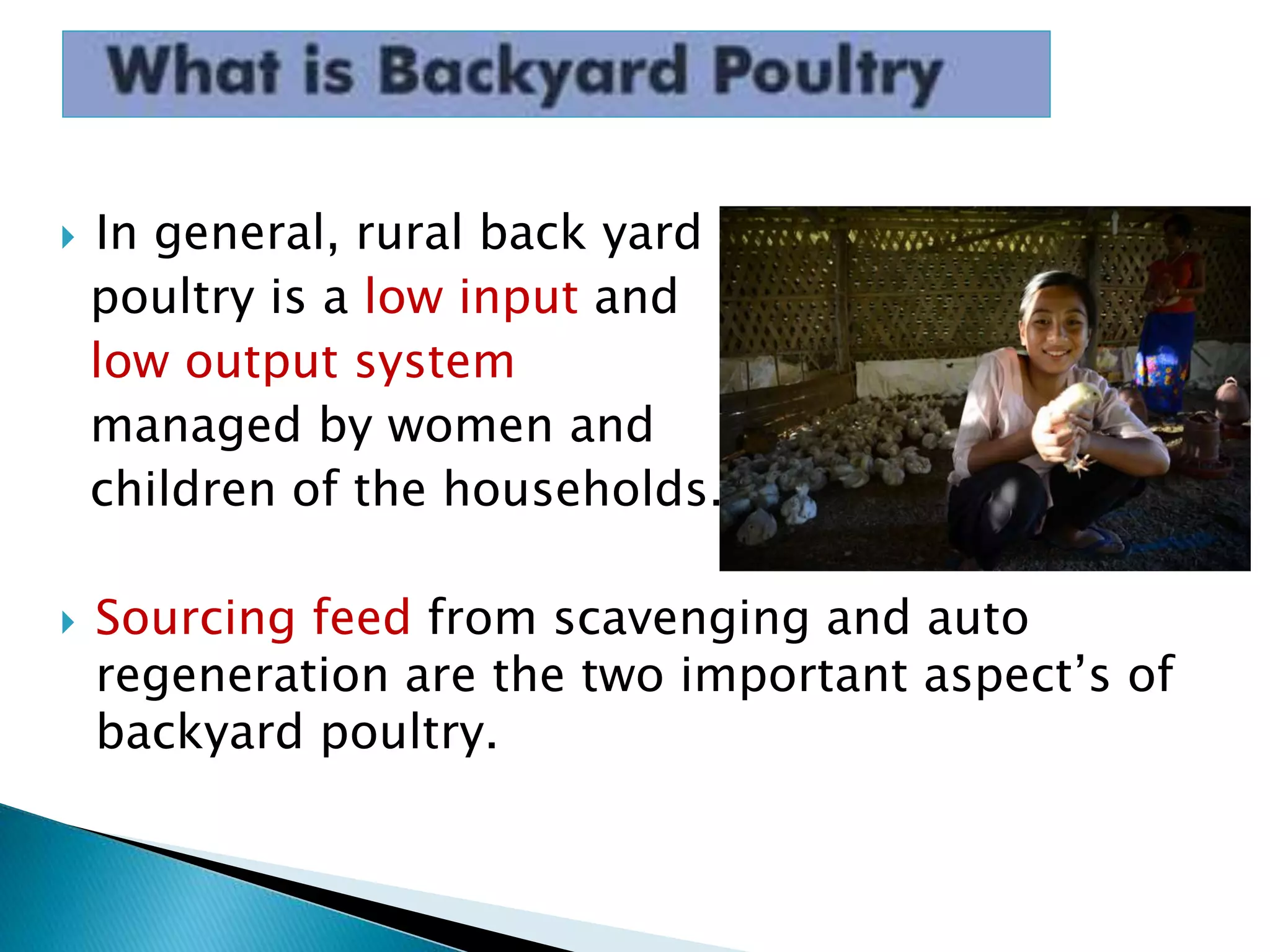
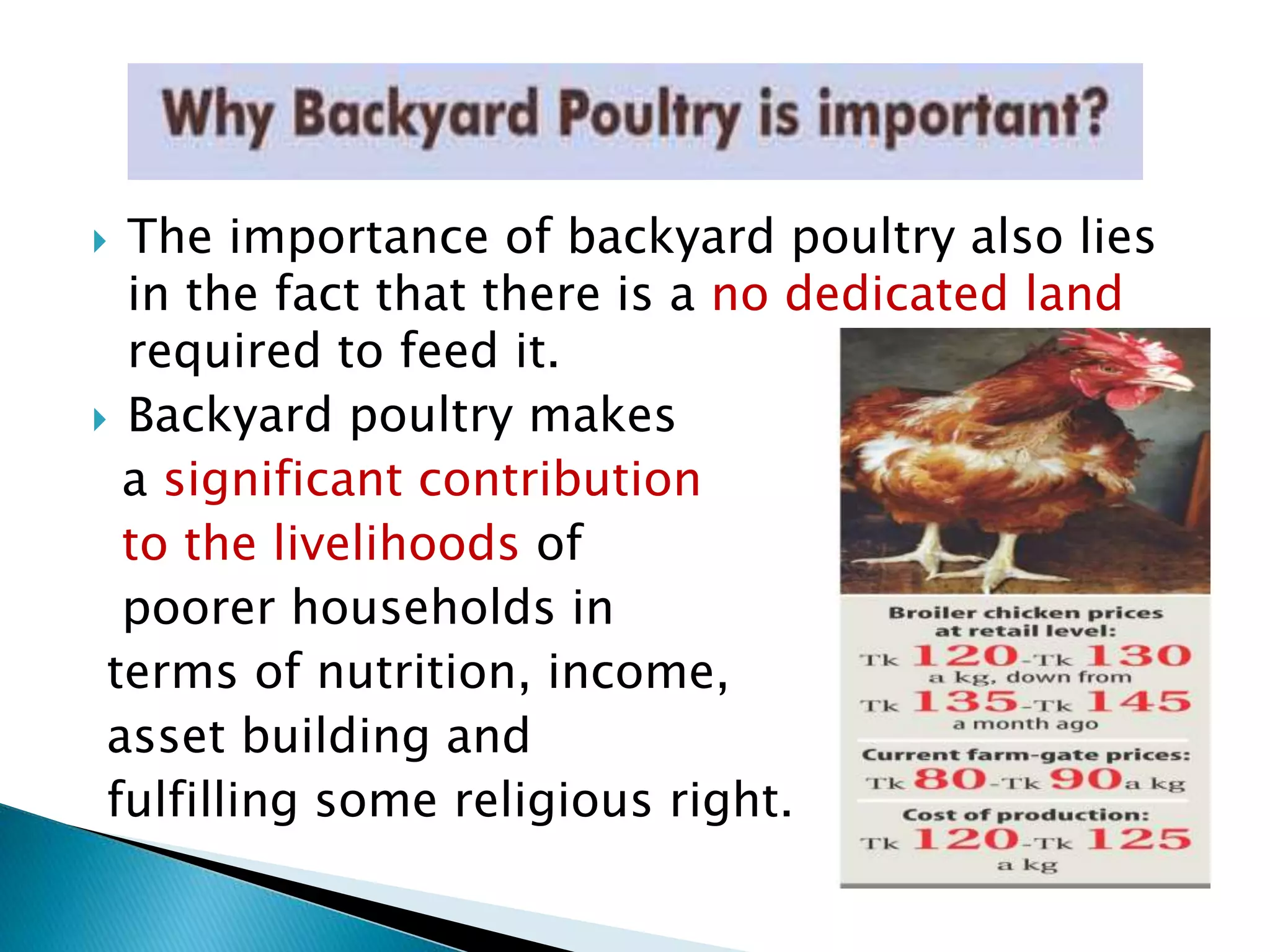
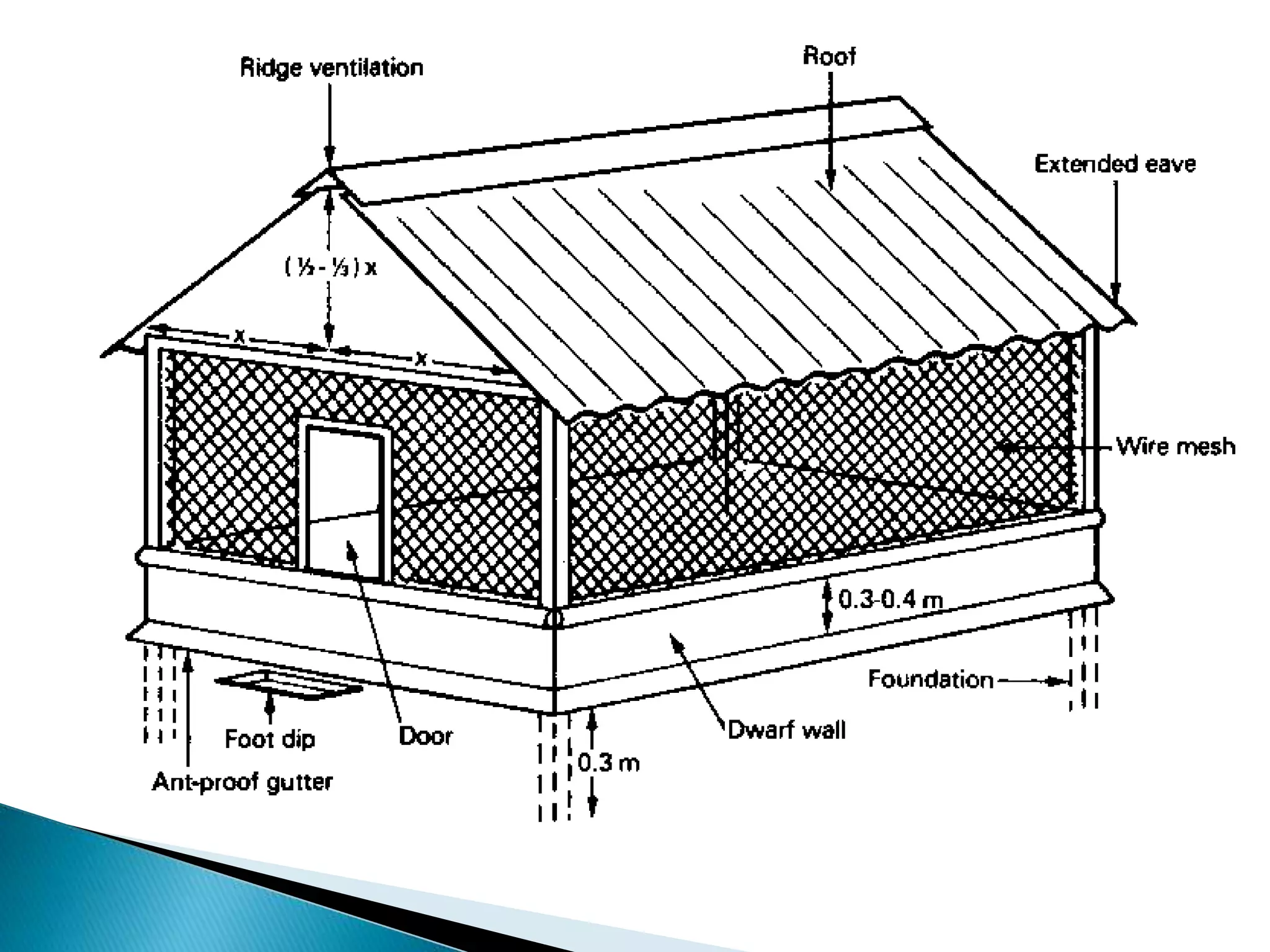
Backyard poultry farming is a small-scale system where a rural household keeps 5-25 birds primarily for family use and consumption. Any surplus eggs or birds are sold locally to generate additional income. It is an important source of nutrition, income and asset building for poorer families. The birds require adequate housing that protects them from weather and predators while providing access to feed, water, light and ventilation. Though production is low, backyard poultry is low-cost and the birds can find food by scavenging, making it a valuable system for rural livelihoods.
















![Reference :-
Strengthening the backyard poultry [a
article by Experiences of AP Drought
Adaptation Initiative (AP DAI)].
Wikipedia
Poultry Production ( by Professor R. A.
SINGH)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/23473a3a-d4b9-4c61-b562-b3fd7a032f13-150514124344-lva1-app6891/75/back-yard-farming-21-2048.jpg)
