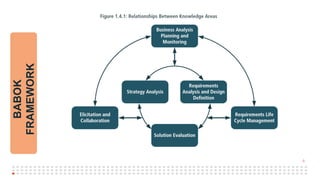
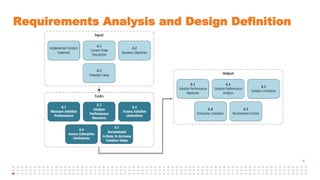
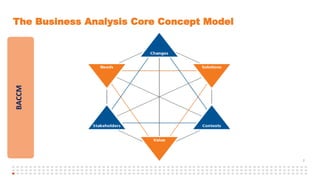
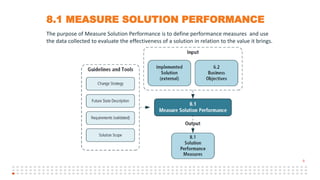
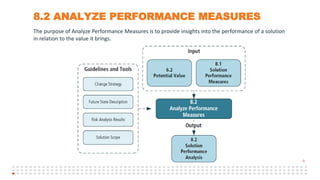
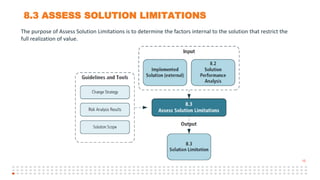
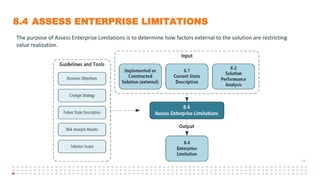
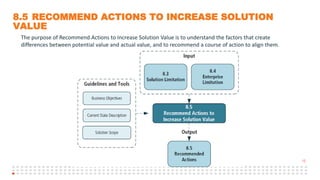
The document summarizes an online study group session hosted by IIBA UK on analyzing the Solution Evaluation chapter of the BABOK guide. It introduces the presenters and provides an overview of the session, which includes reviewing the key sections of chapter 8 and discussing a case study on Pierre's Restaurant implementing an online booking system. The case study is then analyzed based on the different sections of chapter 8, including brainstorming key performance indicators to measure the solution, identifying potential limitations both within the solution and from external enterprise factors, and recommending actions to increase the value delivered by the solution.