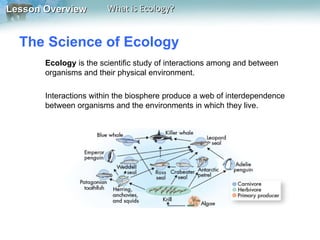
Ecology is the scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their physical environment. The biosphere consists of all life on Earth and parts where life exists. Ecology studies different levels of organization from individual organisms to populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and the biosphere. Ecologists use observation, experimentation, and modeling to understand biotic factors like species interactions and abiotic factors like temperature and water availability that shape environments.