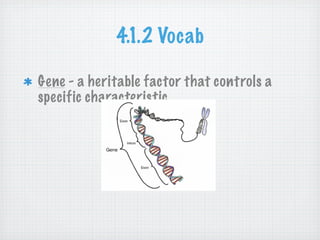
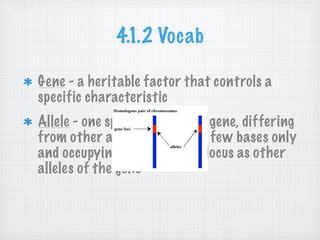
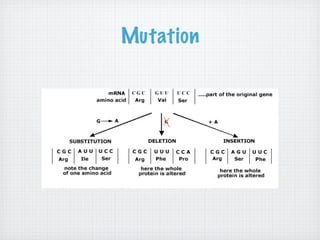
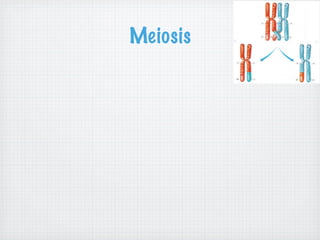
Genetic variation is produced within populations through mutations, sexual reproduction, and meiosis. Mutations introduce new alleles and variation when genes change through single-base mutations or chromosomal rearrangements. Sexual reproduction and meiosis increase genetic variation through recombination of alleles and independent assortment of chromosomes during mating and cell division. This genetic variation provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon.