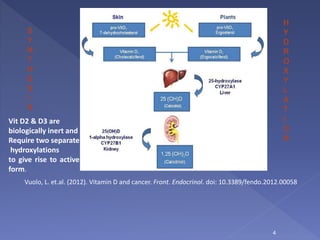
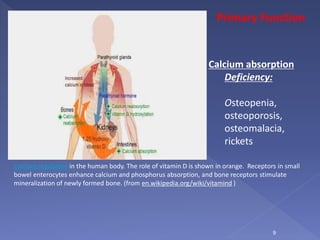
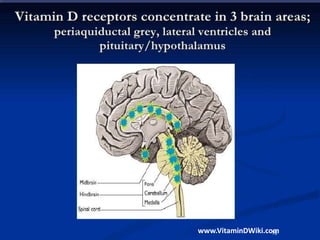
Vitamin D is a hormone precursor that is important for calcium absorption and bone health. It exists in two forms, D2 and D3, and requires two hydroxylation steps to become the active form. Vitamin D deficiency can lead to bone diseases like rickets and osteomalacia as well as increased risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune disorders, and infections. Risk factors for deficiency include inadequate sun exposure, older age, darker skin, obesity, and certain medical conditions or medications. Maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels through supplementation and diet may help reduce disease risk.