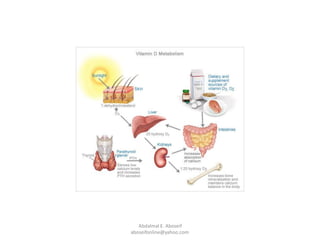
Vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining bone and immune system health. The document discusses that vitamin D deficiency is common in Western countries due to limited sun exposure and may increase risk of conditions like diabetes. Maintaining adequate vitamin D levels through sun exposure, supplementation, or diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and support overall health.