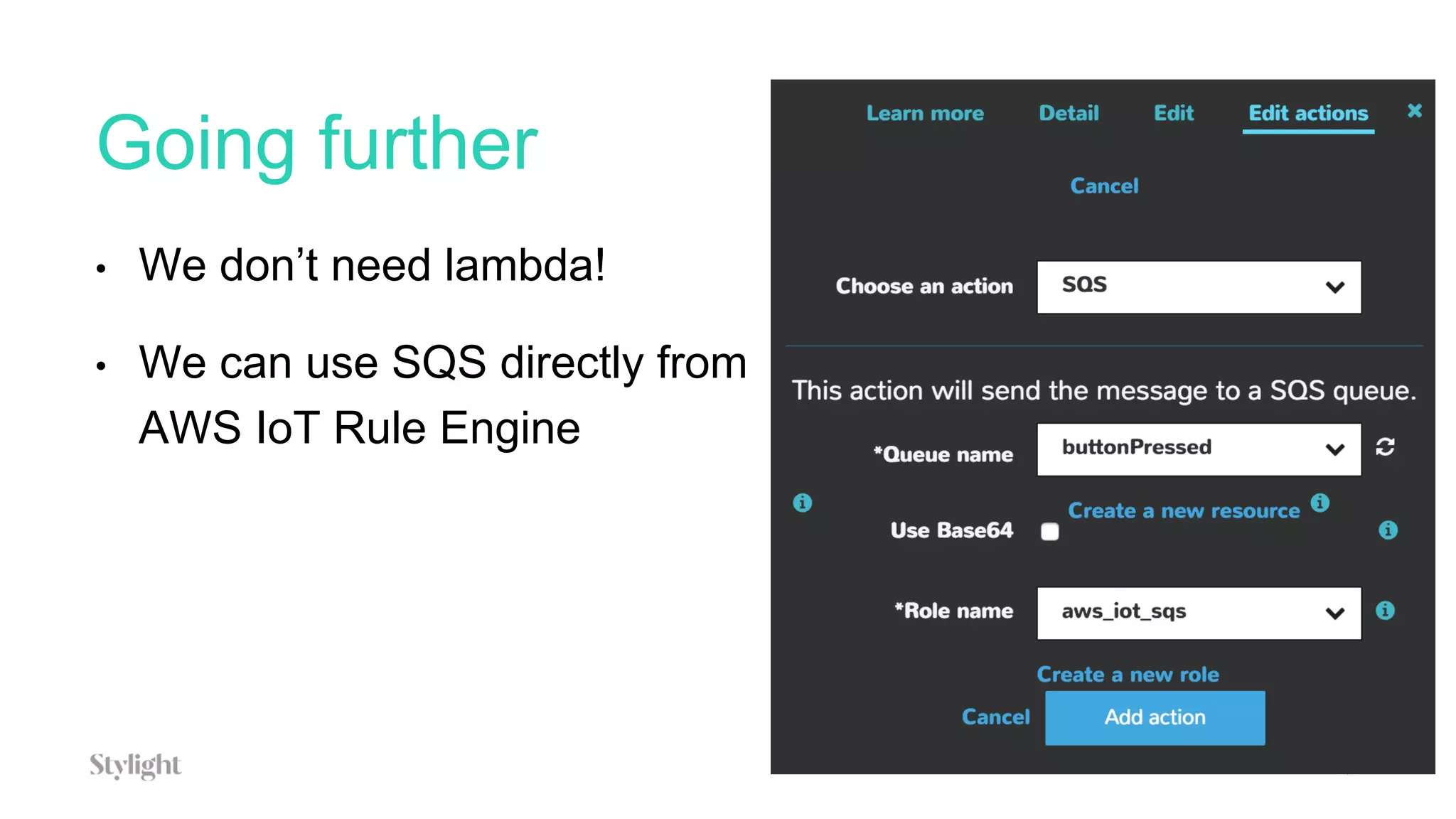
This document discusses using AWS IoT services like Lambda and SQS to power a blockchain project that generates digital certificates of attendance.
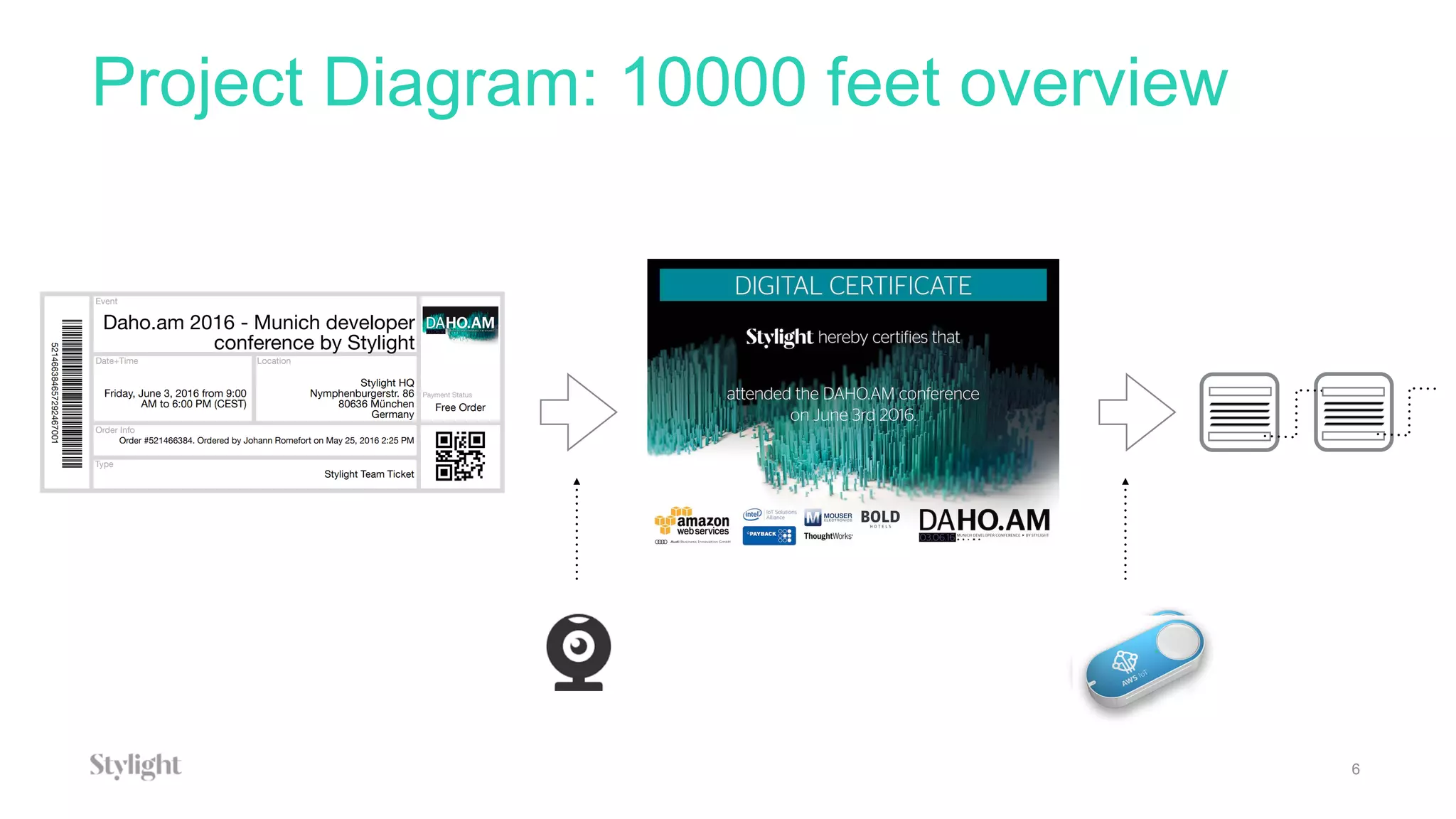
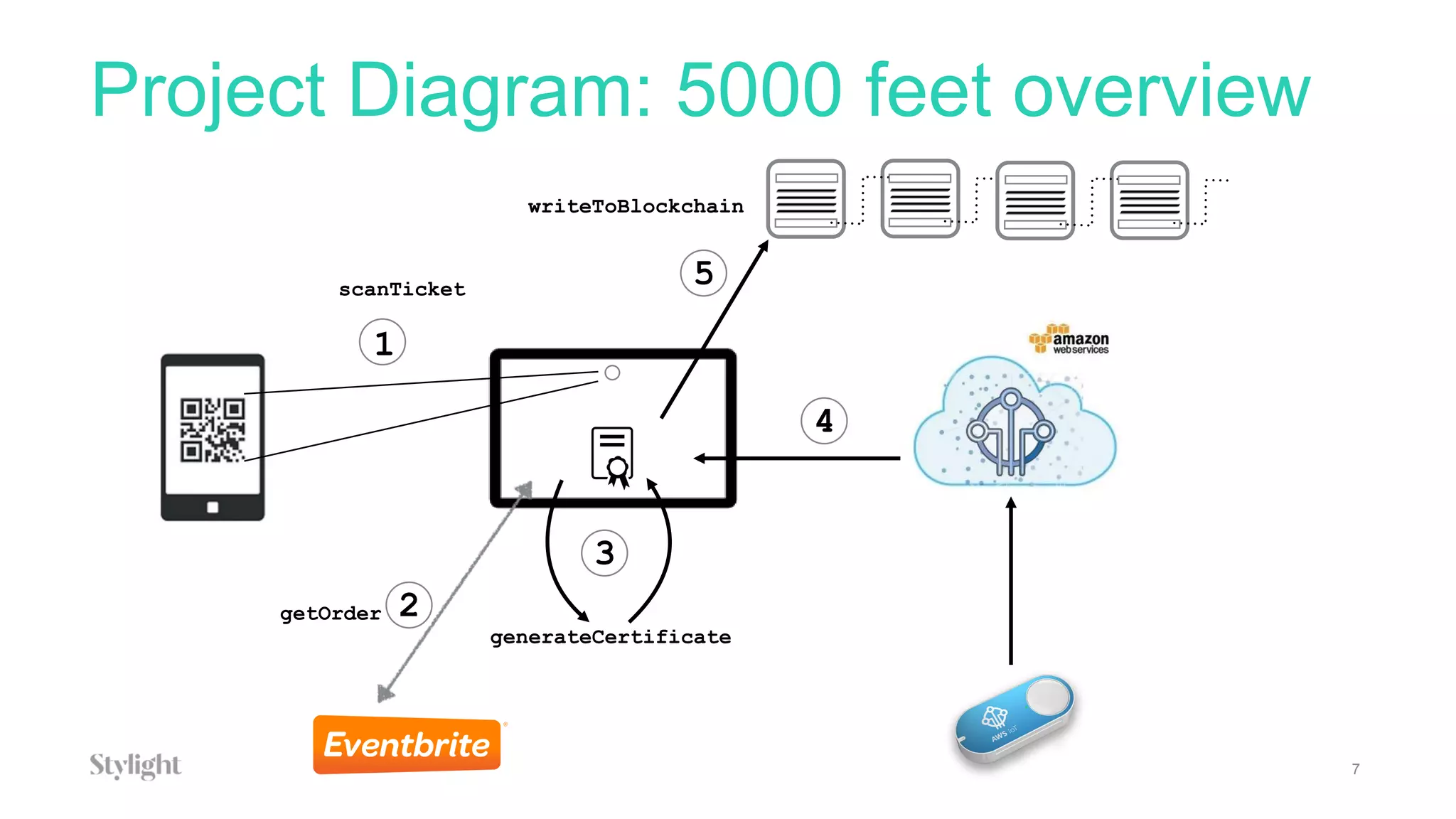
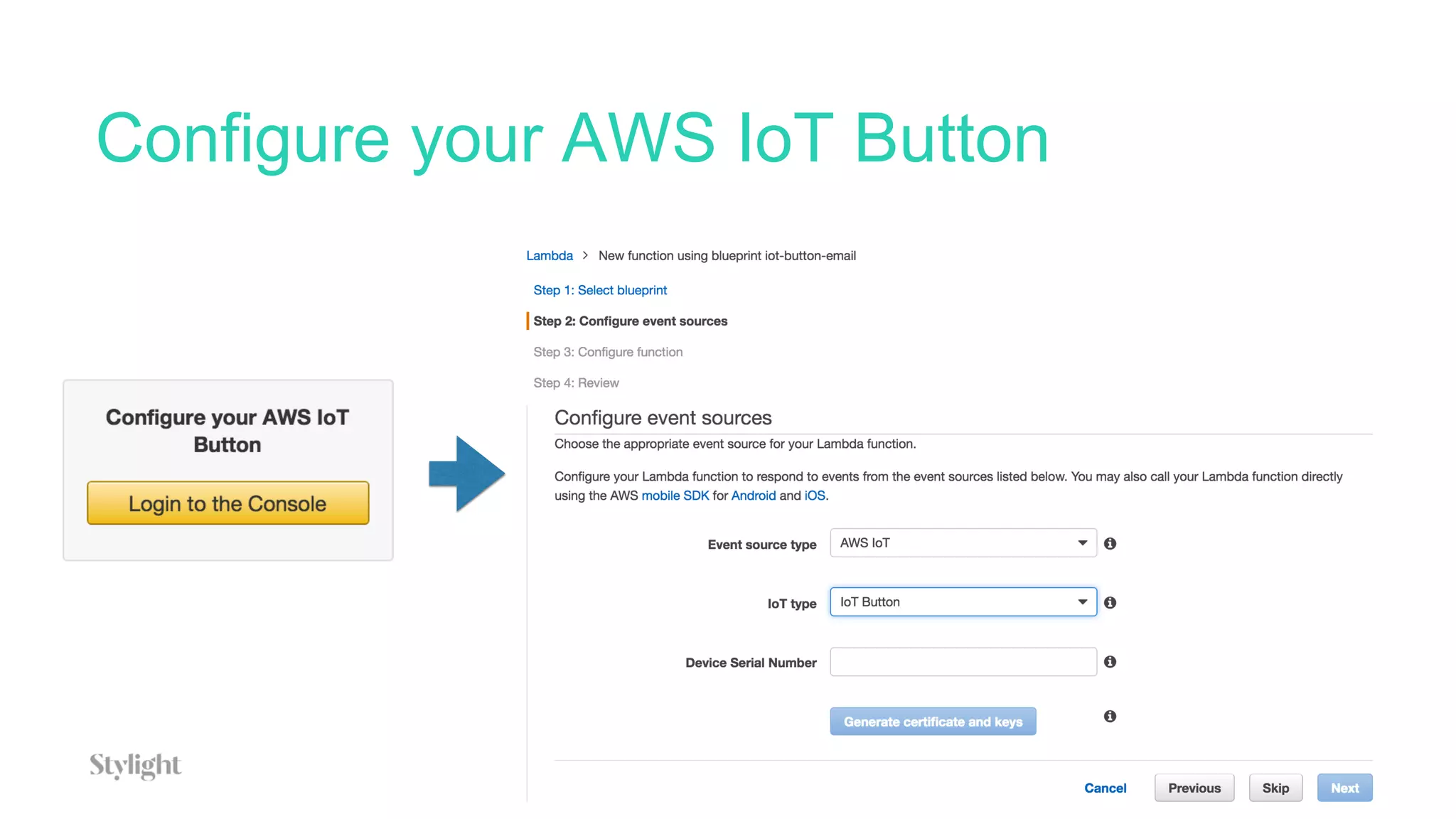
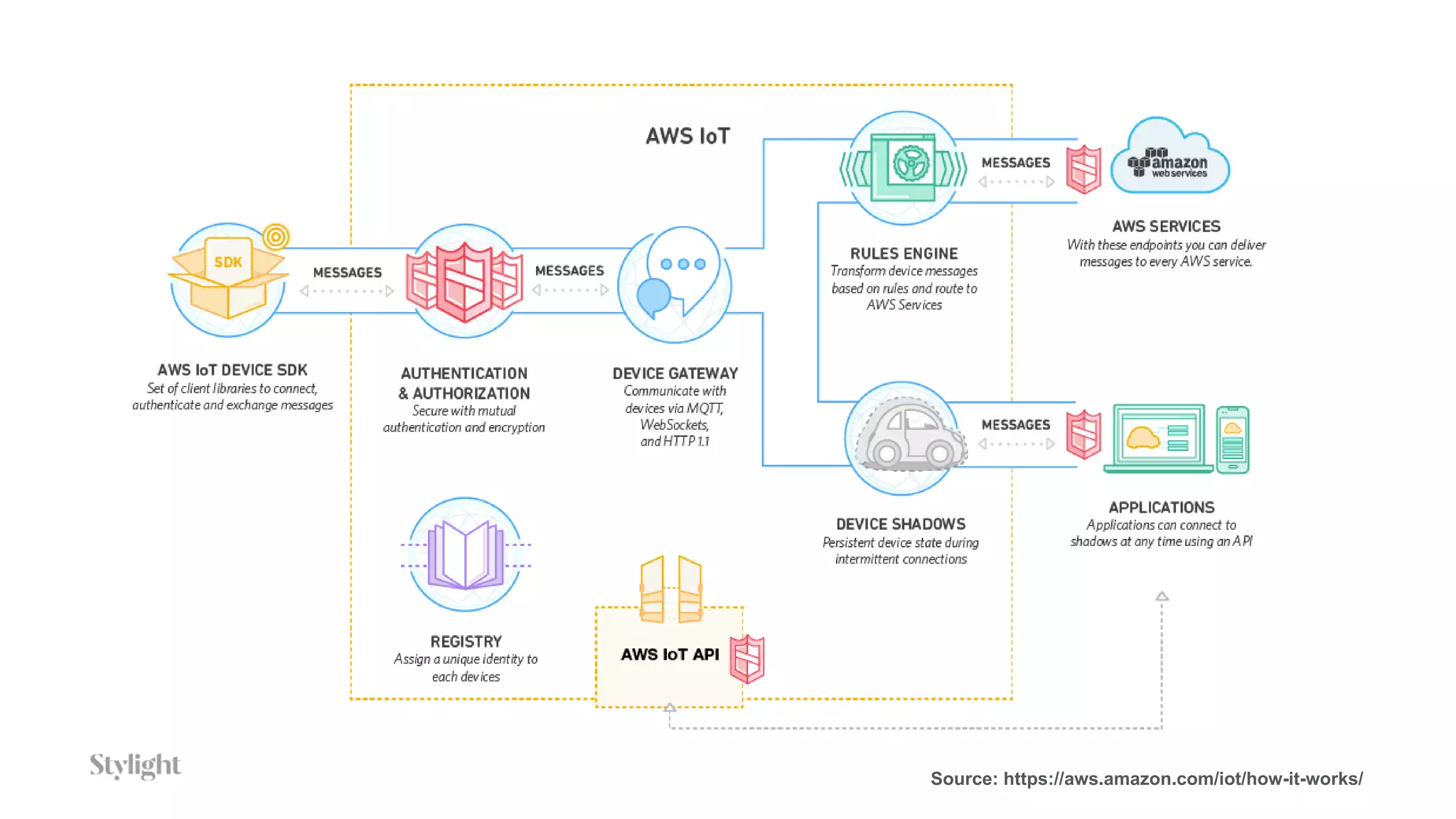
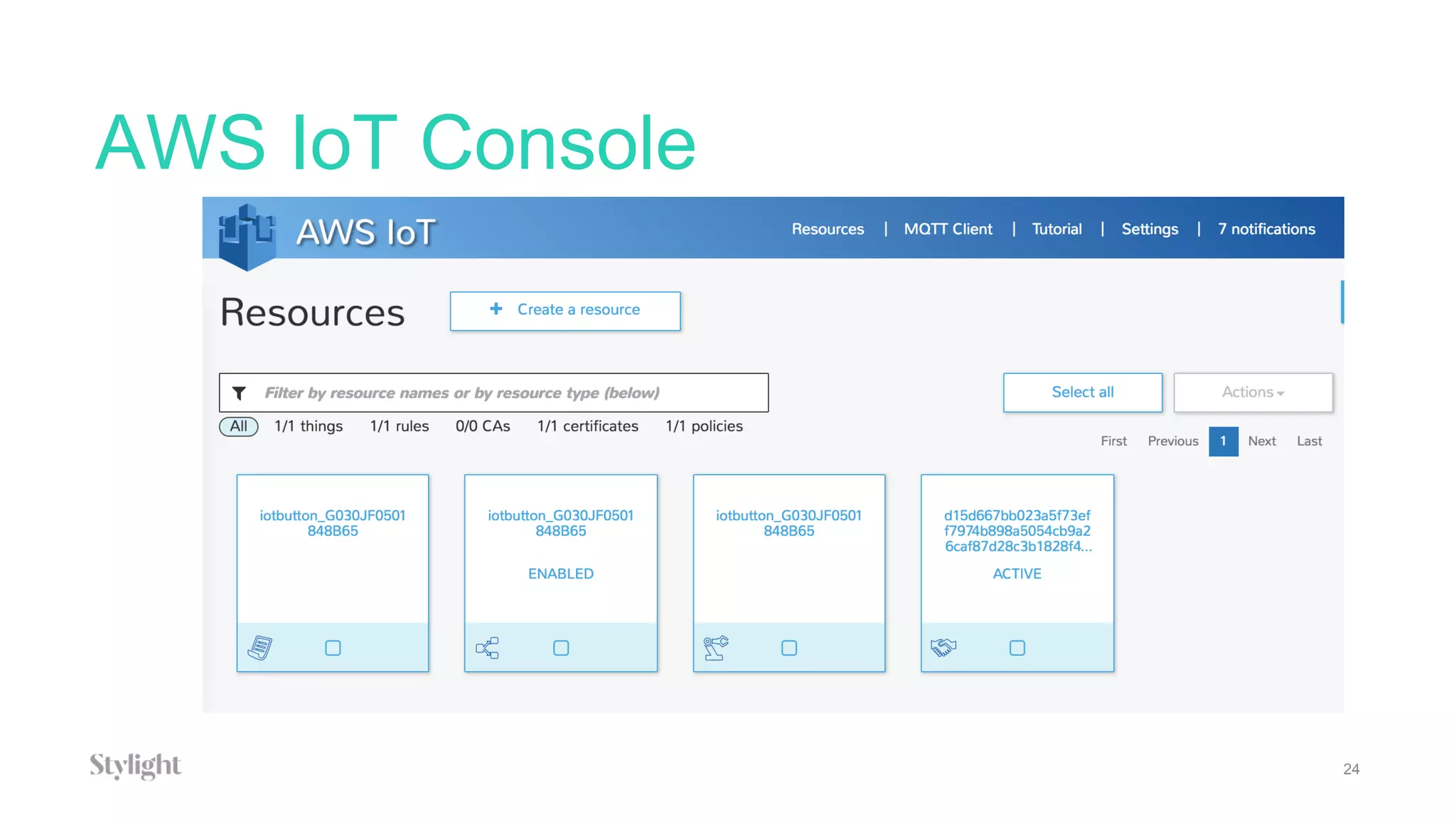
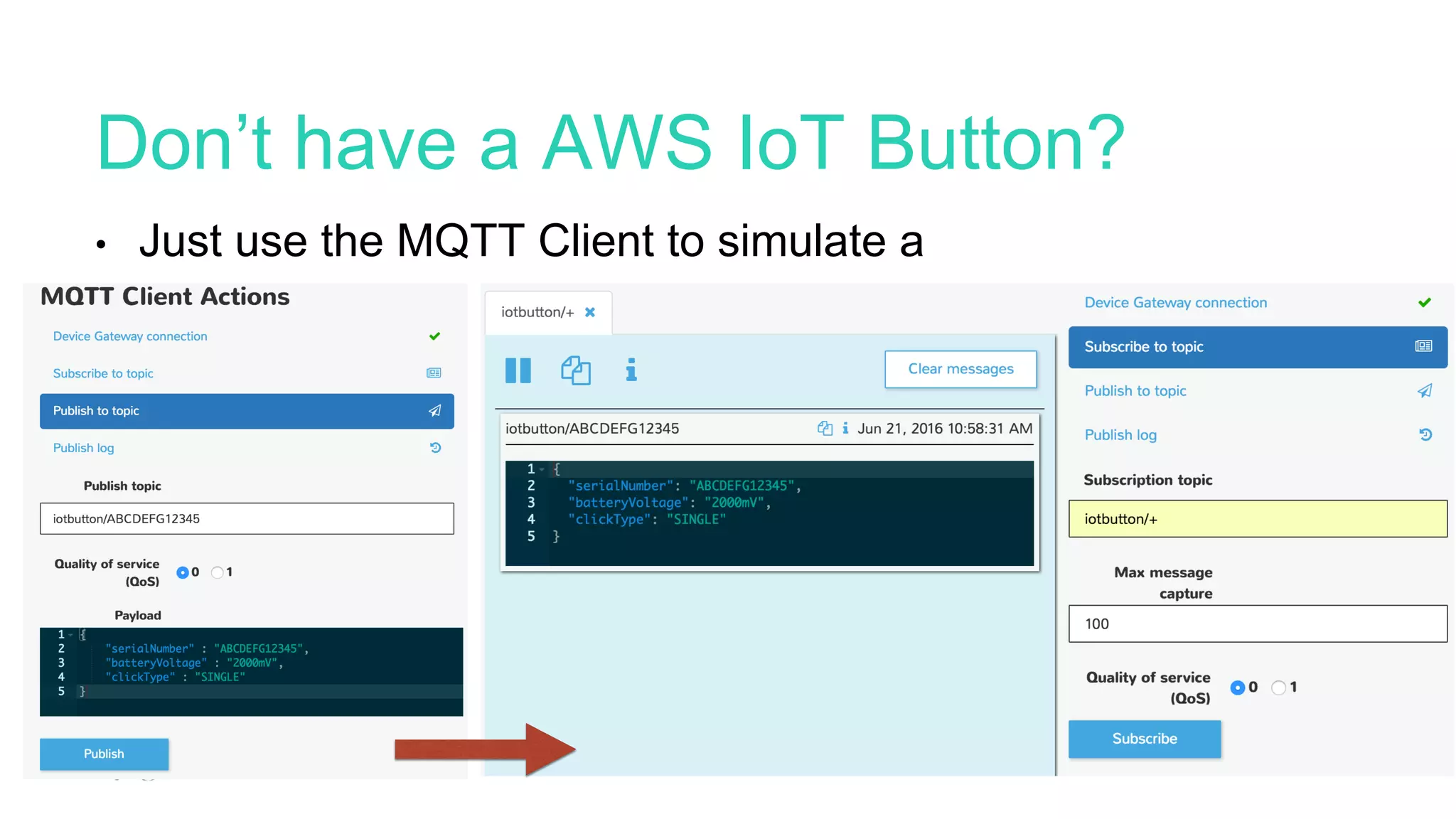
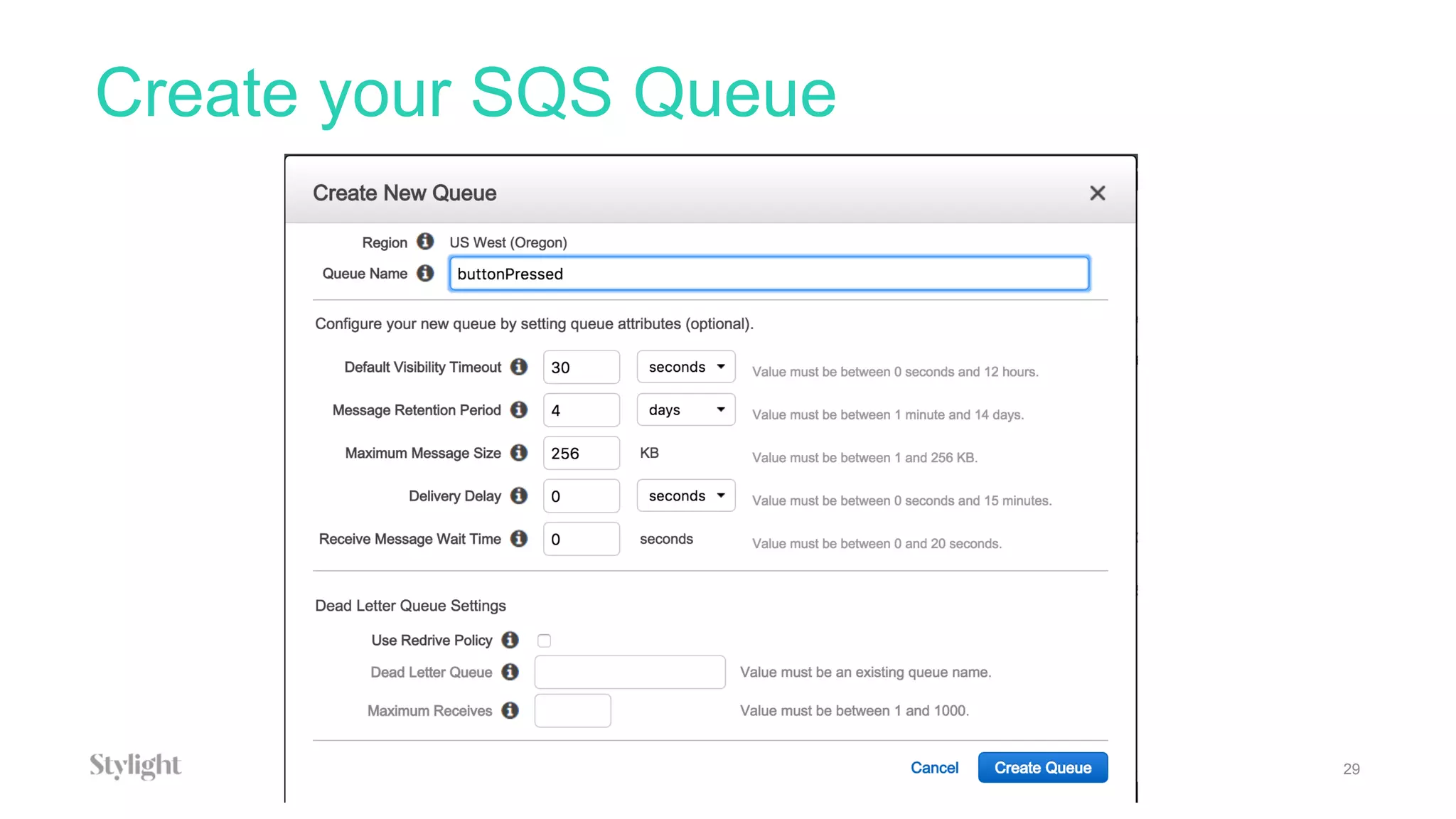
The project involves using an AWS IoT button to scan tickets, pressing the button as input, and generating immutable certificates on the blockchain. AWS IoT, Lambda, and SQS are used to connect the button press to writing on the blockchain.
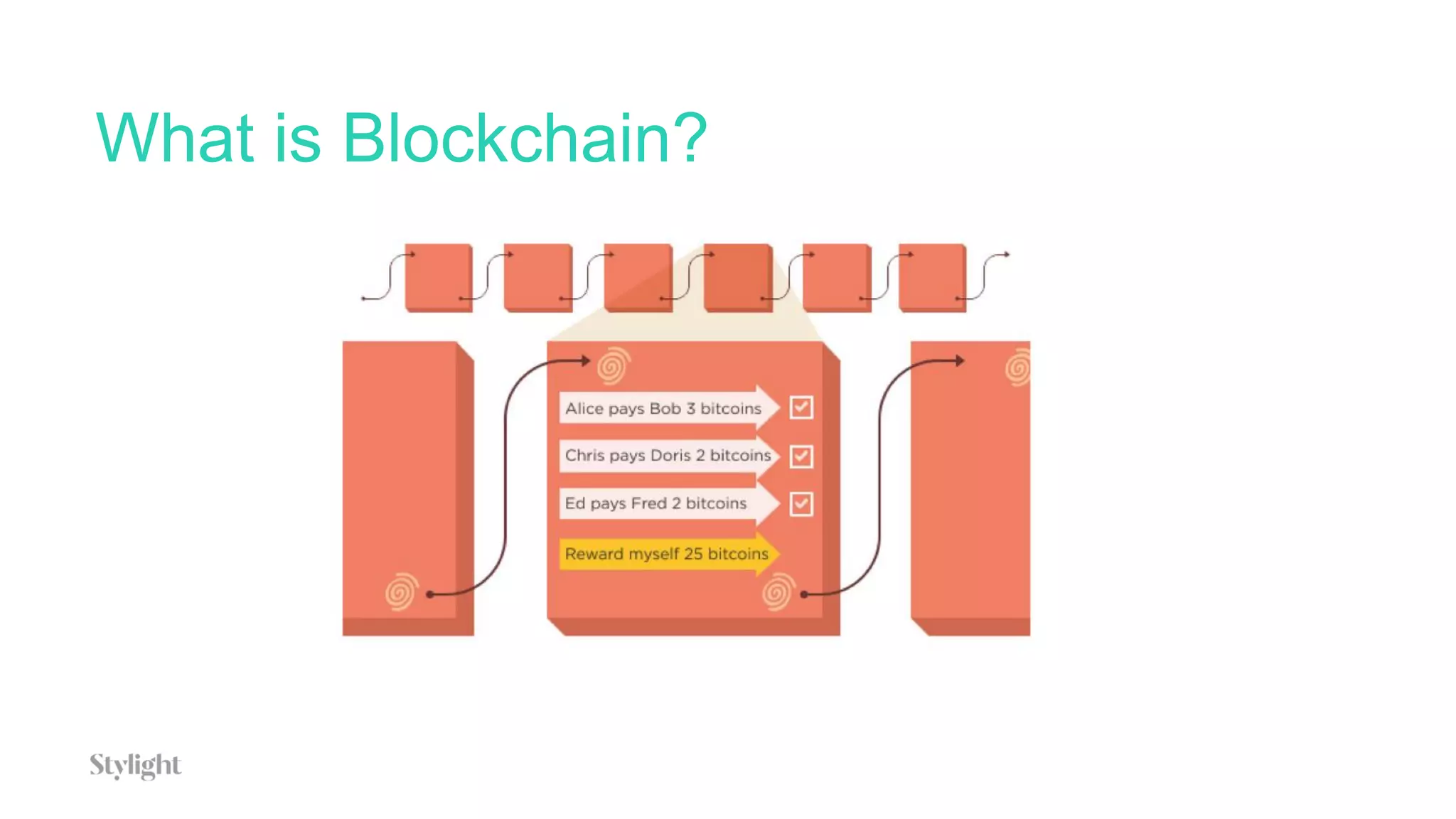
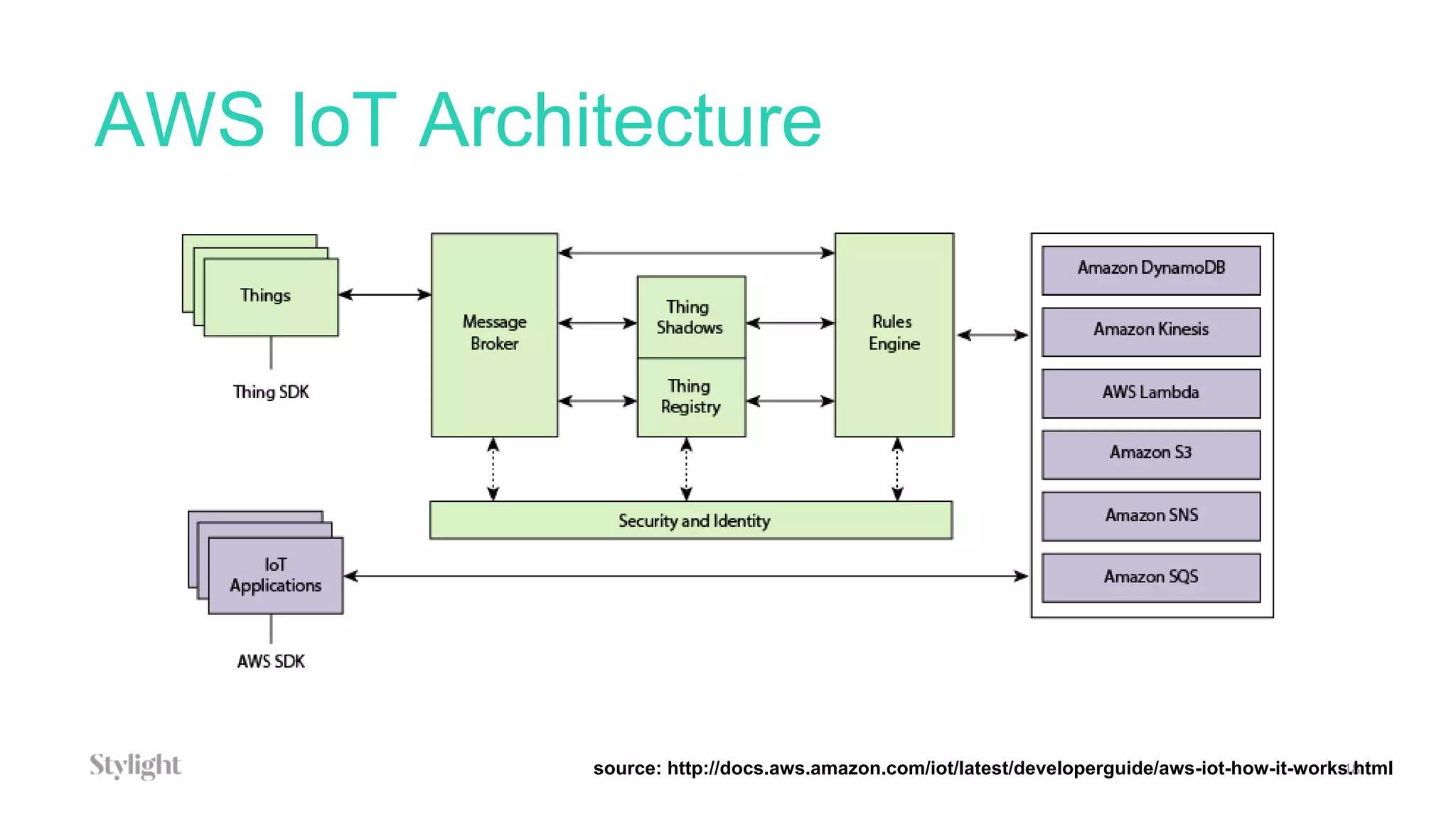
The document provides an overview of blockchain technology and describes how AWS IoT, MQTT, Lambda, SQS, and IoT rules can be configured to connect an IoT button press to writing a transaction on the blockchain to generate certificates.



















![Configure the Policy Document
31
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*"
},
{
"Action": [
"sqs:SendMessage",
"sqs:GetQueueUrl"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:sqs:us-west-2:882247834355:buttonPressed"
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aws-iot-button-lambda-160623140129/75/AWS-IoT-Button-and-Lambda-to-power-a-blockchain-project-AWS-Serverless-Web-Day-31-2048.jpg)