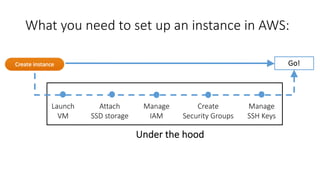
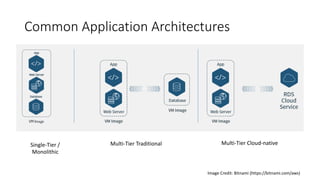
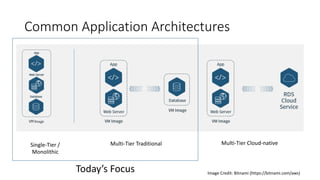
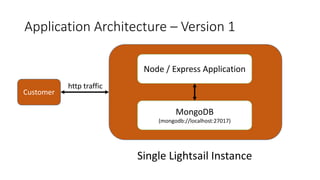
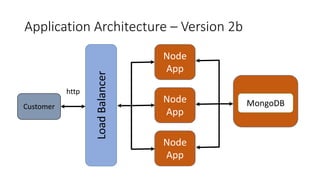
The document is a workshop presentation focused on deploying and scaling a Node.js application using Amazon Lightsail, led by developer advocate Mike Coleman. It covers key topics such as launching a monolithic app, scaling components, and utilizing services like load balancers and snapshots. The workshop aims to teach participants about application architectures and practical setup steps for using Amazon Lightsail effectively.