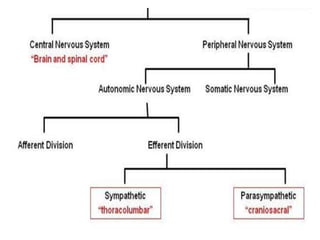
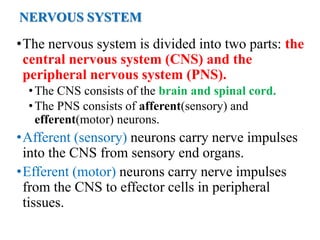
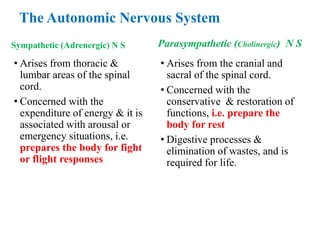
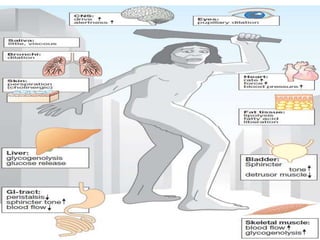
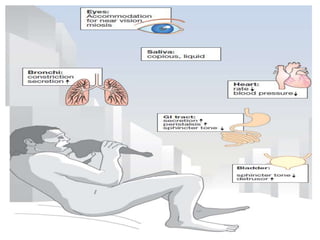
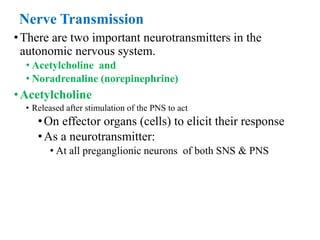
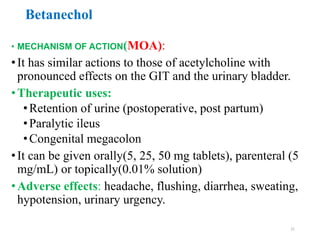
The document discusses the autonomic nervous system and drugs that affect it. It describes how the autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The parasympathetic nervous system uses acetylcholine as its neurotransmitter and targets organs like the heart, gut and glands. Drugs that increase parasympathetic activity are called parasympathomimetics and include acetylcholine, pilocarpine and indirect-acting drugs that inhibit acetylcholinesterase. These drugs generally slow the heart rate, relax smooth muscles and increase gland secretions. Common side effects include sweating, diarrhea and low blood pressure.