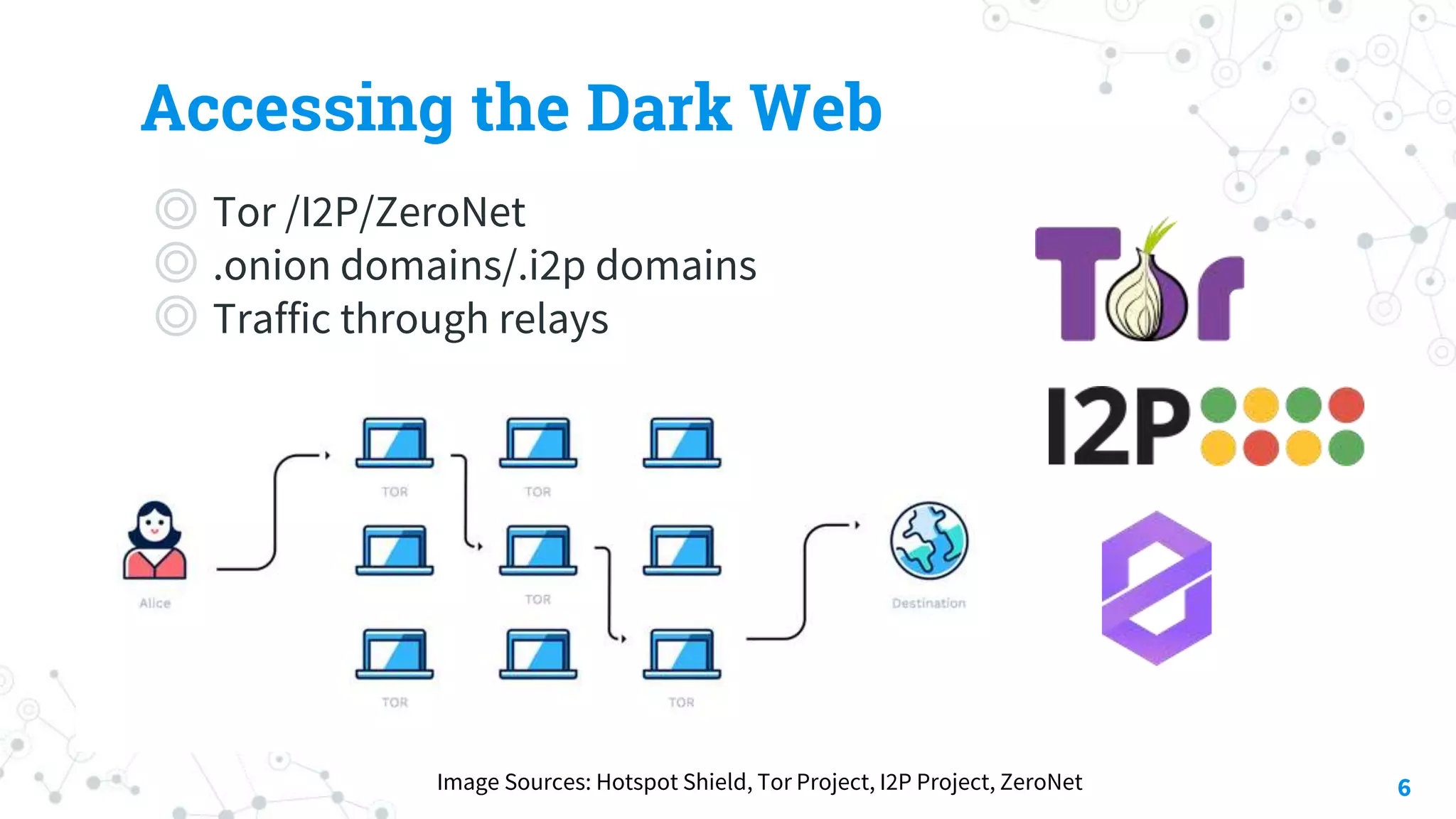
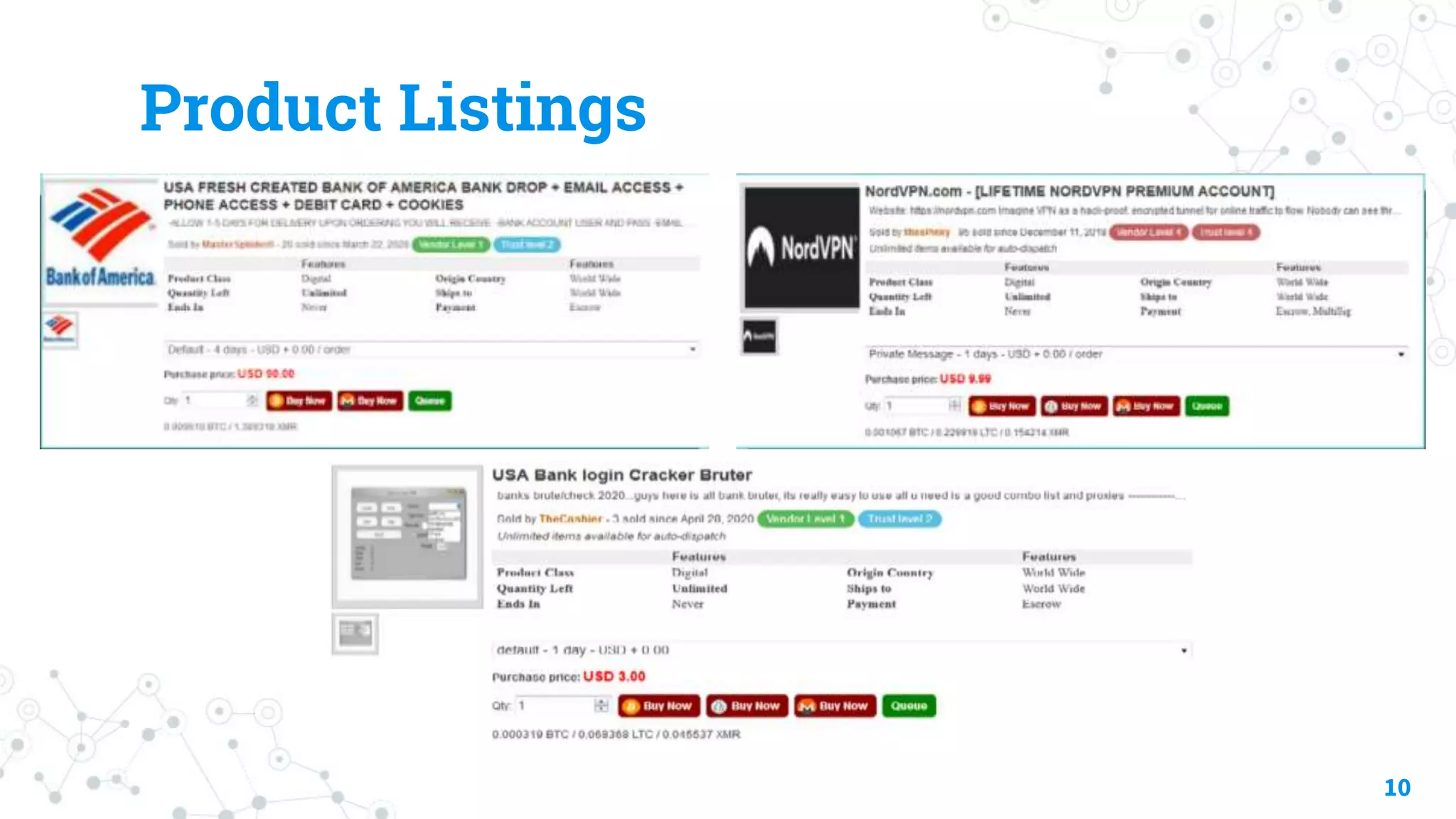
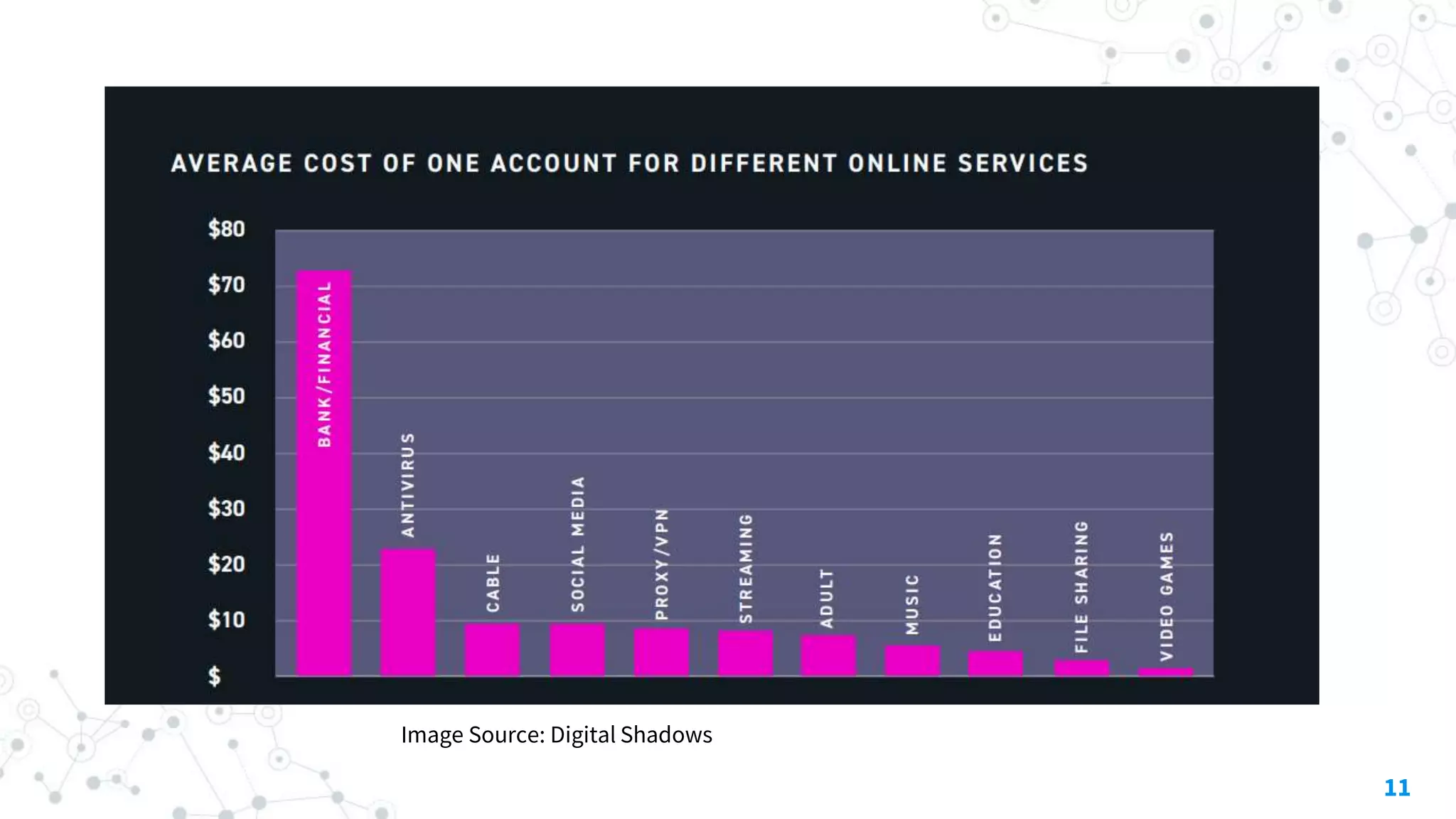
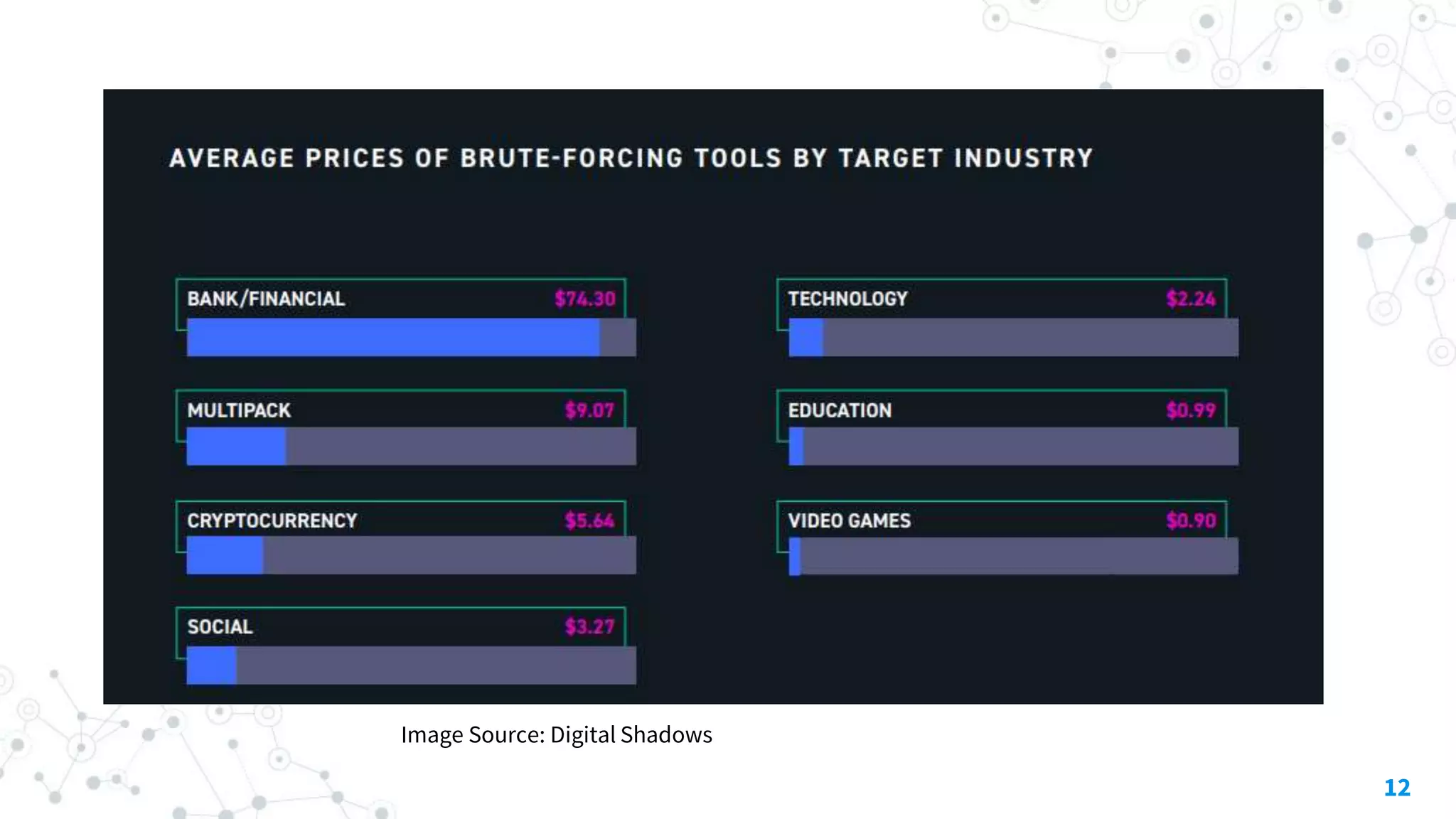
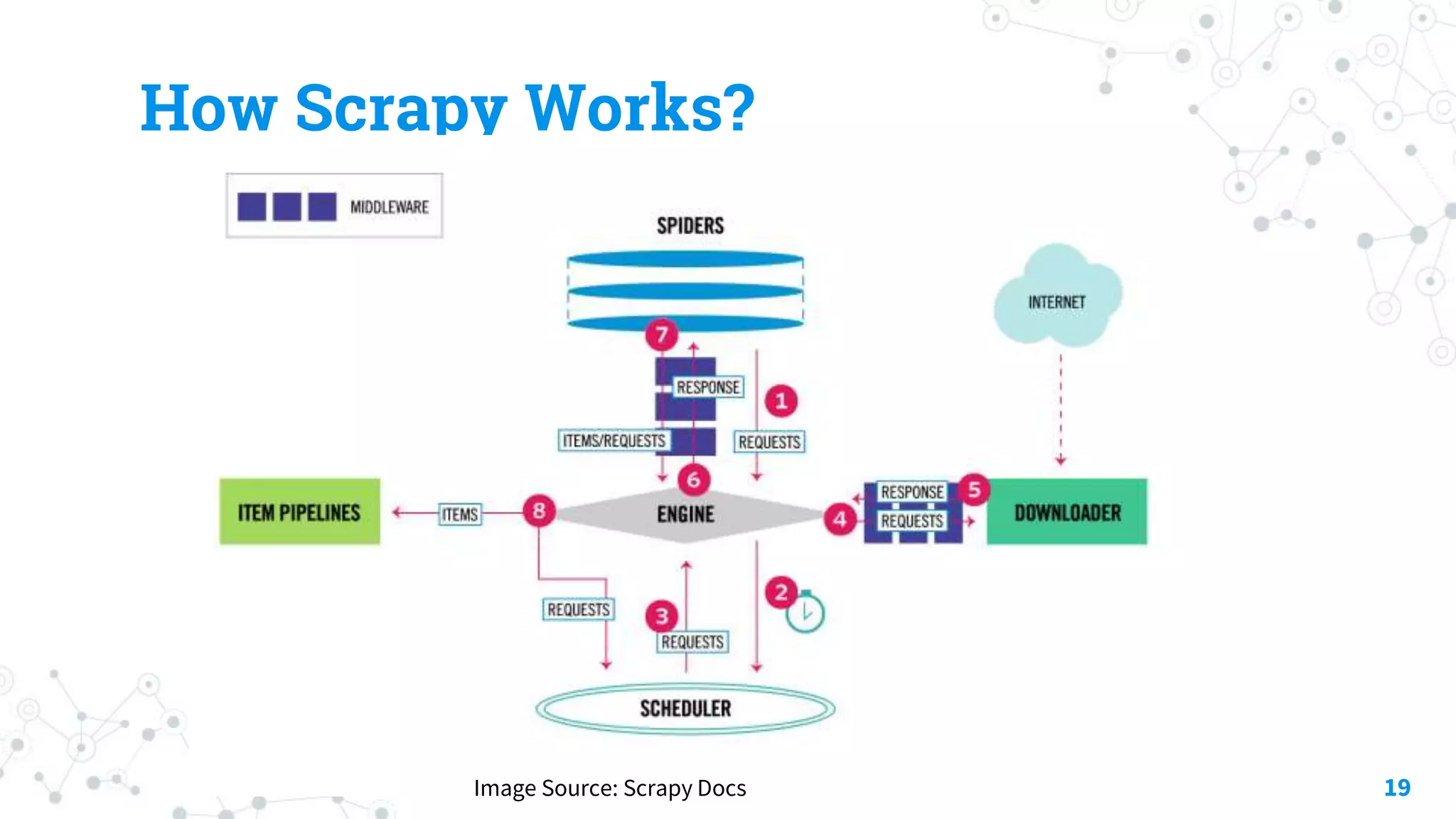
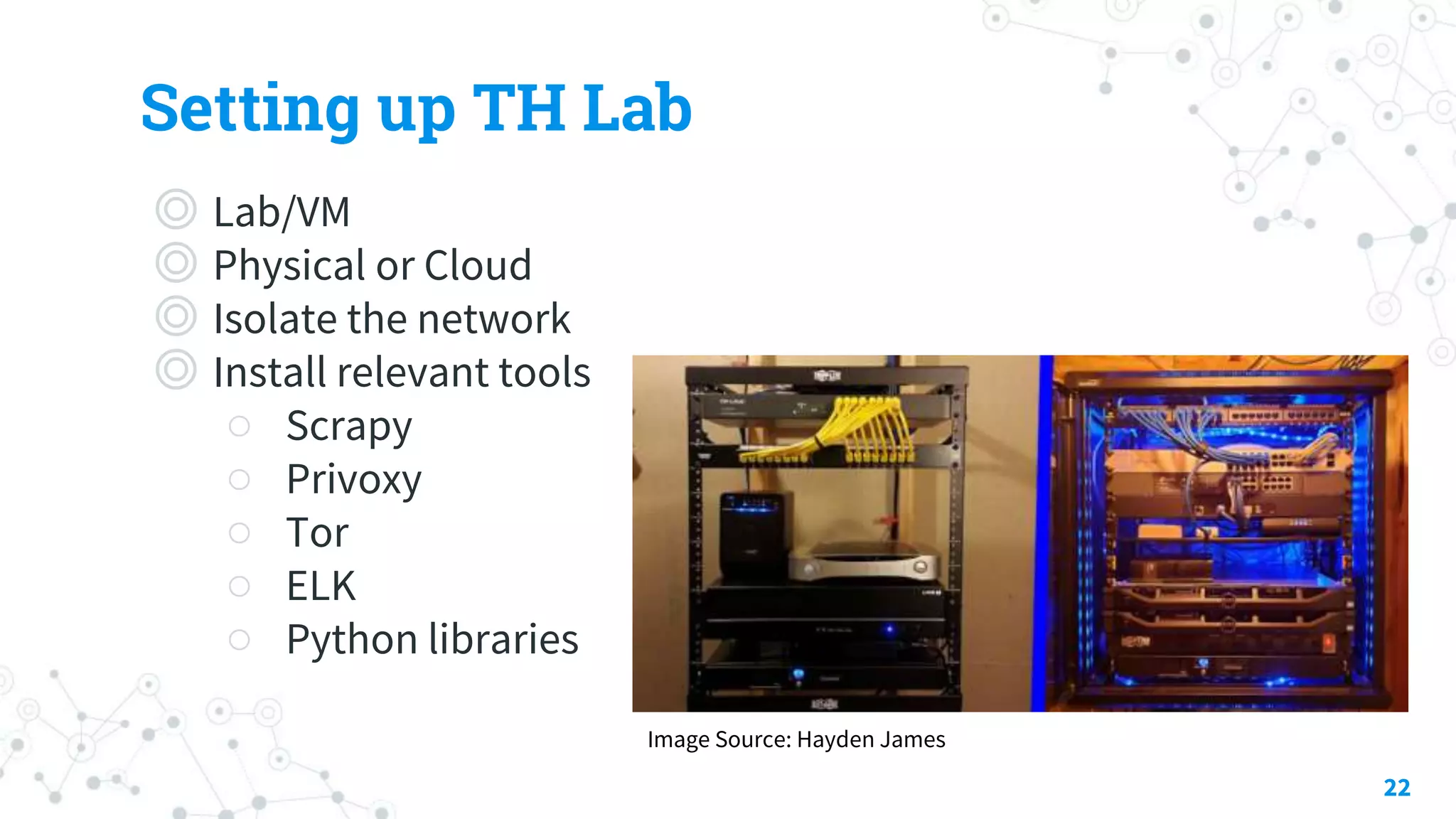
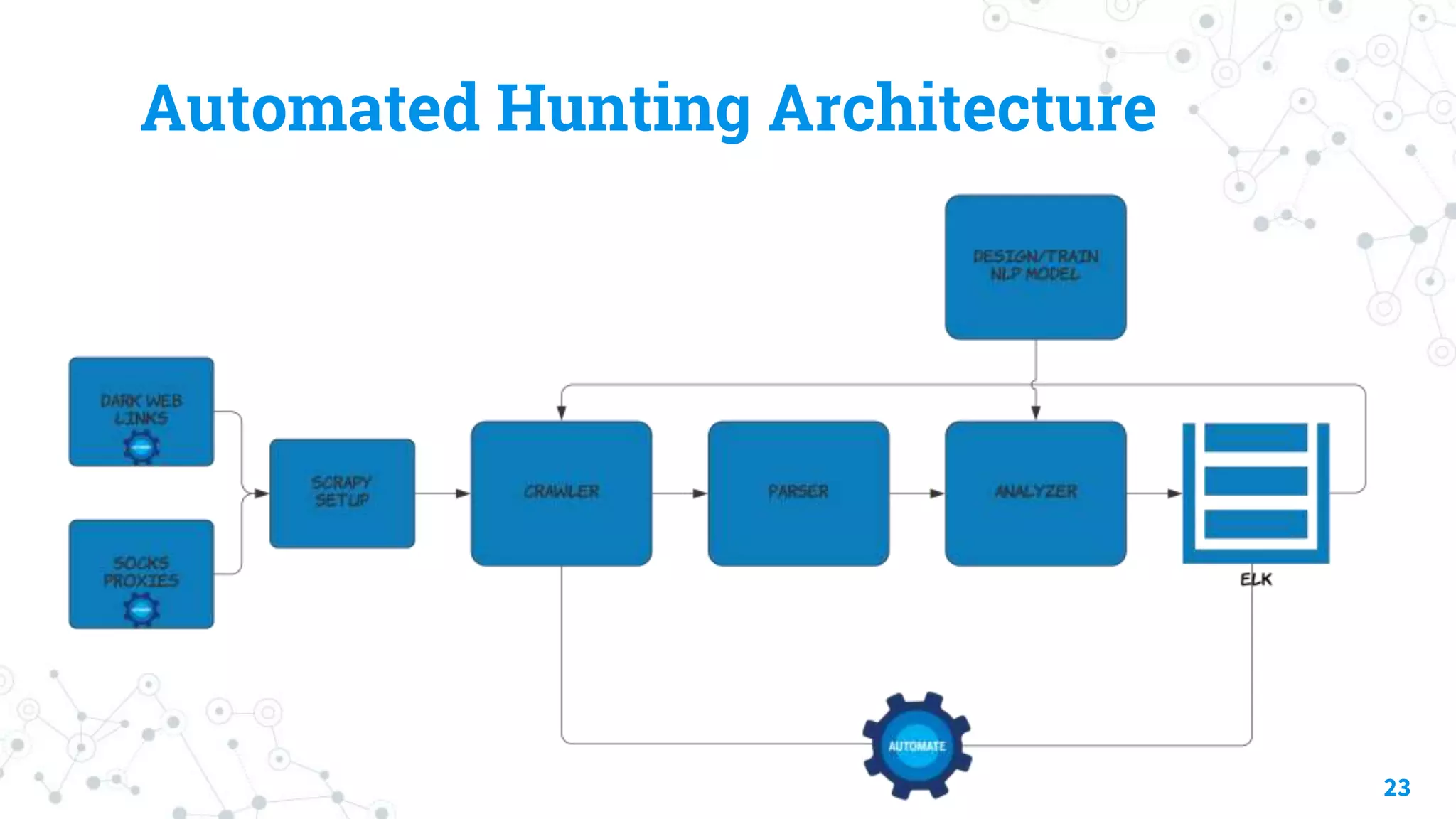
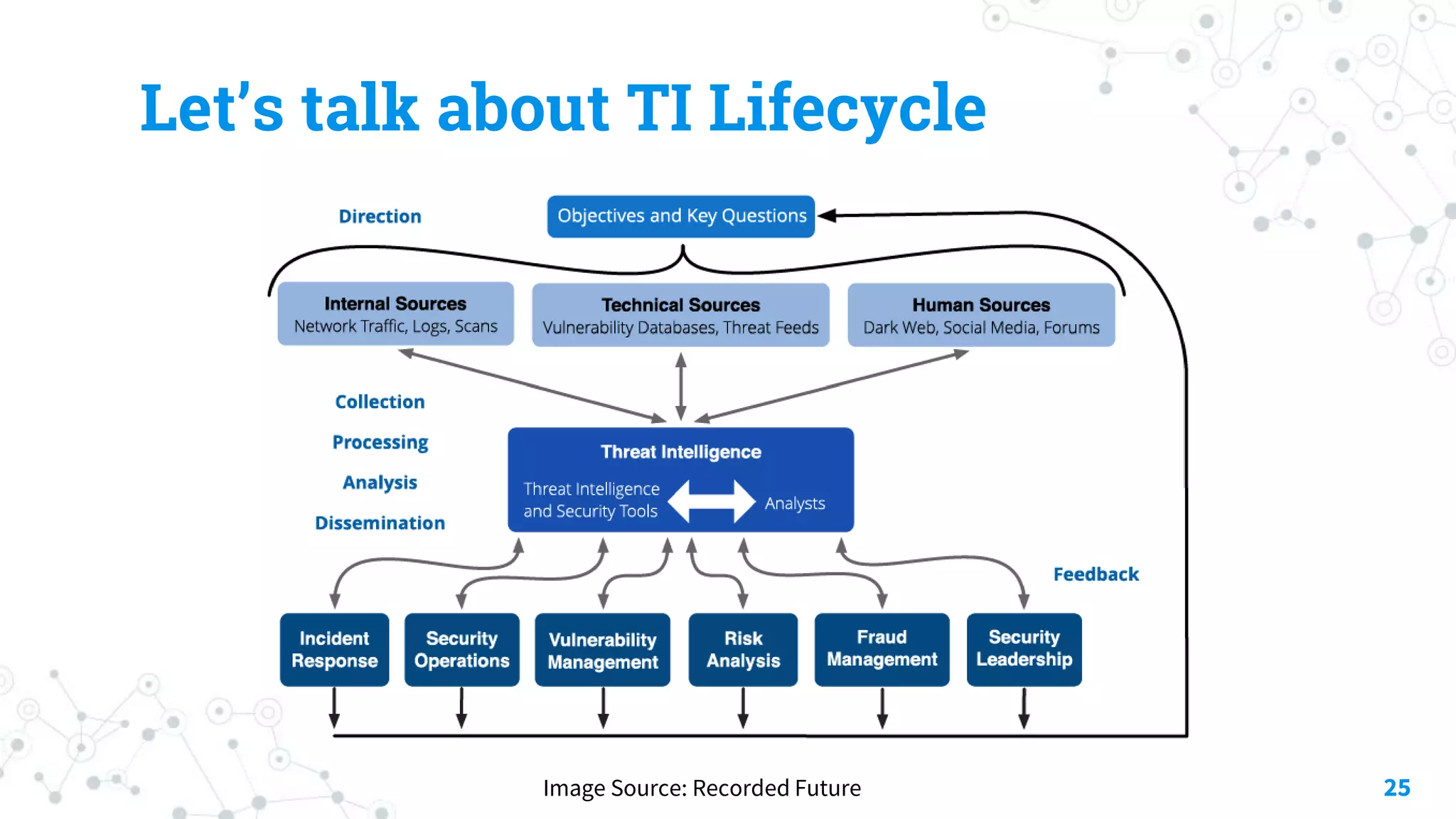
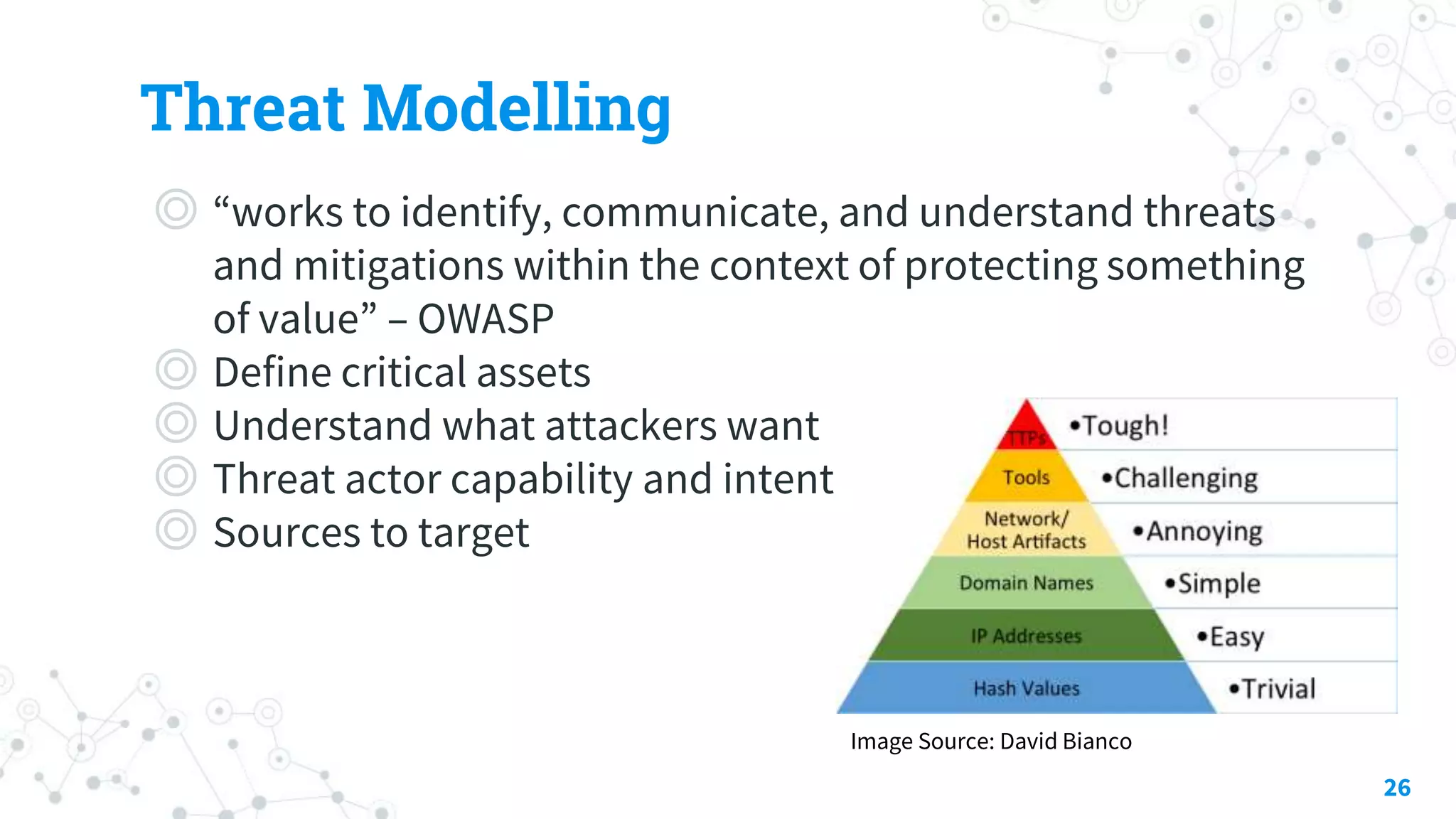
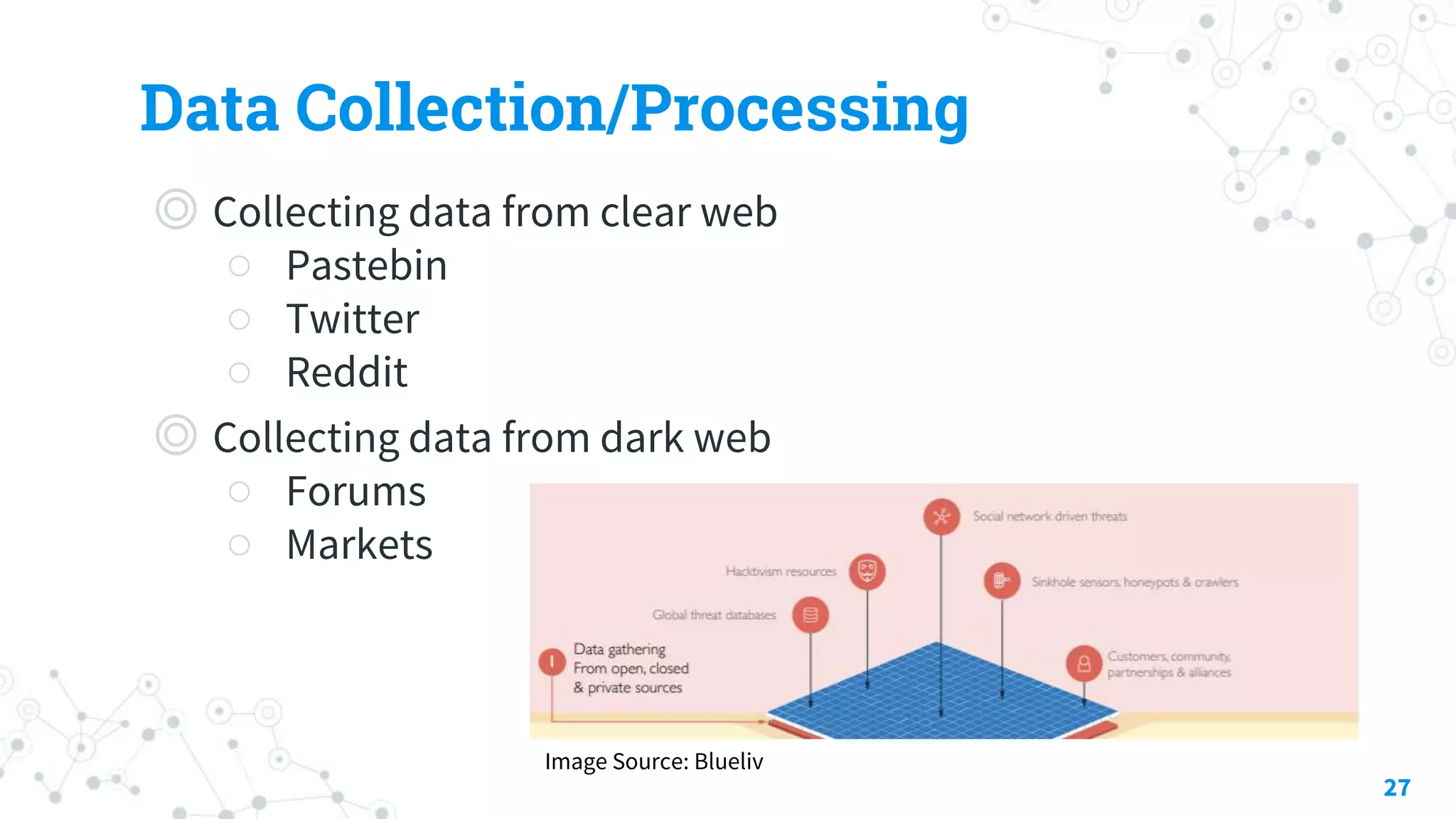
The document discusses automating threat hunting on the dark web, emphasizing its importance for identifying and mitigating cyber threats. It covers methods for hunting, the potential for automation, and the need for operational security (opsec). The conclusion highlights the challenges and resources required for effective dark web threat hunting.