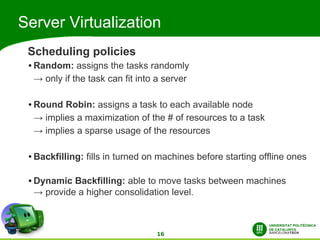
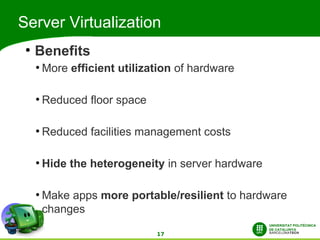
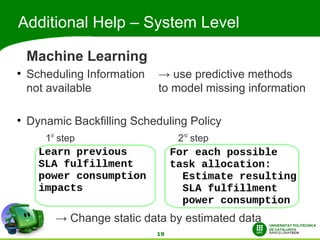
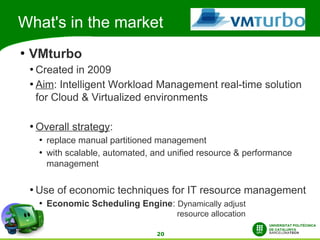
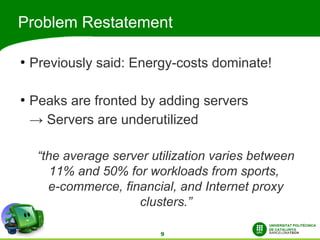
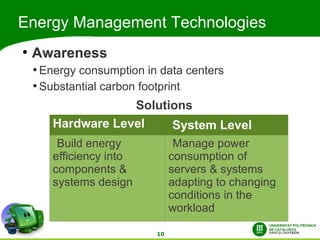
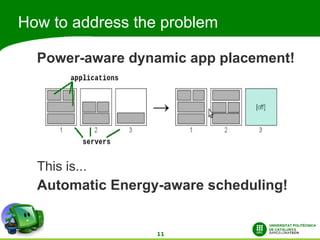
This document discusses automatic energy-aware scheduling for distributed computing. It summarizes the Green500 list which ranks supercomputers by energy efficiency. Server virtualization can improve efficiency by consolidating workloads. Automatic scheduling that places applications dynamically based on power usage could address underutilization. Current solutions include VMturbo's intelligent workload management and using machine learning to model scheduling. The conclusion is that automatic energy-based scheduling should be more widely adopted to further improve supercomputer efficiency.





![Server Virtualization
●
P1: Servers are heavily underutilized
→ Static
consolidation
of workloads
→ Reduction
of servers
Reference [1]
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eedc-greenproject-120514174300-phpapp01/85/Automatic-Energy-based-Scheduling-13-320.jpg)
![Server Virtualization
●
P2: Servers are underutilized for long
periods/day
→ Consolidation
of workloads
→ Servers in a
low power state
Reference [1]
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eedc-greenproject-120514174300-phpapp01/85/Automatic-Energy-based-Scheduling-14-320.jpg)