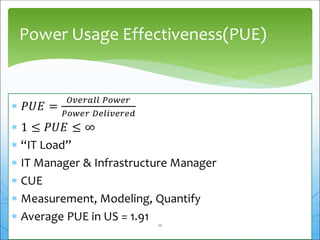
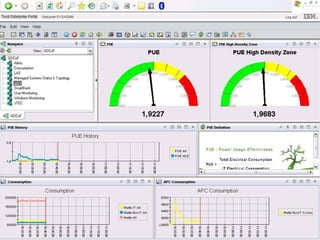
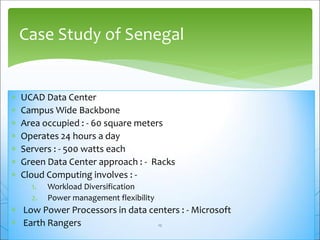
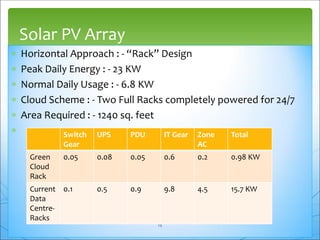
This document discusses green cloud computing from the perspective of data centers. It begins with background on green computing and cloud computing. It then discusses how green cloud computing can help balance energy usage in data centers through server virtualization, energy-aware consolidation, and locating data centers in developing regions. The document presents two case studies, one on a green data center in Senegal and another on benefits realized by a cell phone company in South Africa from implementing a private cloud. It concludes with sections on the Indian scenario for green IT standardization and a call to continue research efforts to maximize efficiency of green data centers.