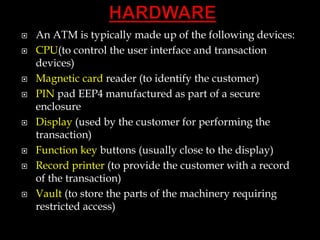
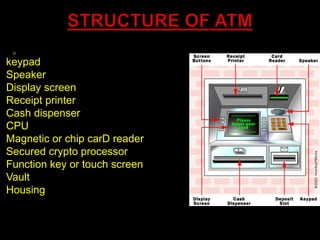
An Automated Teller Machine (ATM) is a device that allows customers to perform financial transactions, primarily cash withdrawals, without human assistance. There are two main types of ATMs: basic units for cash withdrawal and balance inquiries, and complex units that accept deposits and make payments. ATMs operate through a secure process involving customer identification, personal identification number (PIN) verification, and communication with the bank's systems to facilitate transactions.