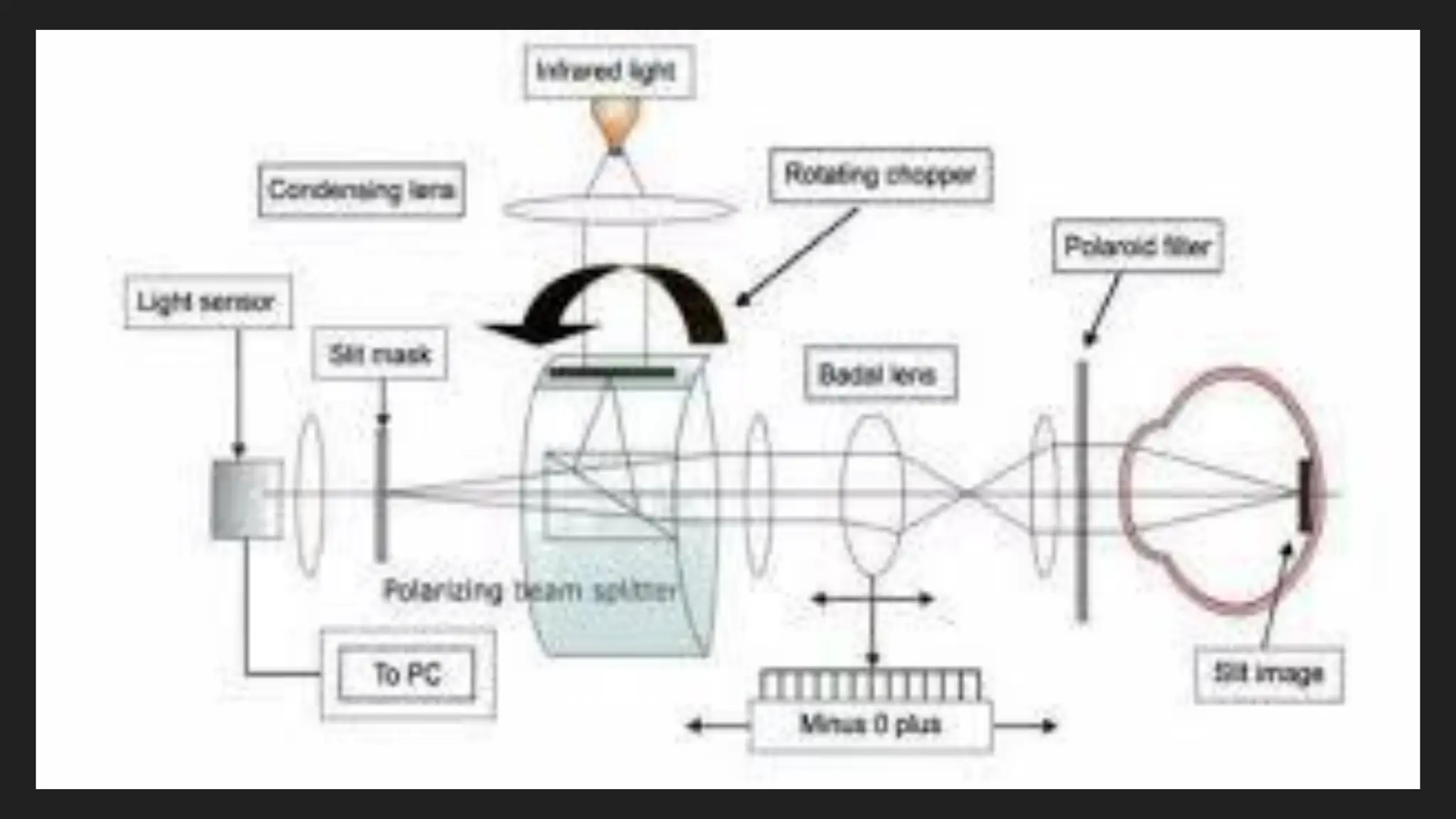
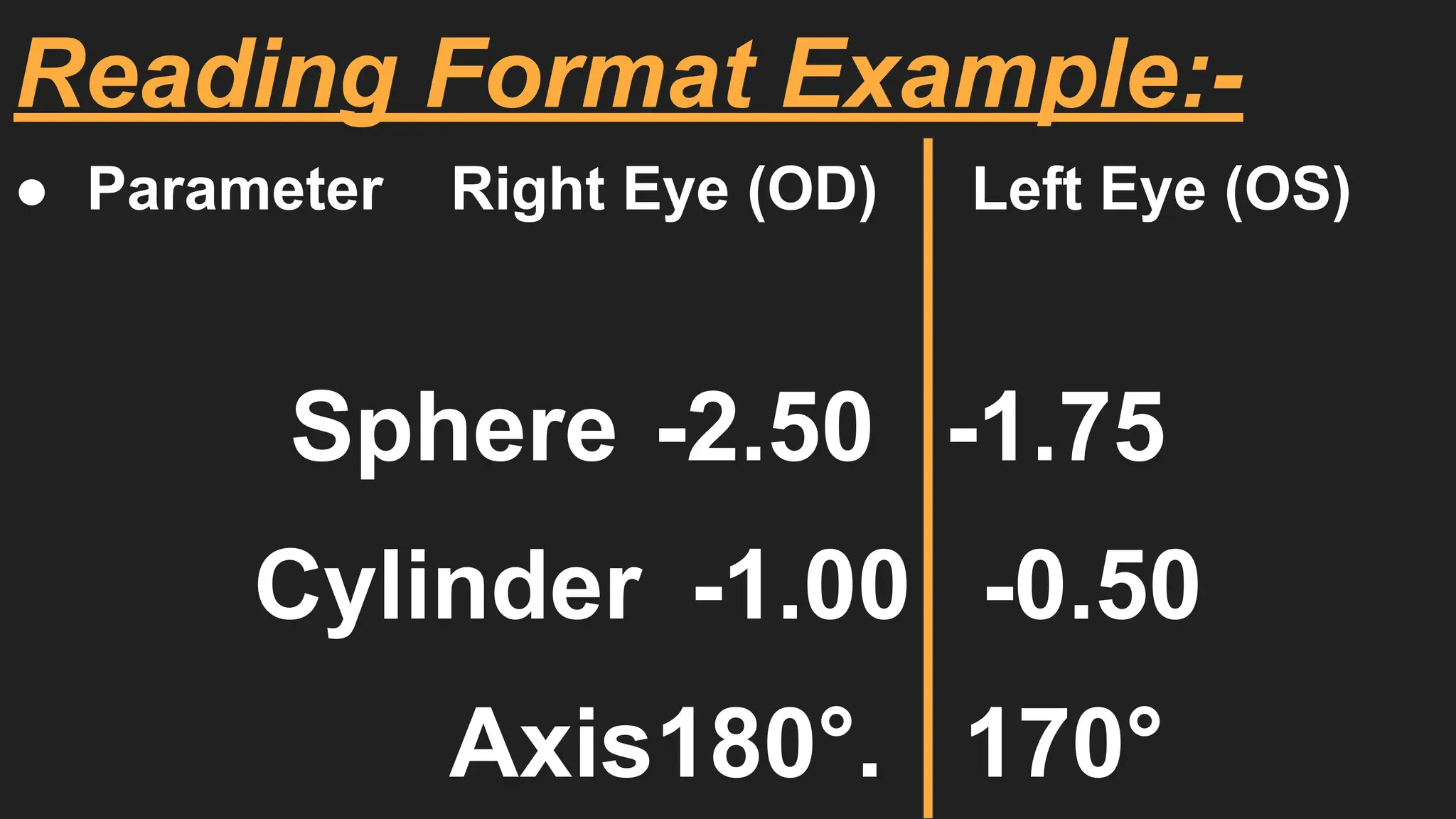
An Auto Refractometer (AR), also called an Autorefractor, is an optical instrument used to automatically measure the refractive error of the eye. It provides objective values of Sphere (Sph), Cylinder (Cyl), and Axis, which help in determining whether a person has myopia, hypermetropia, or astigmatism. This instrument works on the principle of infrared light reflection. During measurement, a beam of infrared light is projected into the eye, and this light passes through the cornea, lens, and reaches the retina. The reflected light then returns back through the same optical path. By analyzing the changes in the reflected light path, the machine calculates the amount of refractive error present in the eye.
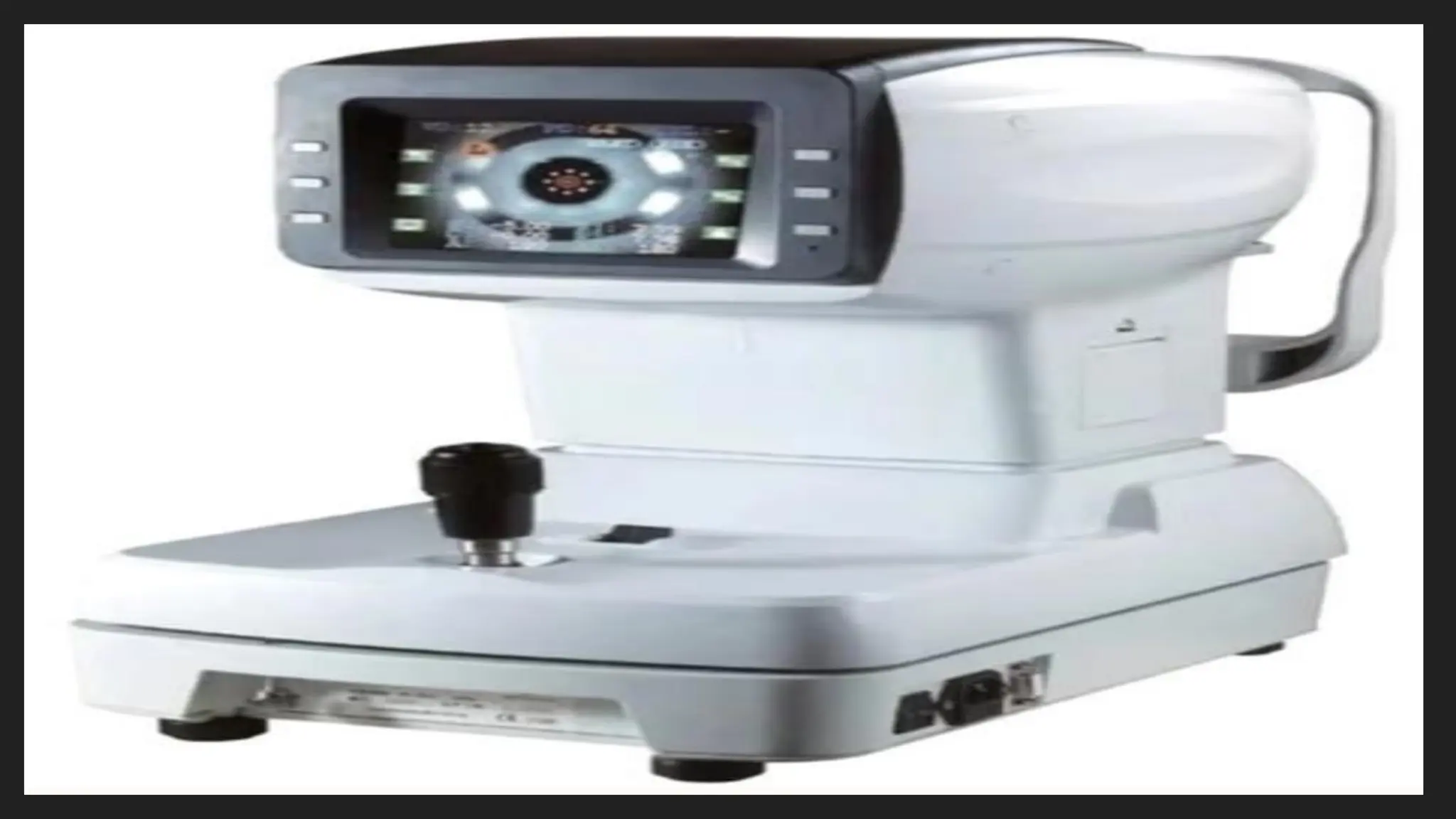
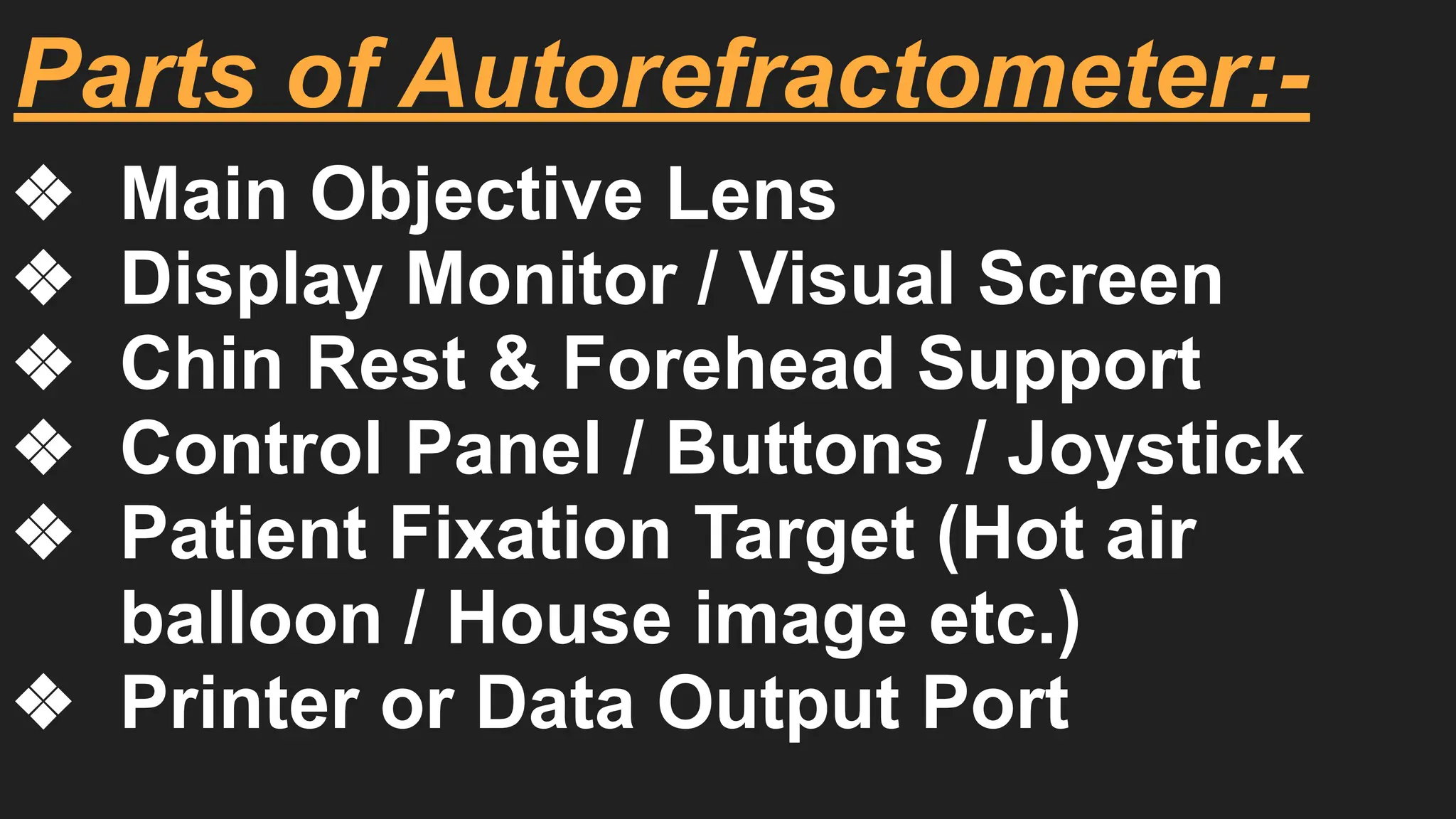
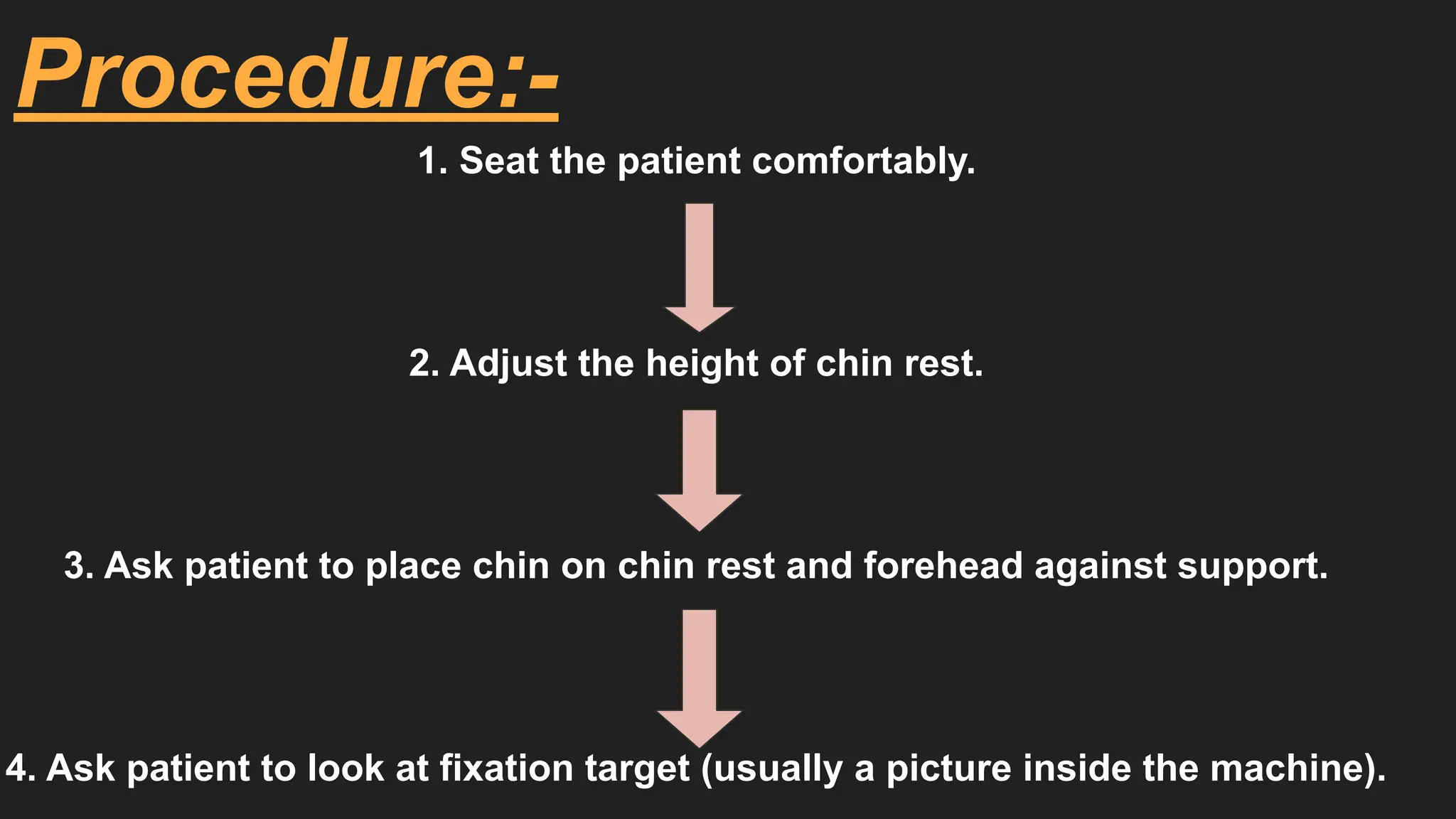
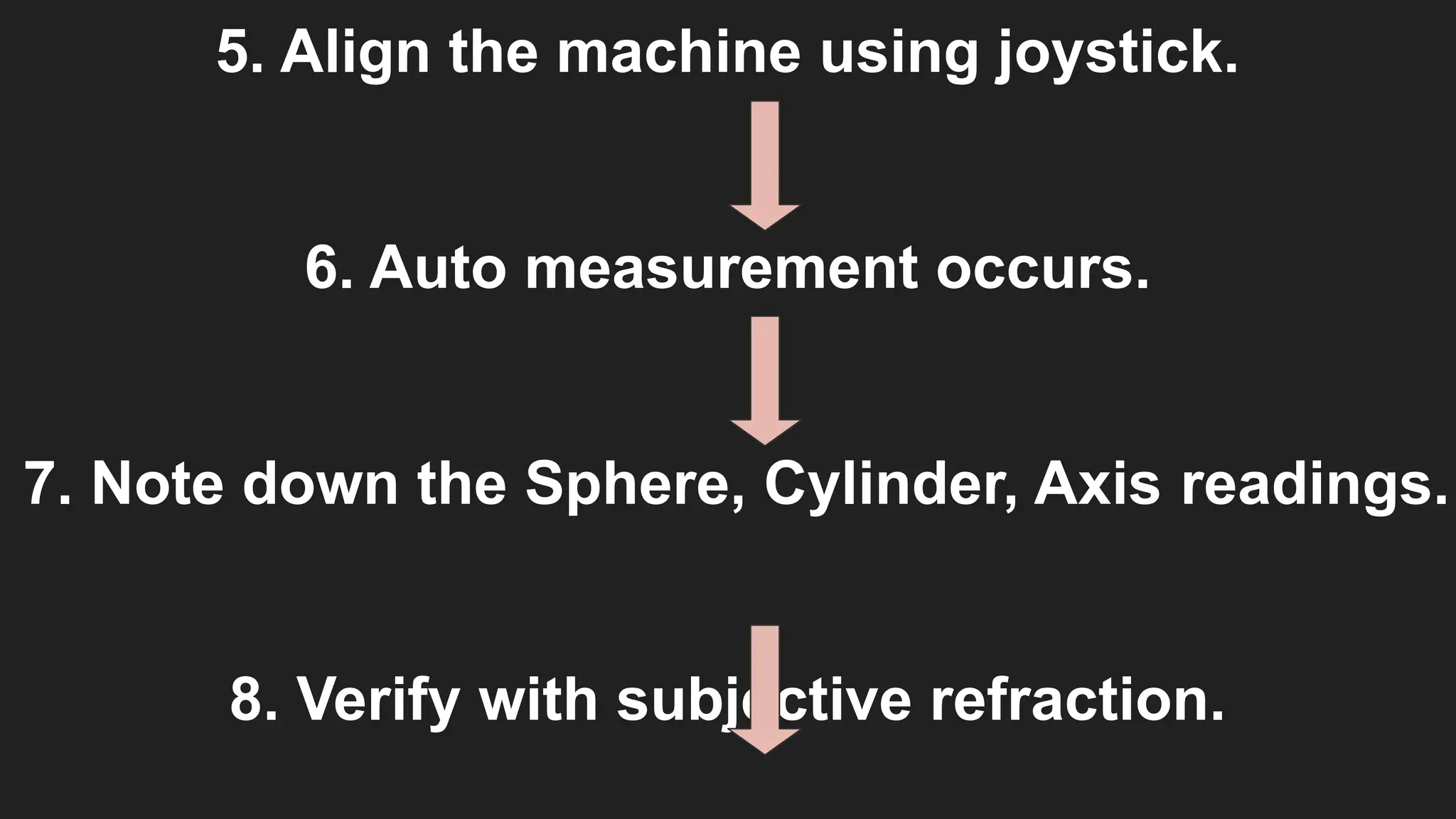
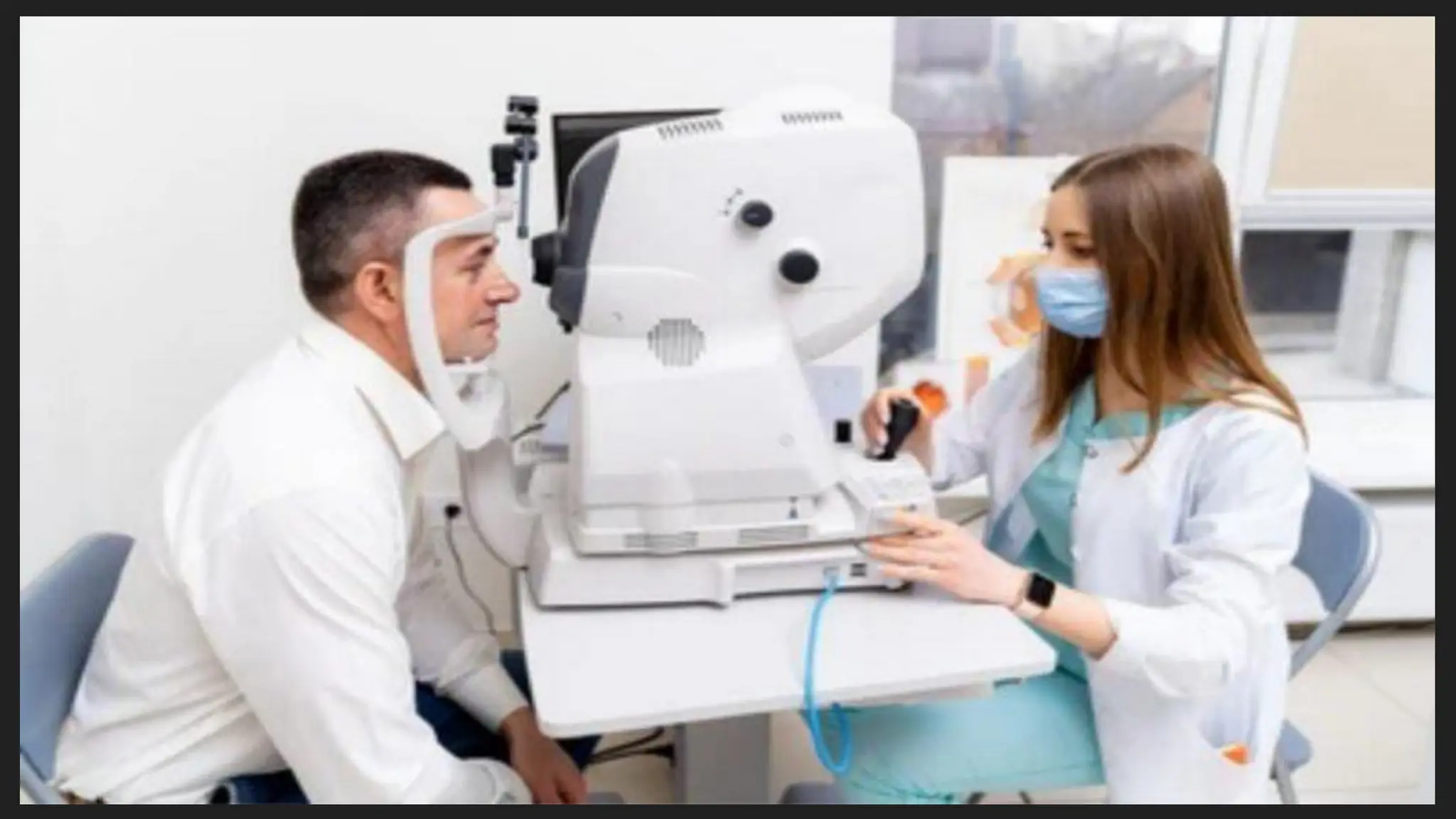
The Autorefractometer consists of several major parts including an objective lens, display monitor, control joystick, chin rest, and forehead support. It also contains a fixation target, usually in the form of a picture like a hot air balloon or house, which keeps the patient’s eye steady and reduces accommodation. Proper patient positioning is essential; the patient is asked to sit comfortably with their chin on the chin rest and forehead touching the support. The examiner aligns the instrument using the joystick, focuses on the pupil, and the machine automatically takes multiple readings to provide an average value.
The autorefractor is extremely beneficial in daily clinical practice. It provides quick and easy measurements, making it especially useful in busy hospitals, optical centers, screening camps, and pediatric examinations. It reduces examiner fatigue and provides an efficient starting point for subjective refraction. However, the readings of the Autorefractometer are not always fully accurate. Factors such as accommodation (especially in children), corneal irregularities, dry eye, cataract, and poor fixation can influence the results. Therefore, although AR provides a good initial estimate, the final spectacle prescription must always be refined through subjective refraction performed by the optometrist.
In summary, the Auto Refractometer is a modern, reliable, and convenient instrument that improves the speed and efficiency of refractive assessments. It provides essential baseline values quickly, but subjective refraction remains the gold standard for finalizing accurate visual correction.
#AutoRefractometer #Autoref #ARMachine #Optometry #OptometristLife #Refraction #ObjectiveRefraction #VisionTest #EyeCheckup #EyeHospital #EyecareProfessionals #Ophthalmology #OphthalmicInstruments #OptometryStudent #OptometryNotes #ClinicalOptometry #RefractionTest #VisionScreening #Myopia #Hypermetropia #Astigmatism #Eyeglasses #SpectaclePower #OpticalClinic #EyeCamp #VisualScience #OptometryStudy #OcularHealth #RefractiveError #SubjectiveRefraction #EyeCareTechnology #EyesightTesting #LensPower #PupilAlignment #EyeExamination #CornealCurvature #VisionAnalyzer #PediatricRefraction #BestForClinics #OptometristIndia #BScOptometry #DiplomaOptometry