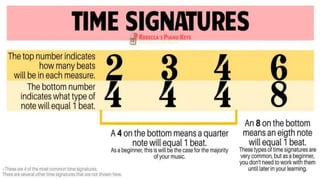
The document discusses music as an auditory art form, defined as the organization of tones and silences to express emotions and ideas. It explores the components of music, including sound qualities like timbre, pitch, intensity, and duration, along with elements like rhythm, melody, harmony, and texture. Additionally, it highlights music's cultural significance and various functions throughout history, from ritual to entertainment.